C# 递归。
一:斐波那契数列 指的是这样一个数列 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13
规律就是这个数列从第3项开始,每一项都等于前两项之和;
代码如下:
static int fib(int n)
{
if (n < 3)
return 1;
else
return fib(n - 2) + fib(n -1);
}二: 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + ....+ N,累加求和,用递归的方式写
代码如下:
static int Add(int n)
{
if( n == 1)
return n;
else
return Add(n - 1) + n;
}
//可以用 ?: 三元运算符简化一下
static int Add2(int n)
{
return n == 1 ? 1 : Add2(n -1) + n;
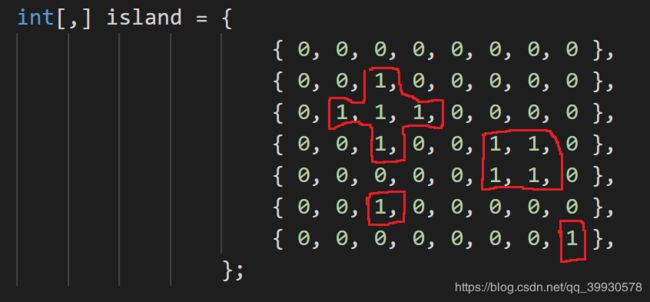
}三:找到二维数组中为1的岛屿的个数,岛屿是可以通过上下左右联通的,比如图中这个二维数组里的岛屿就是有4个。
这个我当时想的是两个for循环数组里的每个元素,是1的就用一个递归去找自己上下左右的元素。但是这样有个问题,如果它找了一圈没有发现有1的话,它还会找到自己,这样就是一个死循环了。然后看了网上的解析,找到是1的把1改为2就行了。
代码如下:
class Island
{
static int[,] island = {
{ 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1 },
};
public static void FindIsland()
{
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++) //循环行
for(int j = 0; j < col; j++) //循环列
{
if(island[i,j] == 1) //有岛屿
{
count ++;
rec(i, j);
}
}
System.Console.WriteLine("Island count: " + count);
}
//行
static int row{
get{
return island.GetLength(0);
}
}
//列
static int col{
get{
return island.GetLength(1);
}
}
static void rec(int i, int j)
{
island[i,j] = 2;
if(i - 1 >= 0 && island[i - 1, j] == 1) //top
rec(i - 1,j);
if(i + 1 < row && island[i + 1, j] == 1) //bot
rec(i + 1,j);
if(j - 1 >= 0 && island[i, j - 1] == 1) //left
rec(i,j - 1);
if(j + 1 < col && island[i, j + 1] == 1) //right
rec(i,j + 1);
}
}
四:闲来无事写了个递归,算吉他的每根吉他弦上每个全音对应的品丝
1.七个自然音唱名:do, re, mi, fa, sol, la, si(这个大家应该都懂),调名嘛:CDEFGAB,唱名调名是相互对应的。
2.吉他嘛,6根弦,从细到粗分为1,2,3,4,5,6弦。标准调弦的吉他的1-6弦的音是 mi si sol re la mi。也就是EBGDAE。
3.音程:CDEFGAB,
C -> D : 2, D -> E : 2, E -> F : 1, F -> G : 2, G -> A : 2, A -> B: 2, B -> C : 1
也就是除了 mi -> fa, si -> do 是隔了一个音程,其他都是隔了两个音程。
4. 问题来了,怎么写了?
①:写个叫吉他的类,class Guitar{};
②:吉他类里写个琴弦的类,class Strings{};
③:琴弦类里有自己的琴弦号(StrID),琴弦音(StrChord),每根琴弦的每个品对应的音(???)
代码如下:
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Train
{
//自然的唱名和调名
public enum NSC
{
C = 1, //do
D = 2, //re
E = 3, //mi
F = 4, //fa
G = 5, //sol
A = 6, //la
B = 7, //si
}
public class Guitar
{
//琴弦类
public class Strings
{
//琴弦号
public int StrID;
//琴弦音
public NSC StrChord;
//每根琴弦的每个品对应的音
public Dictionary PicChords;
}
//琴弦的集合,其实就是6个琴弦
public List GuitarStrs = new List();
//标准调弦的吉他 1 - 6弦是 EBGDAE
List StrChords = new List { NSC.E,NSC.B,NSC.G,NSC.D,NSC.A,NSC.E};
//每根琴弦上所有品的音,这个标准调弦的音
public Dictionary Pins = new Dictionary();
//初始化,也就是把对应的数据都放到吉他的每个琴弦的每个品上
public void Init()
{
//循环6次用来装填6根琴弦的音
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
next(0,StrChords[i]);
Strings strs = new Strings
{
StrID = i + 1, //琴弦
StrChord = StrChords[i], //琴弦音
PicChords = new Dictionary(Pins),
};
GuitarStrs.Add(strs);
Pins.Clear();
}
}
//递归装填每个全音品的音,pin:品丝,chord:自然音
void next(int pin, NSC chord)
{
//超过20品就停止。要用 >= ,不能用 ==
if (pin >= 20)
return;
else
{
//半音就是加一个品,全音就加两个品. (就两个半音, E->F, B->C )
pin = chord == NSC.B || chord == NSC.E ? pin + 1 : pin + 2;
//走到B的时候再从头(C)开始走
chord = chord == NSC.B ? NSC.C : chord + 1;
//递归
next(pin, chord);
}
Pins.Add(pin, chord); //装填
}
}
} 我用了名为NSC的枚举类型存放7个自然音,每根琴弦的每个品对应的音用了Dictionary类型来存放。
后面用了next()方法递归给每个品赋值。
调用:
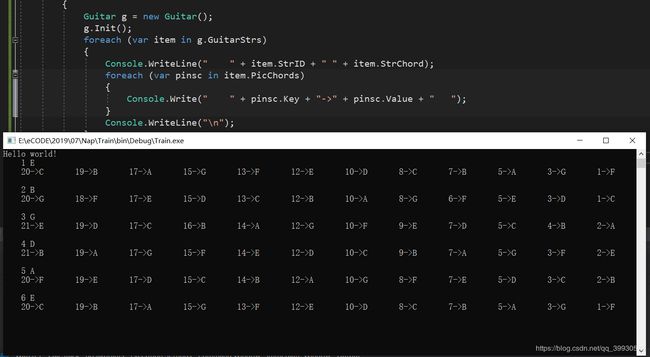
结果:
我弹了一遍,是对的!!!