Java之BufferStream缓冲流
没有看我之前写的 FileInput/OutputStream 和 FileReader/Writer 的两篇博文的朋友,建议补下脑在来BufferStream。
目录直通车
一、 BufferStream的作用
二、 对于非文本文件
1、 下面我做了一个实验,一起来看看吧~
2、 使用Buffered的实验
3、不使用Buffered的实验(全部完整代码)
4、 总结
三、对于文本文件
使用BufferedReader和BufferedWriter实现对文本文件的复制
注意:
1、FileInput/OutputStream最适合用于操作非文本文件(如图片、视频等)。
2、FileReader/Writer最适合用于操作文本文件(如txt文件)。
一一对应如下:
* 抽象基类 节点流(文件流) 缓冲流
* InputStream FileInputStream BufferedInputStream
* OutputStream FileOutputStream BufferedOutputStream
* Reader FileReader BufferedReader
* Writer FileWriter BufferedWriter一、 BufferStream的作用
缓冲流可以用来加速节点流操作文件的速度。
二、 对于非文本文件
1、 下面我做了一个实验,一起来看看吧~
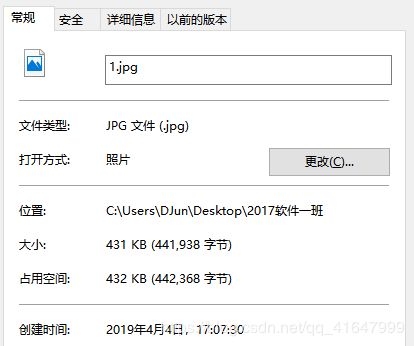
下面就测试一下使用buffer和不使用buffer对这张432kb大小的非文本文件进行复制的速度进行一次对比,在对比的过程中学习如何使用Buffer也何尝不是一种乐趣呢!
2、 使用Buffered
public static void testBufferedStream(String file, String newFile) {
//
File file1 = new File(file);
File file2 = new File(newFile);
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
byte[] readStr = new byte[256];
try {
int len;
fis = new FileInputStream(file1);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
while ((len = bis.read(readStr)) != -1) {
bos.write(readStr, 0, len);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (bis != null) {
bis.close();
}
if (bos != null){
bos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("Complete!");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String file = "src/IOStream/1.jpg";
String newFile = "src/IOStream/BufferedStream.jpg";
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
testBufferedStream(file, newFile);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
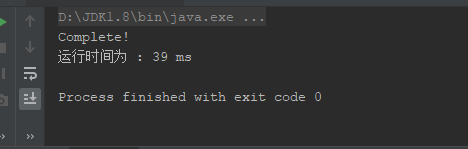
System.out.println("运行时间为 : " + (end - start)+" ms");
}运行效果
3、不使用Buffered(全部完整代码)
import java.io.*;
/**
* 抽象基类 节点流(文件流) 缓冲流
* InputStream FileInputStream BufferedInputStream
* OutputStream FileOutputStream BufferedOutputStream
* Reader FileReader BufferedReader
* Writer FileWriter BufferedWriter
*/
public class TestBufferStream {
/**
* 未使用Buffered复制非文本文件
*/
public static void testNoBufferedStream(String file, String newFile){
File file1 = new File(file);
File file2 = new File(newFile);
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
byte[] readStr = new byte[256];
try {
int len;
fis = new FileInputStream(file1);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
while ((len = fis.read(readStr)) != -1) {
fos.write(readStr, 0, len);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fis != null) {
fis.close();
}
if (fos != null){
fos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("Complete!");
}
}
}
/**
* 使用BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream实现对非文本文件的复制
*/
public static void testBufferedStream(String file, String newFile) {
//
File file1 = new File(file);
File file2 = new File(newFile);
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
byte[] readStr = new byte[256];
try {
int len;
fis = new FileInputStream(file1);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
while ((len = bis.read(readStr)) != -1) {
bos.write(readStr, 0, len);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (bis != null) {
bis.close();
}
if (bos != null){
bos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("Complete!");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String file = "src/IOStream/1.jpg";
String newFile = "src/IOStream/BufferedStream.jpg";
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
testNoBufferedStream(file, newFile);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
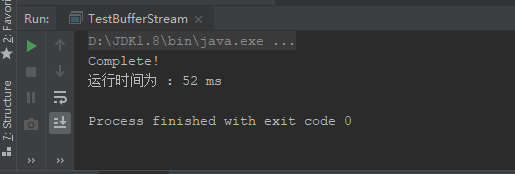
System.out.println("运行时间为 : " + (end - start)+" ms");
}
}
运行效果如下:
4、 总结
很明显使用了Buffered对非文本文件操作速度更快!
三、对于文本文件
使用BufferedReader和BufferedWriter实现对文本文件的复制
public static void testBufferStreamCopy(String file, String newFile){
// 1. 确定处理的文件
File file1 = new File(file);
File file2 = new File(newFile);
// 2. 创建文件读写对象
FileReader fr = null;
FileWriter fw = null;
// 3. 创建对应文件读写对象的缓冲流
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
// 4. 创建记录读取字符数组和长度
int len;
char [] readStr = new char[26];
try{
// 5. 加载文件到读取流
fr = new FileReader(file1);
fw = new FileWriter(file2);
// 6. 加载读取流到缓冲流
br = new BufferedReader(fr);
bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
// 7. 缓冲流对象读取写入文件
// 第一种读取方式
String str;
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null){
bw.write(str+"\n");
bw.flush();
}
// 第二种读取方式
// while ((len = br.read(readStr))!= -1){
// bw.write(readStr,0,len);
// bw.flush();
// }
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 8. 关闭缓冲流
try{
if (br != null){
br.close();
}
if (bw != null){
bw.close();
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("Complete!");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String file = "src/IOStream/HelloWorld.txt";
String newFile = "src/IOStream/2.txt";
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
testBufferStreamCopy(file, newFile);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("运行时间为 : " + (end - start)+" ms");
}