Spring自定义注解
java注解:附在代码中的一些元信息,用于在编译、运行时起到说明、配置的功能。
一、元注解
java提供了4种元注解用于注解其他注解,所有的注解都是基于这四种注解来定义的。
@Target注解:用于描述注解的使用范围,超出范围时编译失败。
取值类型(ElementType):
1.CONSTRUCTOR:用于描述构造器
2.FIELD:用于描述域(成员变量)
3.LOCAL_VARIABLE:用于描述局部变量
4.METHOD:用于描述方法
5.PACKAGE:用于描述包
6.PARAMETER:用于描述参数
7.TYPE:用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明
例如:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
//类名注解,默认即为当前类名
String name() default "className";
}import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//字段注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface MyAnnotation1 {
String name() default "fieldName";
String getFieldValue() default "getField";
String setFieldValue() default "setField";
}@Retention:描述注解的生命周期,即注解的生效范围。
取值范围(RetentionPolicy):
1.SOURCE:在源文件中生效,仅存在java文件中,class文件将会去除注解。
2.CLASS:在class文件中生效,仅保留在class文件中,运行时无法获取注解。
3.RUNTIME:在运行时生效,保留在class文件中且运行时可通过反射机制获取。
例如:
@Target(ElementType.FIELD) //字段注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //在运行期保留注解信息
public @interface MyAnnotation1 {
String name() default "fieldName";
String getFieldValue() default "getField";
String setFieldValue() default "setField";
}@Documented:用于指定javac生成API时显示该注解信息。
例如:
@Target(ElementType.FIELD) //字段注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //在运行期保留注解信息
@Documented //在生成javac时显示该注解的信息
public @interface MyAnnotation1 {
String name() default "fieldName";
String getFieldValue() default "getField";
String setFieldValue() default "setField";
}@Inherited:标明该注解可以由子类继承,及子类可以继承父类的注解。而默认情况下,子类是不继承父类注解的。
例如:
@Target(ElementType.FIELD) //字段注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //在运行期保留注解信息
@Documented //在生成javac时显示该注解的信息
@Inherited //标明MyAnnotation1注解可以被使用它的子类继承
public @interface MyAnnotation1 {
String name() default "fieldName";
String getFieldValue() default "getField";
String setFieldValue() default "setField";
public enum FieldValue{MYTEST,MYFIELD,MYVALUE};
FieldValue realVale() default FieldValue.MYFIELD;
}二、读取注解
通过反射机制我们可以读取注解信息。java在java.lang.reflect包下新增了AnnotatedElement接口,该接口定义了可以接受注解的元素为:Class(类)、Constructor(构造器)、Field(字段)、Method(方法)、Package(包)。
AnnotatedElement是所有注解元素的父接口,所有的注解元素都可以通过某个类反射获取AnnotatedElement对象,该对象有一下4个方法来访问Annotation信息。
(1)
返回该程序元素上存在的、指定类型的注解,如果该类型注解不存在,则返回null。
(2)Annotation[] getAnnotations():返回该程序元素上存在的所有注解。
(3)boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class annotationClass)
判断该程序元素上是否包含指定类型的注解,存在则返回true,否则返回false.
(4)Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations()
返回直接存在于此元素上的所有注释。与此接口中的其他方法不同,该方法将忽略继承的注释。(如果没有注释直接存在于此元素上,则返回长度为零的一个数组。)该方法的调用者可以随意修改返回的数组;这不会对其他调用者返回的数组产生任何影响。
例如:
注解:
package com.dhcc.iscp.web.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //在运行期保留注解信息
public @interface MyAnnotation {
//类名注解,默认即为当前类名
String name() default "className";
}package com.dhcc.iscp.web.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD) //字段注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //在运行期保留注解信息
@Documented //在生成javac时显示该注解的信息
@Inherited //标明MyAnnotation1注解可以被使用它的子类继承
public @interface MyAnnotation1 {
String name() default "fieldName";
String getFieldValue() default "getField";
String setFieldValue() default "setField";
public enum FieldValue{MYTEST,MYFIELD,MYVALUE};
FieldValue realValue() default FieldValue.MYFIELD;
}实体类:
package com.dhcc.iscp.web.annotation;
import com.dhcc.iscp.web.annotation.MyAnnotation1.FieldValue;
@MyAnnotation(name="myTest")
public class MyTest {
@MyAnnotation1
String myTest;
@MyAnnotation1(name="test",getFieldValue="1",setFieldValue="2",realValue=FieldValue.MYVALUE)
String testValue;
public String getMyTest() {
return myTest;
}
public void setMyTest(String myTest) {
this.myTest = myTest;
}
public String getTestValue() {
return testValue;
}
public void setTestValue(String testValue) {
this.testValue = testValue;
}
}
测试类:
package com.dhcc.iscp.web.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class TestAnnotation {
public static void main(String[] args){
MyTest myTest = new MyTest();
Annotation[] annotations = myTest.getClass().getAnnotations(); //获取类的所有注解
for(Annotation anno:annotations){
if(anno instanceof MyAnnotation){
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = (MyAnnotation)anno;
System.out.println("className:"+myAnnotation.name());
}else if(anno instanceof MyAnnotation1){
MyAnnotation1 myAnnotation1 = (MyAnnotation1)anno;
System.out.println("FiledName:"+myAnnotation1.name());
System.out.println("setFieldValue"+myAnnotation1.setFieldValue());
System.out.println("getFieldValue"+myAnnotation1.getFieldValue());
System.out.println("realValue"+myAnnotation1.realValue());
}
}
Field[] fields = myTest.getClass().getDeclaredFields();//获取所有注解字段
for(Field field:fields){
if(field.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation1.class)){
MyAnnotation1 myAnno = (MyAnnotation1)field.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation1.class);
System.out.println(field.getName()+"-name:"+myAnno.name());
System.out.println(field.getName()+"-getFieldValue:"+myAnno.getFieldValue());
System.out.println(field.getName()+"-setFieldValue:"+myAnno.setFieldValue());
System.out.println(field.getName()+"-realValue:"+myAnno.realValue());
}
}
Method[] methods = myTest.getClass().getMethods();//获取所有方法
for(Method method:methods){
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation1.class)){
MyAnnotation1 myAnno1 = (MyAnnotation1)method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation1.class);
System.out.println(myAnno1.getClass());
}
}
}
}
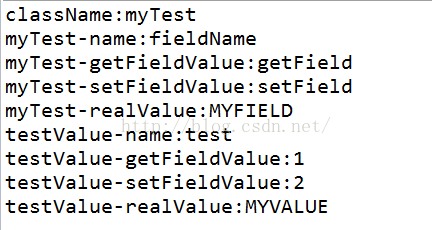
测试结果:
三、自定义注解
自定义注解是通过@interface来声明的,其中的每一个方法实际上是声明了一个配置参数,参数名称即为方法名,参数类型即为返回值类型。
自定义注解的格式:
public @interface 注解名{定义体}
注解参数可支持的类型:
1.所有基本数据类型(int,float,boolean,byte,double,char,long,short)
2.String类型
3.Class类型
4.enum类型
5.Annotation类型
6.以上所有类型的数组
注解参数的定义规则:
a.只能使用public或默认2种访问修饰,例如:String getName();这里getName()就是使用了默认访问权限。
b.参数类型只能使用上面提到的6种情况
c.如果只有一个参数成员,最好将参数名定义为:value()。
d.注解元素必须有确定值,要么在定义的时候设置默认值,要么在使用注解的时候设置参数值。