touchGFX学习
一、touchGFX入门
1.touchGFX软件及visual Studio安装与联调
https://www.jianshu.com/p/777c7a75ade7
2.按钮与消息响应
https://www.jianshu.com/p/ea170dc92317
3.多屏呈现与MVP框架(1)
https://www.jianshu.com/p/1df1a337d584
4.多屏呈现与MVP框架(2)
https://www.jianshu.com/p/90aee3fe2950
5.多屏呈现与MVP框架(3)
https://www.jianshu.com/p/46519a4973fa
二、
官网学习https://touchgfx.zendesk.com/
电子工程世界touchGFX贴子
http://bbs.eeworld.com.cn/search.php?mod=forum&searchid=2368&orderby=lastpost&ascdesc=desc&searchsubmit=yes&kw=touchGFX
touchgfx 添加时钟控件
https://blog.csdn.net/ZenNaiHeQiao/article/details/86029640
三、
由于新工程的建立是以源码包里面的template工程为基础的,强烈建议下载一份源码包,里面还有 touchGFX manual手册
下面开始我们的touchGFX 开发之旅啦。
将你的 下载的压缩包放在无中文路径的目录下,
解压得到 touchgfx-release-x.x.x-eval,目录结构如下:+-- app
| +-- demo
| +-- example
| \-- template
|
+-- doc
+-- touchgfx
| +-- board
| +-- config
| +-- framework
| +-- lib
| \-- os
|
\-- changelog.txt
\-- known_issues.txt
app/目录里面放的是各种demo , example 和 一个空的工程
doc/目录放的是说明文档
touchgfx/目录放的是功能文件,比如板级文件,配置文件,转换工具,lib文件(这是核心文件),os源码(就是freeRTOS)
子目录中有:
/board :板级文件,根据特定平台初始化硬件,操作系统和touchGFX framework
注意 GPIO类是定义一个接口来内部调试用的
/framework: 平台接口和转换工具
+-- framework
| +-- include
| | +-- common
| | +-- mvp
| | +-- platform
| | \-- touchgfx
| |
| \-- tools
| +-- fontconvert
: +-- imageconvert
: \-- textconvert
/lib: 针对各个平台写的核心文件
/OS: 推荐的freeRTOS操作系统和 操作系统抽象层的实现(即OSWrappers.cpp文件)
+-- lib
| +-- board
| +-- core
| +-- linux
| +-- sdl
| \-- win
|
\-- os
介绍完主要目录和工具,可以新建一个新的工程了。与其他工程不同的是,touchGFX的工程必须先在PC机上编译一遍(gcc 或者 visual studio),然后使用 keil , iar, arm-gcc 编译。这是因为 assets/资源文件必须先在PC机上用前面讲到的 /framework/目录下的工具转换好,才可以被后面的编译器所使用。
进入app/template目录,复制整个EmptyApplication文件夹 到同目录下新建的 MyApplication文件夹,既然都已经帮建了一个空的工程,就不用我们自己辛苦从头开始了。
进入MyApplication目录,你看到这样的文件结构,强烈不建议修改它,因为touchGFX的资源文件(字体,文本,图象)必须经过PC转换工具预处理过之后,产生 generated文件夹,该目录下的c文件和头文件都是符合touchGFX内部需要的资源文件,这是我们开发板工程所需要的
+-- assets
| +-- fonts
| +-- images
| \-- texts
|
+-- config
| +-- gcc
| \-- msvs
|
+-- generated
| +-- fonts
| +-- images
| \-- texts
|
+-- gui
+-- platform
+-- simulator
\-- target
(1)assets/ 资源文件 ,分 fonts/ , images/ , texts/ 三个目录,
其中fonts/目录放的是.ttf , .otf 以及 .bdf等字体。
images/目录放的是bmp(24bit rgb,不支持alpha通道)或png图片(24bit RGB 或者 32位 RGBA 格式)texts/目录放的是.xlsx格式的excel文件,这个excel文件的格式是很讲究的,它分成两个sheet,一个是 Typography字体sheet,一个是 Translation文本sheet。这两个sheet的格式如下,
Typography sheet
| Typography Name | 字体名字,在 Translation sheet 中药用到对应的字体 |
| Font | 必须匹配在 assets/fonts/目录下放的字体文件名,如RobotoCondensed-Regular.ttf |
| Size | 字体大小 |
| Bpp | Bits per pixel ,规定为 1,2,4, |
Translation sheet
| Text ID | 字符串ID,在代码中使用该id指代该字符串 |
| Typography Name | 这个字符串用的字体 |
| Alignment | 水平对齐格式, 有 LEFT , RIGHT , CENTER |
| Language column | 引入多语种,列的名称为 GB , DK , USA , CH ,必须是大写字母,且1到3个 |
| Language specific typography | 对于某些语言,用特定的字体覆盖原先的字体, 格式为 language-TYPOGRAPHY ,比如 GB-TYPOGRAPHY |
| Language specific alignment | 对于某些语言,用特定的对齐方式覆盖原先的对齐方式,格式:language-ALIGNMENT |
(2)config/文件资源配置选项,分 gcc和 msvs两种,一种用的是gcc编译(要装一个PC端的软件,在邮箱会给的),一种用的是microsoft visual studio编译,文件为Application.props ,用xml语言描述
就是把前面的 fonts , images , texts 转换成cpp , hpp文件的配置情况,
有如下配置选项。
| Property | Description | GCC name | MSVS name |
| Framework path | 核心文件的相对路径,就是包里面的 /touchGFX 的相对路径 | touchgfx_path | TouchGFXReleasePath |
| Opaque Image Format | 实体画面的格式 | opaque_image_format | OpaqueImageOutputFormat |
| Non-opaque Image Format | 非实体画面的格式 | non_opaque_image_format | NonOpaqueImageOutputFormat |
| Alpha Dither | 是否含有alpha通道的bmp文件是否使用dither技术 | alpha_dither | AlphaDitherImage |
| Screen Orientation | 屏幕的旋转 | screen_orientation | RotateImage90 |
| Text Data Format | 文本的格式 | text_data_format | TextDataFormat |
| Additional C/C++ compiler flags | user_cflags | not supported |
(3)generated/是pc编译后自动产生的,我们可以直接删去,之后编译还是会重新生成的
(4)gui/是我们要着重修改的地方,之后再说
(5)platform/里面就是 os配置文件,至于os源码的位置前面已经说了
(6)simulator/就是pc端的项目放的地方,我比较倾向于用vs ,主要是gcc的makefile文件还不是很熟,不知道怎么修改
(7)target/就是我们的已经支持的开发板,所以有stm32f429-disco和stm32f746或者 stm32f469的原厂板的小伙伴可以直接上手玩的
未完待写。。。。。
MVP
https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_31039061/article/details/96979689
TouchGFX的 MVP机制MVP指的是 Model-View-Presenter
TouchGFX使用的MVP中,一个程序只有一个model,多对view和presenter。每一对 都是程序的一个screen。
Model
负责整个UI程序的状态,它和 backend通信以获得UI需要的状态。它就好比是 网关,负责UI和其他部分的通信。
View
建立UI的图形元素, view拦截用户事件(比如一个 click_event)并采取相应行动,通常是把消息传递给presenter,让presenter采取行动。view 必须知道和它组成一个 pair的 presenter,否则无法给出通知。
Presenter
presenter把model和 view很好地协调起来。presenter处理UI元素的逻辑事件而不关心它长什么样子,这是由view负责的。
当model通知presenter有变化发生时,它采取行动告诉view。反之,当view接收到用户事件时,presenter告诉model相应的变化。
FrontendApplication
一个程序有一个FrontendApplication , 它提供一个在不同的连续的view之间转换的机制。
screens 之间的切换被FrontendApplication处理。
一个切换分为两步,第一步是记住要切换到的screen,第二步才是执行切换。
之前说过一个screen是由一对presenter和view组成的,使用 MVPApplication.hpp文件的 makeTransition 可以切换到对应的 presenter和 view。源码是肯定没有的,只能调用API。
下面展示了MVP的机制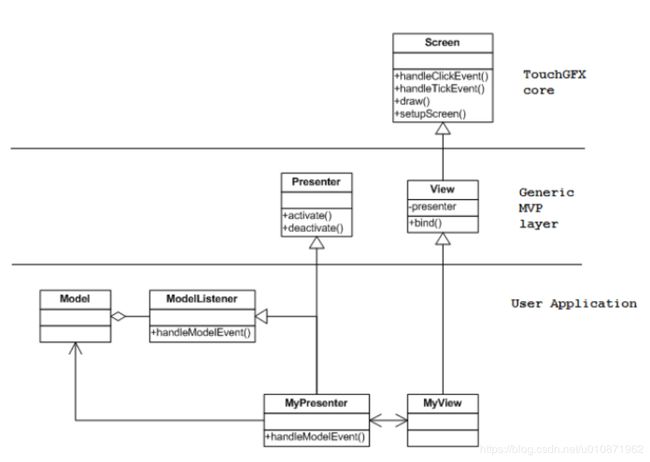
从这个图可以看出,在 User Application 层,通过继承Presenter和ModelListener得到MyPresenter。
Presenter类没有实现和 View的绑定,因此继承的时候要加一个private成员,这里是MyView &view。
class Presenter
{
public:
/**
* @fn virtual void Presenter::activate()
*
* @brief Place initialization code for the Presenter here.
*
* The activate function is called automatically when a screen
* transition causes this Presenter to become active. Place
* initialization code for the Presenter here.
*/
virtual void activate()
{
}
/**
* @fn virtual void Presenter::deactivate()
*
* @brief Place cleanup code for the Presenter here.
*
* The deactivate function is called automatically when a screen
* transition causes this Presenter to become inactive. Place
* cleanup code for the Presenter here.
*/
virtual void deactivate()
{
}
/**
* @fn virtual Presenter::~Presenter()
*
* @brief Destructor.
*
* Destructor.
*/
virtual ~Presenter()
{
}
protected:
/**
* @fn Presenter::Presenter()
*
* @brief Default constructor.
*
* Default constructor.
*/
Presenter()
{
}
};
ModelListener 类
class ModelListener
{
public:
ModelListener() : model(0) {}
/**
* Sets the model pointer to point to the Model object. Called automatically
* when switching screen.
*/
void bind(Model* m) { model = m; }
protected:
Model* model;
};
通过继承类模板 View 得到 MyView ,MyView和MyPresenter的绑定是通过模板实现的
查看源码有:
template
class View : public Screen
{
public:
/**
* @fn View::View()
*
* @brief Default constructor.
*
* Default constructor.
*/
View() : presenter(0)
{
}
/**
* @fn void View::bind(T& presenter)
*
* @brief Binds an instance of a specific Presenter type (subclass) to the View instance.
*
* Binds an instance of a specific Presenter type (subclass) to the View instance.
* This function is called automatically when a new presenter/view pair is activated.
*
* @param [in] presenter The specific Presenter to be associated with the View.
*/
void bind(T& presenter)
{
this->presenter = &presenter;
}
protected:
T* presenter; ///< Pointer to the Presenter associated with this view.
};
这里使用 bind()函数 实现。
继承很简单,这样就实现了。
class MainView : public View