Java基本程序设计结构
Java 基本程序设计结构
文章目录
- Java 基本程序设计结构
- 1 基本程序结构
- 2 Java 项目结构
- 3 注释
- 4 数据类型
- 4.1 整型
- 4.2 浮点型
- 4.3 字符型
- 4.4 布尔型
- 4.5 数据类型转换
- 5 变量
- 5.1 变量的声明与初始化
- 5.2 常量
- 6 字符串
- 6.1 声明与初始化
- 6.2 判断两个字符串是否相等
- 6.3 空串 和 Null串
- 7 输入与输出
- 7.1 读取输入
- 7.2 格式化输出
- 8 控制流程
- 8.1 块作用域
- 8.2 条件语句(if)
- 8.3 循环结构
- 8.4 多重选择:switch
- 8.5 中断控制流程语句
- 9 数组
- 9.1 数组的声明与初始化
- 9.2 访问数组中的元素
- 9.3 for each 循环
- 9.4 多维数组
- 9.5 其他数组知识
- 10 综合实例
1 基本程序结构
一个普通的Java程序Hello.java。
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello,world!");
}
}
这个程序是最基本的Java程序结构。解析如下:
- 关键字public为访问权限修饰符,用于控制程序的其他部分对这段代码的访问级别。
- 关键字class表示Java程序中的全部内容都包含在类中。
- Hello标识符是该类的名字。
public static void main(String[] args)是Java程序入口的固定写法,程序从这里开始执行。System.out.println()是Java中最常用于控制台输出字符串的语句。
2 Java 项目结构
上图展示的是一个Java项目最基本的结构,分析如下:
- 一个Java项目中包含着Java运行的环境、Java代码和配置文件等等。
- 一般来说,Java的代码文件都放在src文件夹下的包(package)中。
- 值得注意的是,程序中的类名必须和Java文件的名字保持一致。
3 注释
注释分为:单行注释、多行注释和文档注释,实现方式如下:
//这是一个单行注释
/*
这是一个
多行注释
*/
/**
* 这是一个文档注释
* @author Jacks丶
* @version 1.0
* @Date 2019-12-18
*/
4 数据类型
| 类型 | 标识符 | 存储需求 | 取值范围 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 整型 | byte | 1个字节 | -2^8 ~ 2^8 - 1 |
| 整型 | short | 2个字节 | -2^15 ~ 2^15 - 1 |
| 整型 | int | 4个字节 | -2^31 ~ 2^31 - 1 |
| 整型 | long | 8个字节 | -2^63 ~ 2^63 - 1 |
| 浮点型 | float | 4个字节 | 有效位数 6 ~ 7 位 |
| 浮点型 | double | 8个字节 | 有效位数 15 位 |
| 字符型 | char | 2个字节 | \u0000 ~ \Uffff |
| 布尔型 | boolean | 1个字节 | true和false |
4.1 整型
- 长整型数需要加后缀L,如4000000000L
- 二进制数需要加前缀0b或0B,如0b11表示3。(Java7后的特性)
- 八进制数需要加前缀0,如011表示9
- 十六进制数需要加前缀0x或0X,如0x11表示17
- 可以用下划线分隔数值,如1_000_000表示一百万
4.2 浮点型
- float型数值有一个后缀F或f(如3.14f),没有f后缀的浮点数值(如3.14)默认为double类型
- 表示溢出或出错的三个特殊的浮点数值:
- 正无穷大
- 负无穷大
- NaN(不是一个数字)
4.3 字符型
特殊字符转义序列:
| 转义序列 | 名称 | Unicode值 |
|---|---|---|
| \b | 退格 | \u0008 |
| \t | 制表 | \u0009 |
| \n | 换行 | \u000a |
| \r | 回车 | \u000d |
| \" | 双引号 | \u0022 |
| \’ | 单引号 | \u0027 |
| \\ | 反斜杠 | \u005c |
4.4 布尔型
布尔型只有两个值:true和false,用于判定逻辑条件,且不能与整型值相互转换。
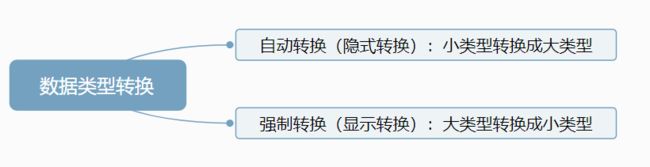
4.5 数据类型转换
这里的大类型和小类型是相对于存储需求来讲的。
double a = 10;//int类型自动转换成double类型。b = 10.0
int x = (int)3.14159;//double类型被强制转换成了int类型,存在的问题是精度丢失,小数点后的数字会丢失。x = 3
强制类型转换格式:
小类型 变量名 = (小类型)大类型数据;
强制类型转换容易造成数据溢出或、精度丢失,一般不推荐使用。
5 变量
Java是一种强类型语言,必须为每一个变量声明一种类型。
5.1 变量的声明与初始化
double salary;
int id;
boolean done;
salary = 20000.0;
id = 1;
done = true;
若变量声明后未初始化便直接调用,编译器会报错,如下所示:
int a;
System.out.println(a);
Error:The local variable a may not have been initialized
在Java中,变量的声明可以放在代码中的任意位置,如下所示:
int a = 1;
System.out.println(a);
int b = 2;
System.out.println(b);
5.2 常量
Java中的常量用final关键字修饰,表示是最终的,不可修改的。
常量名使用全大写,如下所示:
final double PI = 3.14159;
6 字符串
字符串不是基本数据类型,而是引用类型。从概念上理解字符串就是Unicode字符序列。
String介绍
6.1 声明与初始化
String a = "Hello";
String b = ",World!";
String c = a + b;
String d = a.substring(0,3);//a的前三个字符组成新的子串
System.out.println(c);
System.out.println(d);
需要注意的是,String字符串是不可修改的,如果要把"hello"变成"help"可以如下处理:
String e = "hello".substring(0,3) + "p"; //输出help
6.2 判断两个字符串是否相等
需用用到两个方法进行判断:equals 和 equalsIgnoreCase,如下展示:
System.out.println("hello".equals("hello"));//区分大小写
System.out.println("hello".equalsIgnoreCase("HELLO"));//不区分大小写
6.3 空串 和 Null串
空串""是一个长度为0的字符串,可以调用以下代码进行判断:
if(str.length() == 0)
if(str.equals(""))
空串是一个 Java 对象,有长度(0)和内容(空)。
Null串表示目前没有任何对象与该变量关联,可以用以下代码进行判断:
if(str == null)
有时需要同时排查 空串 和 null 串,可以用以下代码进行判断:
if(str == null || str.length() == 0);
if(str != null && str.length() != 0);
7 输入与输出
7.1 读取输入
获取键盘输入,需要使用Scanner包,具体实现如下:
import java.util.Scanner;//导入Scanner包
public class Iodemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);//创建一个获取输入的对象
System.out.println("How old are you?");//输入提示语句
int age = sc.nextInt();//获取输入,赋值给age
System.out.println("Your age is " + age);
}
}
关于Scanner类,查看这篇博客:Java中的 Scanner 类
7.2 格式化输出
最常用的输出代码:System.out.println("输出内容")
可以用字符串拼接的方式来格式化输出,如下所示:
String name = "Jacks";
int age = 20;
System.out.println("My name is " + name + " and my age is " + age + ".");
其他输出代码:
System.out.print(),这个和上面的功能差不多,但是不提供自动换行功能。System.out.printf(),这个是沿用与C语言库函数的printf,用于与C语言中的printf一致。
8 控制流程
8.1 块作用域
块(block),是指由一对大括号括起来的若干条简单的Java语句,确定了变量的作用域,一个块可以嵌入在另一块中,但是不能在嵌套的两个块中声明同名变量。
8.2 条件语句(if)
//1. 普通 if 条件判断语句
if (条件为真) 执行代码;
if(条件为真){
执行代码1;
执行代码2;
...
}
// 2. if 嵌套 else
if(条件为真){
执行代码1;
执行代码2;
...
}else{
执行代码1;
执行代码2;
...
}
// 3. if 嵌套 else if
if(条件1为真){
执行代码1;
执行代码2;
...
}else if(前面条件不满足且条件2为真){
执行代码1;
执行代码2;
...
}else{//前面的条件都不满足
执行代码
}
// if嵌套 else if
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 65;
if (score >= 80 && score <= 100) {
System.out.println("优秀!");
}else if (score >= 70) {
System.out.println("良好");
}else if (score >= 60) {
System.out.println("一般");
}else {
System.out.println("差");
}
}
8.3 循环结构
- while循环
while(条件为真){
循环体代码;
}
//输出5次hello,world
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 5;
while( a > 0 ) {
System.out.println("hello,world");
a--;
}
}
- do…while 循环
do{
循环体代码;
}while(条件为真);
// 先执行代码,再判断条件,打印 5 次hello,world
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 5;
do {
System.out.println("hello,world");
a--;
}while( a > 0 );
}
- for 循环
for(循环初值;循环条件;改变条件){
循环体内容;
}
// 打印 5 次 hello,world
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("hello,world");
}
}
8.4 多重选择:switch
switch(表达式){
case 值1:
执行语句;break;
case 值2:
执行语句2;break;
...
default:
执行语句n;
}
//输入一个 字母 显示对应情况
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入A,B,C,D中任意一个字符:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String choice = sc.next();
switch(choice) {
case "A":
System.out.println("优秀");break;
case "B":
System.out.println("良好");break;
case "C":
System.out.println("一般");break;
case "D":
System.out.println("差");break;
default:
System.out.println("无效输入!");
}
}
case 标签可以是:
- 类型为 char、byte、short或int的常量表达式
- 枚举常量
- 字符串字面量(Java7以后)
8.5 中断控制流程语句
- break
break关键字用于跳出所在循环体,并执行循环体后面的语句。
int a = 0;
while(a < 5){
a++;
if(a == 3) break;
System.out.println("hello,world");
}
这个程序只会打印2次
hello,world,循环执行第三次的时候,a==3,跳出循环体
-
continue
continue关键字用于跳过本次循环,并开始下一次循环。有不少初学者对
break和continue的概念理解混淆,反正记住遇到break,循环就结束了,遇到continue直接回到条件判断,如果条件成立则继续执行循环。
int a = 1;
while(a < 5){
a++;
if(a == 3) break;
System.out.println("hello,world");
}
这个程序会打印 4 次
hello,world,因为循环到第三次的时候,a == 3,又回到条件判断了,显然条件 3 < 5成立,继续执行程序a++,此时a == 4,不再执行continue。
9 数组
数组是一种数据结构,用来存储同一类型值的集合。
9.1 数组的声明与初始化
基本定义格式如下:
数据类型[] 数组名 = new 数据类型[长度]
数据类型[] 数组名 = new 数据类型[]{元素1,元素2,…}
数据类型[] 数组名 = {元素1,元素2,…}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//三种定义数组的方式
int[] a = new int[3];
char[] b = new char[] {'a','b','c'};
String[] c = {"Hello","world","你好","世界"};
//为数组a赋值
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) {
a[i] = i + 1;
}
//遍历数组a中的元素,增强for或称foreach
for(int i : a) {
System.out.print(" " + i);
}
System.out.println("");
//遍历数组b中元素
for(char i : b) {
System.out.print(" " + i);
}
System.out.println("");
//遍历数组c中的元素
for(String i : c) {
System.out.print(" " + i);
}
}
9.2 访问数组中的元素
通过一个整型下标可以访问数组中的每一个值(取值或赋值操作)。
取值:数组名[整型下标],如arrayName[4],访问数组的第5个元素
赋值:数组名[整型下标],如arrayName[3] = 4;将数组的第四个元素赋值为4。
需要注意的是,整型下标的取值范围是 [0 , 数组长度 - 1],数组的长度可以使用 array.length 来表示。
int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int b = a[0];
System.out.println(b);
9.3 for each 循环
for each循环也叫增强for,是一种功能很强的的循环结构,可以用来依次处理数组中的每个元素。
语句格式:
for(变量 : 数组) {
执行循环体;
}
int[] a = {1, 2, 3};
for( int i : a){
System.out.println(i);
}
9.4 多维数组
Java中多维数组的意义为数组中的数组。
- 二维数组定义与初始化
语句格式:
数据类型[][] 数组名 = new int[数组个数][每个数组的长度];
//定义二维数组
int[][] a = {{1,2,3},
{4,5,6},
{7,8,9}};
//遍历二维数组
for(int i = 0;i<a.length;i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) {
System.out.println(a[i][j]);
}
}
//快速打印2位数组
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(a));
- 延伸到多维数组
//定义三维数组
int[][][] b = {{{1,2,3},{4,5,6}},
{{7,8,9},{10,11,12}}};
//遍历三维数组
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < b[i].length; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < b[i][j].length; k++) {
System.out.println(b[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
//快速打印
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(b));
- 不规则数组
暂时用不到,后续添加。
9.5 其他数组知识
Arrays的API文档
- 数组拷贝
将一个数组的变量拷贝到一个新的数组中,可以使用Arrays类中copyOf方法。
语句格式:
数据类型[] 数组名 = Arrays.copyOf(数组名,新数组长度);
int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int[] b = Arrays.copyOf(a, 6);
for (int i : b) {
System.out.println(i);
}
- 排序
讲一个数组进行排序,可以使用Arrays类中的sort方法进行从小到大快速排序。
语句格式:
Arrays.sort(数组名);
int[] a = {1, 3, 7, 4, 5};
Arrays.sort(a);
for (int i : a) {
System.out.println(i);
}
10 综合实例
这是一个猜数字游戏,使用了Random类来产生一个指定范围内的随机整数,额外增加了一个异常处理的操作,目的在于输入不是整数时抛出异常并提醒重新输入。
package com.se.demo;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 猜数字游戏
* @author Jacks丶
*/
public class GuessNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random r = new Random();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int computer = r.nextInt(100); //产生一个[0,100)内的随机数,也就是0~99
//设置提示范围
int min = 0;
int max = 99;
//记录猜的次数
int count = 0;
while(true) {
count++;
//让玩家输入猜的数字
try {
System.out.println("请输入一个["+min+"]到["+max+"]的整数:");
int player = sc.nextInt();
if(player < computer) {//猜小了
min = player;
System.out.println("猜的数字太小了,再猜猜呢?");
}else if(player > computer){//猜大了
max = player;
System.out.println("猜的数字太大了,再猜猜呢?");
}else {//猜对了
System.out.println("恭喜你猜对了!小花花送给你。你一共猜了"+count+"次哦!");
break;
}
} catch (Exception e) {//异常处理
System.out.println("输入无效,请输入整数哦。");
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
}
}
}
}