Mybatis源码深度解析
Mybatis大体架构流程分析
1.读取resource下面的mybatis配置文件获取输入流Reader对象
//获取mybatis配置文件
String configName = "mybatis_config.xml";
//获取输入流
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(configName);
2. 获取SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
3.使用XMLConfigBuilder来解析mybatis配置文件


因为在构造函数设置了parsed为fasle,XMLConfigBuilder只能被使用一次

调用该方法来解析mybatis的配置文件,解析完成之后都会装配到Configuration这个类中。
Configuaration的作用:mybatis核心的配置文件内容,把xml转成javaBean对象
4.将配置文件中的Mapper添加到Configuration类中的mapperRegistry实现注册
5.使用Configuration获取默认的DefaultSqlSessionFactory
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
MybatisMapper接口绑定原理分析
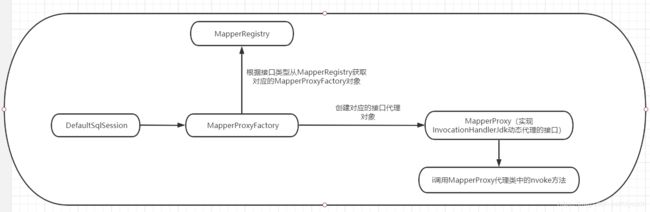
1.获取代理对象
//获取代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
MapperProxy中的Invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
SqlSesssion提供了select/insert/update/delete方法,在旧版本中使用SqlSesssion接口的这些方法,新版本的Mybatis中建议使用Mapper接口的方法,底层还是通过mapperMethod中的excute方法调用SqlSession的这些方法来实现的。
MybatisMapper SQLSession源码分析
SQLSession的作用
SqlSession提供select/insert/update/delete方法
Executor执行器原理分析
//获取session
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
- openSessionFromDataSource,首先是从Configuration中取出相关的配置,生成Transaction,接着又创建了一个Executor,最后返回了DefaultSqlSession对象
- Executor类别
SimpleExecutor:默认的Executor,每个SQL执行时都会创建新的 Statement,继承了BaseExecutor
CachingExecutor:可缓存数据的Executor,用于二级缓存的执行器
BatchExecutor:用于批处理的Executor
ReuseExecutor:相同的SQL会服用的Statement - 默认情况下使用缓存的CachingExecutor
- 在实际项目中每次请求都是新的SqlSession,因为每次请求完之后都会关掉SqlSession,所以不会存在一级缓存导致数据出现。
SelectOne底层原理查询分析
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List<T> list = this.<T>selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
当查询单条数据的时候,最终还是调用selectList查询多个结果集包装当个对象
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
从configuaration中获取到MappedStatement,调用Executor的query方法实现执行
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
先查询二级缓存,是否有缓存,没有的话调用delegate.query方法,delegate是SimpleExecutor执行器
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
//查询一级缓存,没有的话就去查询数据库
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
如果一级缓存中没有该结果,会调用queryFromDatabase查询数据库得到数据,然后再缓存到一级缓存中,下次查询的时候相同的sql语句直接走一级缓存不会查询数据库
Mybatis一级与二级缓存
一级缓存
mybatis的一级缓存是SqlSession级别的缓存,在操作数据库的时候需要先创建SqlSession会话对象,在对象中用一个HashMap来存储数据,此HashMap是当前会话对象私有的,别的SqlSession会话对象是无法访问的
流程:
- 第一次执行select完毕会将查到的数据写入SqlSession内的HashMap中缓存起来,key是查询的完成sql语句,里面有参数,不同的参数是不同的key
- 第二次执行select会从缓存中查询数据,如果select相同并且参数一样,那么就能从缓存汇总返回数据,不用去查数据库了,从而提高效率
- 注意事项:
如果SqlSession执行了insert,update,delete并commit了,那么mybatis就会清空当前SqlSession中所有的一级缓存数据,这样可以保证缓存中存的数据永远和数据库一致,避免出现脏读
当一个SqlSession结束后那么他里面的一级缓存也就不存在了,mybatis是默认开启一级缓存的,不需要配置
当服务器集群的时候,每个sqlSesssion有自己独立的缓存,相互之间不共享,所以每个在服务器集群的时候mybatis的一级缓存会产生数据冲突问题。
如何禁止一级缓存
方案1 在sql语句上 随机生成 不同的参数 存在缺点:map集合可能爆
方案2 开启二级缓存
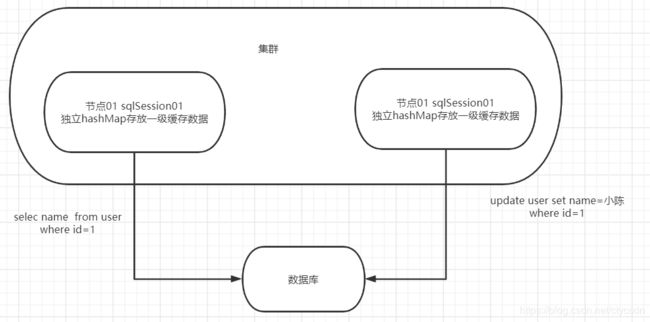
二级缓存
二级缓存是mapper级别的缓存,当多个SqlSession使用同一个Mapper操作数据库的时候,得到的数据会缓存在同一个缓存区域。
springboot项目中使用的配置
在启动类中加上@EnableCaching注解
在需要缓存的mapper中加上@CacheNamespace(implementation = MybatisRedisCache.class)这个注解和二级缓存的类就可以了
TransactionalCache类
继承Cache接口,主要作用是保存SqlSession在事务中需要向某个二级缓存提交的缓存数据(因为事务提交过程中 数据可能会回滚,所以不能直接把数据提交到二级缓存,而是暂存在TransactionCache中,在事务提交后再将过程中存放在其中的数据提交到二级缓存,如果事务回滚,则将数据清除)
private Cache delegate; 对应的二级缓存对象
private boolean clearOnCommit; 是否在commit时清除二级缓存的标记
private Map
private Set entriesMissedInCache;
TransactionalCacheManager
用于管理CachingExecutor使用的二级缓存对象,只定义了一个transactionCaches字段
参考:蚂蚁课堂