C/C++线性结构
目录
1. 数组和顺序表
2. 单链表
2.0 C语言方式实现
2.1 C++方式实现
3. 循环链表
4. 双向链表
5. 队列与栈
5.0 栈C++的实现
5.1 队列的C++实现
1. 数组和顺序表
1.0 向顺序表中的第i个位置插入元素。
顺序表定义:
#define MAXSIZE 10
#define INCREMENT 10
typedef struct
{
int * elem;
int length;
int size;
}Seqlist;
创建顺序表:
Seqlist * createList()
{
Seqlist * l = (Seqlist *)malloc(sizeof(Seqlist));
l->elem = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * MAXSIZE);
l->length = 0;
l->size = MAXSIZE;
return l;
}
在pos位置插入元素:
int InsertElem(Seqlist * l, int pos, int elem)
{
if (l == NULL) return 0;
if (pos < 0 || pos >l->length) return 0;
if (l->length >= l->size)
{
int * new_elem = (int *)realloc(l->elem, sizeof(int) * (l->size + INCREMENT));
if (new_elem == NULL) return 0;
l->elem = new_elem;
l->size = l->size + INCREMENT;
}
for (int i = l->length - 1; i >= pos;i--)
{
l->elem[i + 1] = l->elem[i];
}
l->elem[pos] = elem;
l->length++;
return 1;
}
打印函数:
void printList(Seqlist *l)
{
if (l == NULL) return;
for (int i = 0;i < l->length;i++)
cout << l->elem[i] << " " << endl;
cout << endl;
}
主函数:
int main()
{
Seqlist * l = createList();
for (int i = 0; i < 15;i++)
InsertElem(l, 0, (i + 1));
printList(l);
}
1.1 实现数组逆置。
void reverseSeqList(int a[], int n)
{
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < (n - 1) / 2;i++)
{
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[n - 1 - i];
a[n - 1 - i] = temp;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n;i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}int main()
{
int a[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10;i++)
a[i] = i + 1;
reverseSeqList(a, 10);
}
1.2 实现删除一个数组中的重复元素。
编写一个函数,删除一个只包含正整数的数组中重复元素,例如,一个数组中元素为{2,3,5,2,5,3,6,9,11,6},删除重复元素后数组变为{2,3,5,6,9,11}。
void delElem(int a[], int * n)
{
int i = 0, j;
while (i < *n)
{
j = i + 1;
while (j < *n)
{
if (a[i] == a[j])
{
for (j = j + 1;j < *n; j++)
a[j-1] = a[j];
*n = *n - 1;
}
else
j++;
}
i++;
}
}
int main()
{
int a[10] = { 2,3,5,5,9,4,3,7,4,2 };
int n = 10;
delElem(a, &n);
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
1.3 求数组元素两两之间的差绝对值的最小值。
要求得出最小值即可,不要求得出是那两个数。
int findMin(int a[], int n)
{
int min_val = abs(a[0] - a[1]);
for (int i = 0; i < n;i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1;j < n;j++)
{
if (abs(a[i] - a[j]) < min_val)
min_val = abs(a[i] - a[j]);
}
}
return min_val;
}
int main()
{
int a[5] = { 1,3,5,8,9 };
int x = findMin(a, 5);
cout << x << " " << endl;
}
1.4 两个有序数组的交集。
给定两个有序数组arr_1和arr_2,数组中的元素是递增的,且个数组中没有重复的元素。计算两个数组的交集。例如,array_1 = {2,5,6,8,9},array_2 = {1,5,6,7,8},他们的交集为{5,6,8}
int getIntersection(int arr_1[], int len_1, int arr_2[], int len_2,int intersection[])
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i < len_1 && j < len_2)
{
if (arr_1[i] > arr_2[j])
j++;
if (arr_1[i] < arr_2[j])
i++;
if (arr_1[i] == arr_2[j])
{
intersection[k] = arr_1[i];
i++;
j++;
k++;
}
}
return k;
}
上述算法中参考数组的二路归并法。用变量i指向array_1的第一个元素,变量 j 指向array_2的第一个元素。执行下面的操作:
1)如果array_1[i]等于array_2[j],则该元素是交集元素,将其放到intersection数组中,然后执行i++,j++,。
2) 如果array_1[i]大于array_2[j],则执行j++。
3)如果array_[1]小于array_2[j],则执行i++。
4)一旦 i 等于数组array_1的长度,或者j 等于array_2的长度,循环终止。
1.5 判断数组中的元素是否连续。
现有一个整型数组,其元素0~65535之间的任意数字,已知相同的数字不会重复出现,而0可以重复出现,且0可以通配成任意一个数字,设计算法判断该数组中元素是否连续。
有一个很巧妙的解决方法。如果一个数组包含n个元素,并且该数组中元素是连续的,那么它一定具有“数组中最大值与最小值之差为 n - 1”的性质。如果这些元素中包含0这样的通配数字,并且要保证数组中元素是连续的,那么数组中的非0最大值与非0最小值之差不能超过n - 1.
例如,数组中元素为{5,7,6,0,9,10},该数组包含6个元素,非0元素最大值为10,非0元素最小值为5,两者之差等于5,即等于n-1 ,即6 -1,所以该数组是连续的。
例如,数组{2,3,7,0,0},非0最大值是7,非0最小值是2,7-2 = 5 > n - 1 = 4。所以数组不是连续的。
int isContinuousArray(int array[], int len)
{
int max_val = array[0], min_val = array[0];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
if (array[i] > max_val && array[i] != 0)
max_val = array[i];
else if (array[i] < min_val && array[i] != 0)
min_val = array[0];
}
if (max_val - min_val > len - 1)
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
int main()
{
int arr_1[6] = { 5,7,6,0,9,10 };
int arr_2[5] = { 2,3,7,0,0 };
int ret = isContinuousArray(arr_2, 5);
if (ret)
cout << "Is continus!" << endl;
else
cout << "Not continus!" << endl;
}
1.6 判断数组中是否有重复元素。
给定一个长度为N的数组,其中每个元素的取值范围都是1~N。判断数组中是否有重复的数字。
由于原数组长度为N,并且取值范围是1~N,如果数组中不包含重复元素,那么数组中元素一定是1~N内每个都出现一次,这N个数的和是N * (N + 1) / 2。所以所有元素之和不等于N * (N + 1) / 2,那么数组一定包含重复元素。
int haveRepeatElem(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum != (n * (n + 1) / 2))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}int main()
{
int arr_1[6] = { 1,3,2,5,4,6 };
int ret = haveRepeatElem(arr_1, 6);
if (ret)
cout << "have repeat!" << endl;
else
cout << "not repeat!" << endl;
}
2. 单链表
2.0 C语言方式实现
LinkList.h文件
#pragma once
#include
using namespace std;struct Header
{
int length;
struct Node * next;
};struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node * next;
};typedef struct Header Head;
typedef struct Node List;Head * createList();
int insertList(Head * head,int pos,int val);
int deleteList(Head * head, int val);
List * findList(Head * head, int val);
int destoryList(Head * head);
void printList(Head * head);
Linklist.c文件
Head * createList()
{
Head * head = (Head *)malloc(sizeof(Head));
if (head == NULL) return NULL;
head->length = 0;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}int insertList(Head * head, int pos, int val)
{
if (head == NULL || pos < 0 || pos > head->length)
return 0;
List * pVal = (List *)malloc(sizeof(List));
pVal->data = val;List * pCur = head->next;
if (pos == 0)
{
head->next = pVal;
pVal->next = pCur;
}
else
{
for (int i = 1; i < pos; i++)
pCur = pCur->next;
pVal->next = pCur->next;
pCur->next = pVal;
}
head->length++;
return 1;
}int deleteList(Head * head, int val)
{
if (head == NULL) return 0;List * pCur = head->next;
List * pTmp = NULL;if (pCur->data == val)
{
head->next = pCur->next;
free(pCur);
head->length--;
return 1;
}
else
{
for (int i = 1; i < head->length;i++)
{
pTmp = pCur;
pCur = pCur->next;
if (pCur->data == val)
{
pTmp->next = pCur->next;
free(pCur);
head->length--;
return 1;
}
}
}
}List * findList(Head * head, int val)
{
if (head == NULL) return NULL;List * pCur = head->next;
for (int i = 0; i < head->length;i++)
{
if (pCur->data == val)
return pCur;
else
pCur = pCur->next;
}
}int destoryList(Head * head)
{
if (head == NULL) return 0;List * pCur = head->next;
List * pTmp = NULL;
while (pCur != NULL)
{
pTmp = pCur;
pCur = pCur->next;
free(pTmp);
}
head->length = 0;
head->next = NULL;
}void printList(Head * head)
{
if (head == NULL) return;
List * pCur = head->next;
while (pCur != NULL)
{
cout << pCur->data << " ";
pCur = pCur->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
测试主函数
int main()
{
Head * head = createList();
for (int i = 0;i < 10; i++)
{
insertList(head,0,(i + 1));
}
cout << "插入10个数字后遍历 :\n";
printList(head);
cout << "删除元素值为7的结点后遍历 :\n";
deleteList(head, 7);
printList(head);
cout << "查找值为5的结点并输出其值:\n";
List * p = findList(head, 5);
cout << p->data << " " << endl;
cout << "销毁\n";
destoryList(head);
}
2.0.0 合并两个单链表。
void mergeList(Head * list1, Head * list2)
{
if (list1 == NULL || list2 == NULL) return;
List * pCur = list1->next;
while (pCur->next != NULL) //定位到list1的最后一个结点
pCur = pCur->next;pCur->next = list2->next;
list1->length += list2->length;}
int main()
{
Head * list1 = createList();
for (int i = 0;i < 5; i++)
{
insertList(list1,0,(i + 1));
}
printList(list1);Head * list2 = createList();
for (int i = 0;i < 5; i++)
{
insertList(list2, 0, (i + 5));
}
printList(list2);mergeList(list1, list2);
printList(list1);
}
2.0.1 单链表的逆置
void reverseList(Head * list)
{
if (list == NULL) return;
List * pCur = list->next;
List * q = NULL;
List * r = NULL;
while (pCur != NULL)
{
r = q;
q = pCur;
pCur = pCur->next;
q->next = r;
}
list->next = q;
}
int main()
{
Head * list1 = createList();
for (int i = 0;i < 5; i++)
{
insertList(list1,0,(i + 1));
}
printList(list1);reverseList(list1);
printList(list1);
}
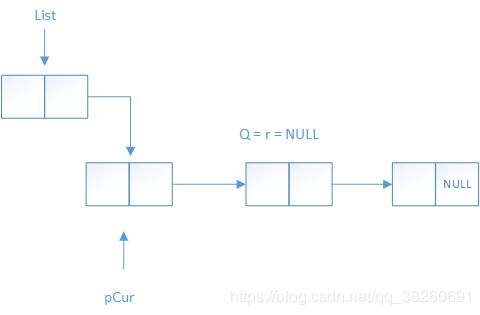
上述算法中, 初始状态下,即while循环未开始前的链表如下所示:
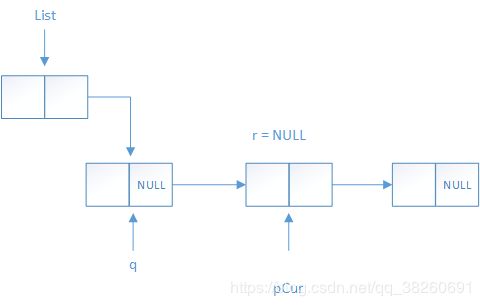
第一次循环后,指针r = NULL,指针q指向源链表的第一个结点,指针pCur指向原链表的第二个结点,将指针q的next域回指r,也即将源链表的第一个结点的next置NULL.此时示意图如下:
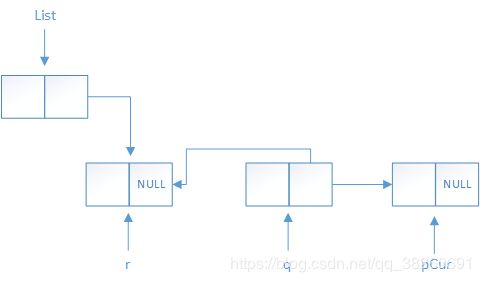
第二次循环后,由于while循环中第一句将q赋值给r,也就是说第二次循环中,指针r指向le源链表的第一个结点。
此时,指针pCur指向第三个结点,指针q指向第二个结点。将q的next域指向r也即指向第一个结点。此时示意图如下:
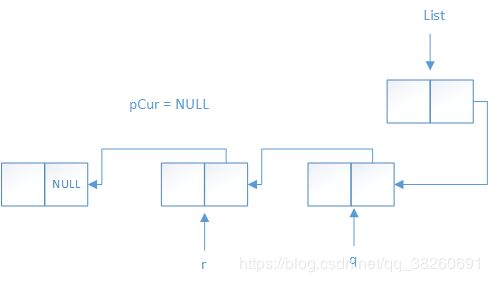
循环结束后,指针pCur指向NULL,指针q指向原链表的最后一个结点,指针r指向原连表倒数第二个结点,此时,还需要最后一步操作,将头结点指向原链表的最后一个结点,即可实现单链表的逆置。
2.0.2 找出单链表倒数第K个元素
由于实现中采用了带头结点的形式,所以已知了链表的长度,倒数第K个结点的正数位序为length-K,只需要在for循环中找出该结点即可。
List * findK(Head * list, int k)
{
if (list == NULL) return NULL;
if (k < 0 || k > list->length) return NULL;List * pCur = list->next;
for (int i = 0; i < list->length - k; i++)
pCur = pCur->next;
return pCur;
}
2.1 C++方式实现
template
class LinkList
{
private:
struct Node
{
T data;
Node * next;
};
int _length;
Node * _head;
public:
LinkList();
~LinkList();void Insert(int pos, const T &val);
void Remove(int pos);
int Search(const T &val) const;
T Visit(int pos) const;void Print() const;
int size() const { return _length; }
bool Empty() const { return _length == 0; }
};template
LinkList::LinkList() : _length(0)
{
_head = new Node;
_head->next = NULL;
}template
LinkList::~LinkList()
{
if (!Empty())
{
Node * pCur = _head->next;
Node * pTmp = NULL;
while (pCur != NULL)
{
pTmp = pCur;
pCur = pCur->next;
delete pTmp;
}
delete _head;
_head = NULL;
_length = 0;
}
}template
void LinkList::Insert(int pos, const T &val)
{
if (pos < 0 || pos > _length) return;Node * pVal = new Node;
pVal->data = val;
pVal->next = NULL;Node * pCur = _head->next;
if (pos == 0)
{
_head->next = pVal;
pVal->next = pCur;
_length++;
return;
}
else
{
for (int i = 1; i < pos; i++)
pCur = pCur->next;
pVal->next = pCur->next;
pCur->next = pVal;
_length++;
return;
}
}template
void LinkList::Remove(int pos)
{
if (Empty()) return;
if (pos < 0 || pos > _length) return;Node * pCur = _head->next;
if (pos == 0)
{
_head->next = pCur->next;
delete pCur;
_length--;
}
else
{
Node * pTmp = NULL;
for (int i = 1; i < pos; i++)
pCur = pCur->next;
pTmp = pCur->next;
pCur->next = pTmp->next;
delete pTmp;
_length--;
}
}template
int LinkList::Search(const T &val) const
{
if (Empty()) return 65535;
Node * pCur = _head->next;
int count = 0;
while (pCur != NULL)
{
if (pCur->data == val)
return count;
else
{
count++;
pCur = pCur->next;
}
}
return 65535;
}template
T LinkList::Visit(int pos) const
{
if (Empty()) return static_cast(65535);
if (pos <0 || pos > _length) return static_cast(65535);
Node * pCur = _head->next;
if (pos == 0)
{
return pCur->data;
}
else
{
for (int i = 1;i < pos; i++)
pCur = pCur->next;
return pCur->next->data;
}
}template
void LinkList::Print() const
{
if (Empty()) return;
Node * pCur = _head->next;
while (pCur != NULL)
{
cout << pCur->data << " ";
pCur = pCur->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
3. 循环链表
循环链表最后一个结点的指针域指向第一个结点。
3.0 判断一个列表是否构成循环。
此处指的循环,并非单指链表最后一个结点指向第一个结点,而是更广泛的指链表中任意两个或更多结点构成回环的情况,比如,在单链表中最后一个结点指向了倒数第二个结点,亦可称之为循环。
在带头结点的单链表中,因为已知长度,即结点个数信息,则比较好处理。遍历该链表,并记下结点个数,倘若记下的结点个数大于了链表长度,而还未遍历完单链表,则该链表是循环链表。
如果在不带头结点的单链表中,有一个更直接的办法:初始条件下,设置两个指针slow和fast,slow指向链表的第一个结点,fast指向第二个结点。然后slow和fast皆顺序遍历链表,在遍历过程中,slow一次只访问一个结点,fast访问两个结点。在slow和fast每完成一次访问后都要判断slow是否等于fast,或者fast是否为NULL。如果fast等于slow说明是循环链表,如果fast等于NULL说明不是循环链表。
理解该算法时,可以形象的想象成两个运动员赛跑,如果赛道是直的那么一定是跑得快的先到终点。如果是无尽头的循环跑到则跑的快的终有和跑的慢的相遇的时候。
int isLoopList(Head * list)
{
if (list == NULL) return 0;
Node * pfast = list->next->next;
Node * pslow = list->next;
while (1)
{
if (pfast == NULL || pfast->next == NULL)
return 0;
else if (pfast == pslow || pfast->next == pslow)
return 1;
else
{
pfast = pfast->next->next;
pslow = pslow->next;
}
}
}
4. 双向链表
下面以C++类封装一个双向链表。
#pragma once
#include
using namespace std;template
class DList
{
private:
struct Node
{
T data;
Node * pre;
Node * next;
};
int _length;
Node * _head;
public:
DList();
~DList();void Insert(int pos, const T &val);
void Remove(int pos);
int Search(const T &val) const;
T Visit(int pos) const;void Print() const;
int Size() const { return _length; }
bool Empty() const { return _length == 0; }
};template
DList::DList() : _length(0)
{
_head = new Node;
_head->pre = _head->next = NULL;
}template
inline DList::~DList()
{
if (!Empty())
{
Node * pCur = _head->next;
Node * pTmp;
while (pCur != NULL)
{
pTmp = pCur->next;
delete pCur;
pCur = pTmp;
}
_length = 0;
}
delete _head;
}template
void DList::Insert(int pos, const T &val)
{
if (pos < 0 || pos > _length) return;
Node * pVal = new Node;
pVal->data = val;
pVal->pre = pVal->next = NULL;
Node * pCur = _head->next;
if (Empty())
{
_head->next = pVal;
}
else
{
if (pos == 0)
{
_head->next = pVal;
pVal->pre = NULL;
pVal->next = pCur;
pCur->pre = pVal;
}
else
{
for (int i = 1; i < pos; i++)
pCur = pCur->next;
pVal->next = pCur->next;
pCur->next->pre = pVal;
pVal->pre = pCur;
pCur->next = pVal;
}
}
_length++;
}template
void DList::Remove(int pos)
{
if (pos < 0 || pos >_length || Empty()) return;
Node * pCur = _head->next;
if (pos == 0)
{
_head->next = pCur->next;
pCur->next->pre = NULL;
delete pCur;
}
else
{
for (int i = 1; i < pos; i++)
pCur = pCur->next;
Node * pTmp = pCur->next;
pTmp->next->pre = pCur;
pCur->next = pTmp->next;
delete pTmp;
}
_length--;
}template
int DList::Search(const T &val) const
{
if (Empty()) return 65535;
Node * pCur = _head->next;
int count = 0;
while (pCur != NULL)
{
if (pCur->data == val)
return count;
else
{
pCur = pCur->next;
count++;
}
}
return 65535;
}template
T DList::Visit(int pos) const
{
if (pos < 0 || pos > _length || Empty()) return static_cast(65535);
Node * pCur = _head->next;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++)
pCur = pCur->next;
return pCur->data;
}template
void DList::Print() const
{
if (Empty()) return;
Node * pCur = _head->next;
while (pCur != NULL)
{
cout << pCur->data << " ";
pCur = pCur->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
主函数
int main()
{
DListdlist;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
dlist.Insert(0, i + 1);
dlist.Print();int ret = dlist.Search(7);
cout << ret << endl;ret = dlist.Visit(ret);
cout << ret << endl;dlist.Remove(3);
dlist.Print();
}
5. 队列与栈
5.0 栈C++的实现
#pragma once
#include
using namespace std;
template
class LinkStack
{
private:
struct Node
{
T data;
Node * next;
};
Node * _top;
int _size;
public:
LinkStack();
~LinkStack();void Push(const T &val);
T Pop();
T Top();
bool Empty() const { return _size == 0; }
int Size() const { return _size; }
};template
LinkStack::LinkStack() : _size(0)
{
_top = NULL;
}template
LinkStack::~LinkStack()
{
if (!Empty())
{
Node * pCur = _top;
Node * p;
while (pCur != NULL)
{
p = pCur->next;
delete pCur;
pCur = p;
}
_size = 0;
}
}template
void LinkStack::Push(const T &val)
{
Node * pVal = new Node;
pVal->data = val;
pVal->next = _top;
_top = pVal;
_size++;
}template
T LinkStack::Pop()
{
if (Empty()) return static_cast(65535);
Node * pCur = _top;
_top = _top->next;
T val = pCur->data;
delete pCur;
_size--;
return val;
}template
T LinkStack::Top()
{
if (Empty()) return 65535;
return _top->data;
}
测试主函数:
int main()
{
LinkStackstack;
srand(time(NULL));
cout << "入栈 : \n";
for (int i = 0; i < 10;i++)
{
int ret = rand() % 100 + 1;
cout << ret << " ";
stack.Push(ret);
}
cout << endl;
cout << "出栈 : \n";
for (int i = 0; i < 10;i++)
{
cout << stack.Pop() << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
5.0.1 十进制数转换为其他进制数
char * Convert(int num,int r)
{
LinkStackstack;
while (num != 0)
{
stack.Push(num % r);
num = num / r;
}
char * buf = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * (stack.Size() + 1));
int i = 0;
while (!stack.Empty())
{
int ret = stack.Pop();
if (ret > 9) buf[i] = char(ret + 'A' - 10);
else buf[i] = char(ret + 0x30);
i++;
}
buf[i] = '\0';
return buf;
}
int main()
{
char * buf = Convert(1000, 16);
cout << buf << endl;}
5.0.2 括号匹配问题
已知表达式中只允许两种括号:圆括号()和方括号[ ] 。它们可以任意嵌套使用。要求括号必须成对出现。编写一个函数,从终端输入一组括号,以字符#结束,判断输入的括号是否匹配合法。
int Match(char ch1, char ch2)
{
if (ch2 == '(' && ch1 == ')') return 1;
if (ch2 == '[' && ch1 == ']') return 1;
return 0;
}
void matchBracket()
{
LinkStacks;
char ch1, ch2;
scanf("%c", &ch1);
while(ch1 != '#')
{
if (s.Empty())
s.Push(ch1);
else
{
ch2 = s.Pop();
if (Match(ch1, ch2) != 1)
{
s.Push(ch2);
s.Push(ch1);
}
}
scanf("%c", &ch1);
}
if (s.Empty())
cout << "完全匹配\n";
else
cout << "匹配错误\n";
}int main()
{
matchBracket();
}
5.0.2 用两个栈实现一个队列
用C++实现如下
方法:入队操作时,将元素压入栈s1中;出队操作时判断s2是否为空,如果s2不为空,则直接取出s2的栈顶元素;如果s2为空,则将s1的元素逐个弹出并压入s2,再取s2的栈顶元素。函数emptyQueue通过判断栈s1和s2是否都为空来实现。函数getCount通过计算s1和s2的当前容量之和来实现。
template
class SQueue
{
private:
LinkStack_s1, _s2;
public:
void enQueue(const T &x);
T deQueue();
bool emptyQueue();
int getCount();
};template
void SQueue::enQueue(const T & x)
{
_s1.Push(x);
}template
T SQueue::deQueue()
{
if (_s2.Empty())
{
if (_s1.Empty())
return T(0);
else
{
while (!_s1.Empty())
_s2.Push(_s1.Pop());
}
}
T x = _s2.Pop();
return x;
}template
bool SQueue::emptyQueue()
{
if (_s1.Empty() && _s2.Empty())
return true;
else return false;
}template
int SQueue::getCount()
{
return _s1.Size() + _s2.Size();
}
测试主函数
int main()
{
SQueuesq;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
sq.enQueue(i + 1);
int ret;
ret = sq.getCount();
cout << ret << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << sq.deQueue() << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
5.1 队列的C++实现
#pragma once
#include
using namespace std;template
class LinkQueue
{
private:
struct Node
{
T data;
Node * next;
};
Node * _front;
Node * _rear;
public:
LinkQueue() { _front = _rear = NULL; }
~LinkQueue() { Clear(); }void Clear();
void enQueue(const T &val);
T deQueue();
T getHead() const;
bool Empty() const { return _front == NULL; }
int getSize() const;
};template
inline void LinkQueue::Clear()
{
Node * pCur = _front;
Node * p;
while (pCur != NULL)
{
p = pCur->next;
delete pCur;
pCur = p;
}
}template
inline void LinkQueue::enQueue(const T & val)
{
Node * pVal = new Node;
pVal->data = val;
pVal->next = NULL;
if (_front == NULL)
_front = _rear = pVal;
else
{
_rear->next = pVal;
_rear = pVal;
}
}template
inline T LinkQueue::deQueue()
{
if (Empty()) return T(65535);
Node * pCur = _front;
_front = _front->next;
T val = pCur->data;
if (_front == NULL)
_rear = NULL;
delete pCur;
return val;
}template
inline T LinkQueue::getHead() const
{
if (Empty()) return T(65535);
return _front->data;
}template
inline int LinkQueue::getSize() const
{
if (Empty()) return 0;
Node * pCur = _front;
int count = 0;
while (pCur != NULL)
{
count++;
pCur = pCur->next;
}
return count;
}
测试主函数
int main()
{
LinkQueuelq;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
lq.enQueue(i + 1);
for (int i = 0;i < 10; i++)
{
cout << lq.deQueue() << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}