ThreadLocal原理理解与源码分析
java中的ThreadLocal相信很多人都有使用过,但很多人仅知道它的用法和作用(本地变量副本,用于管理数据库连接,Session等),但对它的原理可能还没有太多认识. 最近自己翻了下它的源码,把自己的理解和想法写下来与大家分享.
ps:本文参考的源码版本为JDK1.8
1. 什么是ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal,很多地方叫做线程本地变量,也有些地方叫做线程本地存储,其实意思差不多。ThreadLocal为变量在每个线程中都创建了一个副本,那么每个线程可以访问自己内部的副本变量。
从名字上可以看出,它是和线程有关的.那么它和线程的关系是怎么样,如何发挥作用的呢? 我们可以看看Thread类相关的源码
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained
* by the ThreadLocal class. */
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
/*
* InheritableThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is
* maintained by the InheritableThreadLocal class.
*/
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;从上面可以看出,ThreadLocal在线程类中主要是通过其内部类ThreadLocalMap作为threadLocals和inheritableThreadLocals变量. 其中threadLocals存放当前线程相关的本地变量副本,而inheritableThreadLocals则是存放从父线程继承而来的本地变量副本,它的元素对应的实际类型是InheritableThreadLocal,这是ThreadLocal的一个子类,实现了特定的childValue方法.
2. ThreadLocal源码分析
此处尝试对整个ThreadLocal的主要源码进行基本的分析.源码里会包含一些长注释,对于关键的注释,这里会保留,并加上自己的分析
另外,ThreadLocal的关键方法为get(),set(),remove()和initialValue(),大家可以重点关注源码里这几个方法的实现
2.1 基本属性
public class ThreadLocal<T> {
//ThreadLocal对象是作为ThreadLocalMap的一个key,所以此处通过nextHashCode方法获取自己的唯一标记,用于后面计算位置
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
//原子类保证线程安全,保证每个对象的hashcode唯一,并且是静态的,用于nextHashCode方法生成threadLocalHashCode
private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode =
new AtomicInteger();
//生成threadLocalHashCode的增量基数,但为什么是这个数,暂没细究
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
//返回threadLocalHashCode的计算值
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}
/**
* Creates a thread local variable.
* @see #withInitial(java.util.function.Supplier)
*/
public ThreadLocal() {
}
/**
* ThreadLocalMap is a customized hash map suitable only for
* maintaining thread local values. No operations are exported
* outside of the ThreadLocal class. The class is package private to
* allow declaration of fields in class Thread. To help deal with
* very large and long-lived usages, the hash table entries use
* WeakReferences for keys. However, since reference queues are not
* used, stale entries are guaranteed to be removed only when
* the table starts running out of space.
*/
//定义了一个类似于HashMap这样的内部类,里面的Entry使用ThreadLocal对象作为key,并用弱引用的方式指向它
static class ThreadLocalMap {
/**
* The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using
* its main ref field as the key (which is always a
* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()
* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the
* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to
* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.
*/
//Entry继承的WeakReference用于ThreadLocal(看 super(k);), 所以当外部的ThreadLocal对象指针一旦置为null,该对象就会在下一次gc中回收掉
static class Entry extends WeakReference> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
/**
* The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two.
*/
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; // 下面Entry[] table的初始大小,必须为2的幂数
/**
* The table, resized as necessary.
* table.length MUST always be a power of two.
*/
private Entry[] table; //利用Entry[]模拟Map的实现
/**
* The number of entries in the table.
*/
private int size = 0; // table中的元素个数
/**
* The next size value at which to resize.
*/
private int threshold; // table下一次要扩容时的阈值
/**
* Set the resize threshold to maintain at worst a 2/3 load factor.
*/
private void setThreshold(int len) {
threshold = len * 2 / 3;
}
/**
* Increment i modulo len.
*/
private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) { //返回下一个索引值
return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);
}
/**
* Decrement i modulo len.
*/
private static int prevIndex(int i, int len) { //返回上一个索引值
return ((i - 1 >= 0) ? i - 1 : len - 1);
}
/**
* Construct a new map initially containing (firstKey, firstValue).
* ThreadLocalMaps are constructed lazily, so we only create
* one when we have at least one entry to put in it.
*/
//使用懒加载的方式,最少有一个entry才会创建ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1); //通过上面定义threadLocalHashCode计算table位置,可以理解为一个hash的过程
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
}
} 关于这个ThreadLocalMap的INITIAL_CAPACITY为什么是2的N次方,这在HashMap里面也是有体现的,这里INITIAL_CAPACITY为16那么16-1=15在二进制中就是1111.当他和TheadLocal的INITIAL_CAPACITY相与(&)的时候,得到的数绝对是<=INITIAL_CAPACITY.这和threadLocalHashCode%INITIAL_CAPACITY的效果是一样的,但是效率比前者好处很多倍, 那么此时我们已经得到一个下标位置,我们直接new了一个Entry(ThreadLocal,Object),放入该table数组当中,这个时候把table的size置为1,阈值设为INITIAL_CAPACITY的2/3(达到最大长度的2/3的时候会扩容).
现在通过代码已经渐渐的明白了ThreadLocal的本质,就是内部用一个以ThreadLocal为Key的ThreadLocalMap为不同的线程存储变量副本,这个map的基本元素为继承了弱引用的Entry.
关于Entry,这里说一下,当外部的ThreadLocal指针置为null后,整个程序就只有Entry的某个key值指向它,而它是弱引用的,这代表他将会被下一次的GC回收掉. 这中间的关系可以用以下这张图(摘自网络)来描述:
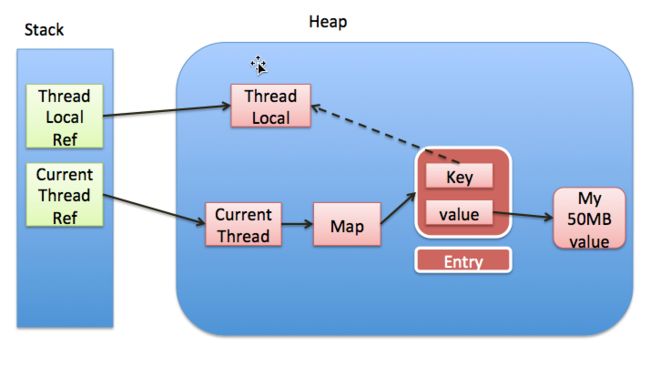
但是这中间还有个问题,由于位置下标是采用类似hash的方法计算出来,那么两个不同ThreadLocal有可能计算出相同的下标,这就造成了hash冲突,在ThreadLocal里面用的解决Hash冲突是用的线性探查法(Linear Probing)来解决的,当i下标有值的时候则找到i+1处,然后依次往下推.
2.2 initialValue方法
/**
* Returns the current thread's "initial value" for this
* thread-local variable. This method will be invoked the first
* time a thread accesses the variable with the {@link #get}
* method, unless the thread previously invoked the {@link #set}
* method, in which case the {@code initialValue} method will not
* be invoked for the thread. Normally, this method is invoked at
* most once per thread, but it may be invoked again in case of
* subsequent invocations of {@link #remove} followed by {@link #get}.
*
* This implementation simply returns {@code null}; if the
* programmer desires thread-local variables to have an initial
* value other than {@code null}, {@code ThreadLocal} must be
* subclassed, and this method overridden. Typically, an
* anonymous inner class will be used.
*
* @return the initial value for this thread-local
*/
//返回以这个ThreadLocal为key的value对象的初始值,此处默认为null,用户在刚创建ThreadLocal时,也可用子类的方式重写此方法返回自定义的初始值. 一般此方法会在get方法找不到值时被第一次调用,若在调用remove方法后又调用了get方法,那么此方法也会被再次调用
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
/**
* Creates a thread local variable. The initial value of the variable is
* determined by invoking the {@code get} method on the {@code Supplier}.
*
* @param the type of the thread local's value
* @param supplier the supplier to be used to determine the initial value
* @return a new thread local variable
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified supplier is null
* @since 1.8
*/
//1.8版本后,提供通过Supplier设置initValue的接口,方法返回的SuppliedThreadLocal是ThreadLocal的子类
public static ThreadLocal withInitial(Supplier supplier) {
return new SuppliedThreadLocal<>(supplier);
}
/**
* An extension of ThreadLocal that obtains its initial value from
* the specified {@code Supplier}.
*/
//重写了initialValue方法的子类
static final class SuppliedThreadLocal extends ThreadLocal {
private final Supplier supplier;
SuppliedThreadLocal(Supplier supplier) {
this.supplier = Objects.requireNonNull(supplier);
}
@Override
protected T initialValue() {
return supplier.get();
}
} initialValue主要是给提供我们自定义初始值的接口
2.3 get方法
/**
* Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this
* thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the
* current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned
* by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.
*
* @return the current thread's value of this thread-local
*/
//获取ThreadLocal在当前线程存放的值
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); //返回第一节所说的threadLocals属性值
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); //将自身对象作为key,在Map中查找对应的Entry,具体的查找逻辑参考下一节
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
//map为null,需要从初始化的地方取值,该方法分析详见下面部分
return setInitialValue();
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
static class ThreadLocalMap {
/**
*篇幅问题,省略部分上面已出现的属性
*/
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i]; //从计算出的下标尝试一次取得对应的value
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e); //第一次尝试没拿到,通过这个方法继续尝试
}
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == key) //如果key相同,直接返回
return e;
if (k == null) //如果ThreadLocal变为null,说明已被GC,通过expungeStaleEntry处理这个无效的Entry,也叫脏Entry
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
/**
* Expunge a stale entry by rehashing any possibly colliding entries
* lying between staleSlot and the next null slot. This also expunges
* any other stale entries encountered before the trailing null. See
* Knuth, Section 6.4
*
* @param staleSlot index of slot known to have null key
* @return the index of the next null slot after staleSlot
* (all between staleSlot and this slot will have been checked
* for expunging).
*/
//清除staleSlot位置的无效Entry,并返回下一个Entry元素为null的下标
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//清除该位置的Entry数据
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
size--;
// Rehash until we encounter null
Entry e;
int i;
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == null) { //继续往后清除key为null的无效Entry
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1); //重新计算Entry下标,类似于重新hash
if (h != i) {
tab[i] = null;
// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until
// null because multiple entries could have been stale.
while (tab[h] != null) //对于下标出现变化的Entry,将其与下一个无效Entry的位置互换
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
return i;
}
}
get方法会在找不到值时调用setInitialValue方法在table中设置初始值,并返回.
2.4 set和setInitialValue方法
set方法和setInitialValue方法的逻辑其实是比较类似的,只是后者调用了initialValue方法设置初始而已
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue(); //通过initialValue方法取得要设置的值
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value); //若map不为空,通过ThreadLocalMap内部的set方法设值,否则通过下面的createMap创建一个
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
/**
* Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
* InheritableThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map
*/
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue); //通过上面2.1节里的ThreadLocalMap构造方法创建该线程的threadLocals
}
static class ThreadLocalMap {
/**
*篇幅问题,省略部分上面已出现的属性
*/
private void set(ThreadLocal key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); //计算下标位置
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == key) { //如果key已存在,则直接替换它value
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) { //如果在遍历过程中,遇到了无效Entry,则在该位置更新Entry的key-value
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
//若前面遍历不成功,新建一个Entry,并检查threshold是否要扩容
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold) // 若cleanSomeSlots没有清除任何无效Entry,则要检查threshold确定是否调用rehash方法扩容及重新hash
rehash();
}
private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal key, Object value,
int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
Entry e;
int slotToExpunge = staleSlot;
for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len); //找到在前面的第一个无效Entry的位置
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = prevIndex(i, len))
if (e.get() == null)
slotToExpunge = i;
for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) { //尝试遍历后面的Entry,再次检查是否key已存在
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == key) { //如果找到该key,重新设置value,并与staleSlot位置的无效Entry进行互换,以保证hash计算下标时的顺序
e.value = value;
tab[i] = tab[staleSlot];
tab[staleSlot] = e;
if (slotToExpunge == staleSlot) //确保接下来expungeStaleEntry要清除的Entry位置不是刚互换后的位置
slotToExpunge = i;
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len); //expungeStaleEntry方法清除指定位置上的一个无效Entry,cleanSomeSlots方法则批量清除无效Entry,详见下面的分析
return;
}
if (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot) //若我们前面得到的slotToExpunge与staleSlot相同,则更新slotToExpunge的值
slotToExpunge = i;
}
//如果确实找不到key对应的Entry,则直接替换无效的Entry
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value);
if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot) //清除无效Entry
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
}
private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {
boolean removed = false;
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
do {
i = nextIndex(i, len); //从参数i位置后面开始检查Entry
Entry e = tab[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == null) {
n = len;
removed = true;
i = expungeStaleEntry(i); //清除特定位置下的无效Entry
}
} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0); //控制清除过程的遍历次数为{ log2(n) }
return removed;
}
private void rehash() { //此方法对table进行扩容及重新hash
expungeStaleEntries(); //先清除table内所有的无效Entry
if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4) //用更严格的标准(threshold - threshold / 4)判断是否扩容.之所以要更严格是为了避免数据滞后
resize();
}
private void resize() {
Entry[] oldTab = table;
int oldLen = oldTab.length;
int newLen = oldLen * 2; //对table进行双倍扩容
Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {
Entry e = oldTab[j];
if (e != null) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null; // 置空以便GC回收
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1); //重新hash
while (newTab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, newLen);
newTab[h] = e;
count++;
}
}
}
setThreshold(newLen);
size = count;
table = newTab;
}
private void expungeStaleEntries() { //清除table内所有的无效Entry,比较耗性能,所以只能扩容前进行
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = tab[j];
if (e != null && e.get() == null)
expungeStaleEntry(j);
}
}
}
2.5 remove方法
remove方法相对比较容易理解
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
static class ThreadLocalMap {
/**
*篇幅问题,省略部分上面已出现的属性
*/
private void remove(ThreadLocal key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); //计算下标
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
e.clear(); //父类Reference的clear方法,把弱引用置空
expungeStaleEntry(i); //清除该Entry
return;
}
}
}
}3. 总结
从上面源码的分析可知,ThreadLocal的实现实质上是通过其内部的ThreadLocalMap类实现的,它的set(),get(),remove()方法都是调用ThreadLocalMap的相应方法. 而且真正存储时把被弱引用包装了的ThreadLocal对象作为key, 通过hash这个key寻找它在table的位置,并采用简单的线性探查法解决hash冲突