基于SpringBoot开发一个Restful服务,实现增删改查功能
SpringBoot介绍
Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。
简单的来说就是,只需几个jar和一些简单的配置,就可以快速开发项目。
基于SpringBoot开发一个Restful服务
一、开发准备
1.1 数据库和表
在MySql中创建一个数据库和一张表,数据库的名称为 springboot,表名称为 book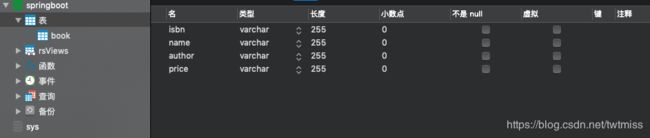
1.2 maven相关依赖
因为我们使用Maven创建的,所以需要添加SpringBoot的相关架包。
这里Maven的配置如下:
springBoot最核心的jar
spring-boot-starter :核心模块,包括自动配置支持、日志和YAML;
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.3.RELEASE
missLove
springboot
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
springboot
Demo project for Spring Boot
1.8
8.0.13
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
mysql
mysql-connector-java
${mysql.version}
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
1.3.2
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
true
二、工程说明
成功创建好数据库以及下载好相应架包之后。
我们来正式开发SpringBoot项目。
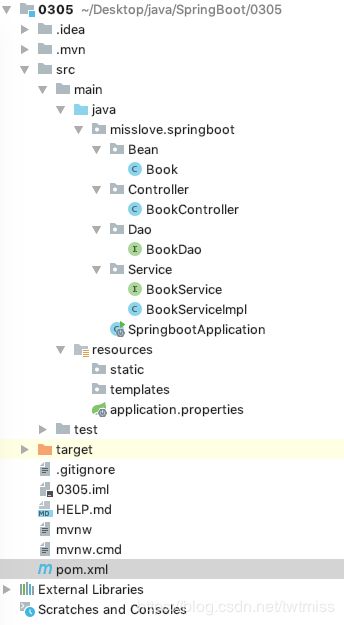
2.1工程结构图:
首先确定工程结构,这里就直接上图了。
2.2 自定义配置文件
一般我们需要一些自定义的配置,例如配置jdbc的连接配置,在这里我们可以用 application.properties 进行配置。数据源实际的配置以各位的为准。
## 数据源配置
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=qwerqwer
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
## Mybatis 配置
# 配置为 com.pancm.bean 指向实体类包路径。
#mybatis.typeAliasesPackage=misslove.springboot.beans
# 配置为 classpath 路径下 mapper 包下,* 代表会扫描所有 xml 文件。
#mybatis.mapperLocations=classpath\:mapper/*.xml
三、代码编写
在创建好相关工程目录之后,开始编写相应的代码。
3.1 实体类编写
由于在数据库中创建了一张book表,所以这里我们就只创建一个Book实体类,里面的字段对应book表的字段。
示例代码如下:
package misslove.springboot.Bean;
public class Book {
String name;
String author;
String price;
String isbn;
public Book(){}
public Book(String name, String author, String price, String isbn){
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
this.isbn = isbn;
}
public String getIsbn() {
return isbn;
}
public void setIsbn(String isbn) {
this.isbn = isbn;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public String getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(String price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
3.2 Dao层编写
在以前的Dao层这块,hibernate和mybatis 都可以使用注解或者使用mapper配置文件。在这里使用spring的JPA来完成基本的增删改查。
说明:
一般有两种方式实现与数据库实现CRUD:
第一种是xml的mapper配置。
第二种是使用注解,@Insert、@Select、@Update、@Delete 这些来完成。本篇使用的是第二种。
package misslove.springboot.Dao;
import misslove.springboot.Bean.Book;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface BookDao {
@Insert("insert into book(isbn,name,author,price) values (#{isbn},#{name},#{author},#{price})")
void addBook(Book book);
@Update("update book set name=#{name}, author=#{author},price=#{price}")
void updateBook(Book book);
@Select("select * from book")
List findBook();
@Delete("delete from book where isbn=#{isbn}")
void deleteBook(String isbn);
}
说明:
- mapper : 在接口上添加了这个注解表示这个接口是基于注解实现的CRUD。
- Insert、Select、Update、Delete:对应数据库的增、查、改、删。
3.3 Service 业务逻辑层
代码如下:
Service层接口:
package misslove.springboot.Service;
import misslove.springboot.Bean.Book;
import java.util.List;
public interface BookService {
boolean addBook(Book book);
boolean deleteBook(String isbn);
List findBook();
boolean updateBook(Book book);
}
Service层实现类
package misslove.springboot.Service;
import misslove.springboot.Dao.BookDao;
import misslove.springboot.Bean.Book;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService{
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Override
public boolean addBook(Book book){
try{
bookDao.addBook(book);
return true;
}catch (Exception e){
return false;
}
}
@Override
public boolean deleteBook(String isbn){
try{
bookDao.deleteBook(isbn);
return true;
}catch (Exception e){
return false;
}
}
@Override
public boolean updateBook(Book book){
try{
bookDao.updateBook(book);
return true;
}catch (Exception e){
return false;
}
}
@Override
public List findBook(){
return bookDao.findBook();
}
}
3.4 Controller 控制层
控制层这块和springMVC很像,但是相比而言要简洁不少。
说明:
- RestController:默认类中的方法都会以json的格式返回。
- RequestMapping: 接口路径配置。
- method : 请求格式。
- RequestParam: 请求参数。
具体实现如下:
package misslove.springboot.Controller;
import misslove.springboot.Service.BookService;
import misslove.springboot.Bean.Book;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
import static org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/book")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
//@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST, value = "/add")
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String add(@RequestBody Book book){
System.out.println(book.getName());
if(bookService.addBook(book)){
return "添加成功";
}
else {
return "添加失败";
}
}
//@RequestMapping(method = DELETE, value = "/delete")
@RequestMapping(method = DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String delete(@RequestParam("isbn") String isbn){
if(bookService.deleteBook(isbn)){
return "删除成功";
}else {
return "删除失败";
}
}
//@RequestMapping(method = PUT, value = "/edit")
@RequestMapping(method = PUT)
@ResponseBody
public String edit(@RequestBody Book book){
if(bookService.updateBook(book)){
return "修改成功";
}else {
return "修改失败";
}
}
//@RequestMapping(method = GET, value = "/find")
@RequestMapping(method = GET)
@ResponseBody
public List find(){
return bookService.findBook();
}
}
说明:
使用 @RequestMapping(method = ***, value = "/***") 这种样式的话,需要在URL里填入相应的URL地址postman选用对应的method方法,如http://localhost:8080/book/find
使用@RequestMapping(method = ***)这种样式的话,在postman里选用对应的method方法即可,如http://localhost:8080/book
3.5 Application 主程序
SpringApplication 则是用于从main方法启动Spring应用的类。
默认,它会执行以下步骤:
1.创建一个合适的ApplicationContext实例 (取决于classpath)。
2.注册一个CommandLinePropertySource,以便将命令行参数作为Spring properties。
3.刷新application context,加载所有单例beans。
4.激活所有CommandLineRunner beans。
直接使用main启动该类,SpringBoot便自动化配置了。
ps:即使是现在我依旧觉得这个实在是太厉害了。
该类的一些注解说明。:
SpringBootApplication:开启组件扫描和自动配置。
MapperScan: mapper 接口类扫描包配置
代码如下:
package misslove.springboot;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = "misslove.springboot.Dao")
public class SpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
四、代码测试
代码编写完之后,我们进行代码的测试。
启动Application 之后,使用postman工具进行接口的测试。
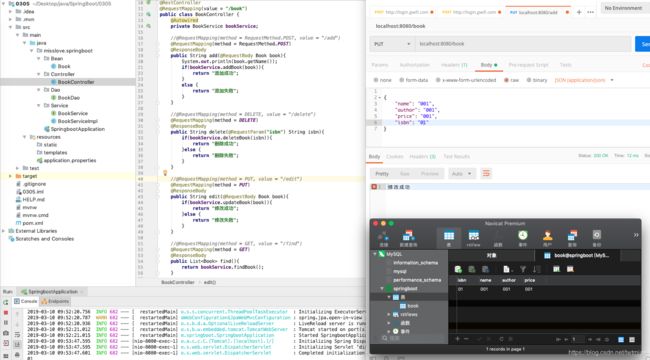
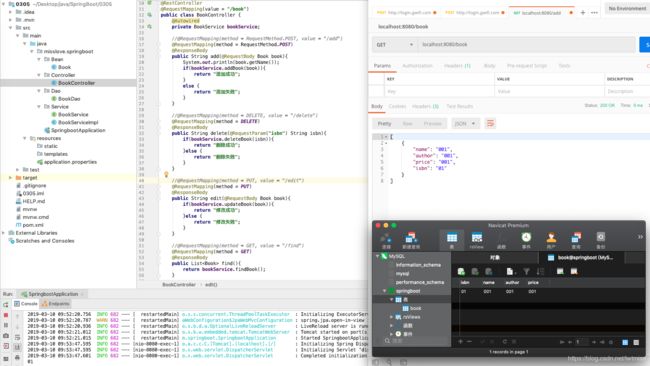
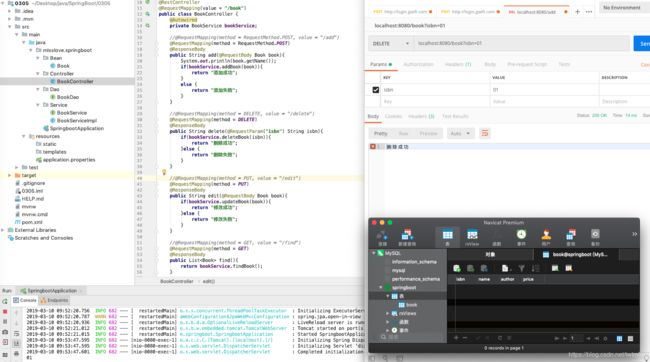
测试结果如下:
添加:
修改:
查询:
删除:
引用: https://www.cnblogs.com/xuwujing/p/8260935.html
项目github地址: https://github.com/twtmiss/Spring-Boot-RestFul/tree/master/MVC_mysql