并发编程(十四):阻塞队列之LinkedBlockingQueue
一,关联源码链接
* 并发编程(四):AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码分析
* 并发编程(五):AQS之重入锁ReentrantLock
* 并发编程(七):AQS之Condition
二,LinkedBlockingQueue 概述
1,LinkedBlockingQueue
LinkedBlockingQueue 底层通过链表实现,每一个元素被包装成 Node 节点挂在内部定义的单向链表上,LinkedBlockingQueue 默认长度为 Integer.MAX_VALUE,当然可以通过构造器指定长度。LinkedBlockingQueue 内部定义了两个 ReentrantLock 进行读写锁控制,并通过两个 Condition 进行线程为空或者线程已满后的读写唤醒。
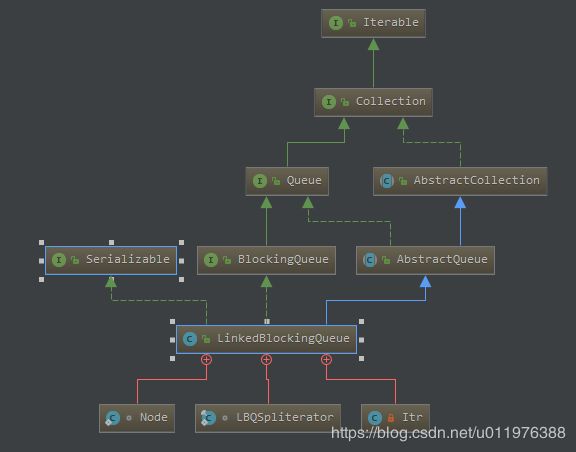
2,类图
* Node 内部类是链表部分
* Itr 内部类为迭代器部分
3,常用API
/* 初始化部分 */
// 无参构造,默认长度为Integer.MAX_VALUE
public LinkedBlockingQueue();
// 有参构造,初始化长度为指定长度
public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity);
// 有参构造,初始化列表为阻塞队列
public LinkedBlockingQueue(Collection c);
/* 数据读写部分 */
// 添加元素,队列已满抛异常
public boolean add(E e);
// 添加元素,队列已满返回false
public boolean offer(E e);
// 添加元素,队列已满阻塞
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException;
// 获取元素,为空返回null,不移除
public E peek();
// 获取元素,为空返回null,移除
public E poll();
// 获取元素,为空阻塞,移除
public E take() throws InterruptedException;
// 元素移除
public boolean remove(Object o);
/* 迭代器部分 */
// 构造迭代器
public Iterator iterator();
Itr();
// 是否有下一个元素
public boolean hasNext();
// 获取下一个元素
public E next();
// 移除元素
public void remove(); 4,功能DEMO
* 基本与 ArrayBlockingQueue 一致
三,锁处理机制
1,锁处理机制
/** Lock held by take, poll, etc */
private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Lock held by put, offer, etc */
private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();* LinkedBlockingQueue 内部提供了两个 ReentrantLock 实例,分别表示读锁和写锁,在对 LinkedBlockingQueue 元素进行操作时,会根据操作类型分别添加读锁和写锁
* 在迭代操作时候,同时对读锁和写锁进行加锁,保证数据正常
2,锁通信机制
/** Wait queue for waiting takes */
private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();
/** Wait queue for waiting puts */
private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();* 锁通信中,与 ArrayBlockingQueue 一致,同样提供了非空和非满两个 Condition,在对数据操作中,进行沉睡和唤醒操作
四,源码分析
1,初始化源码分析
* LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity)
public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
// 无参构造,默认长度为 Integer.MAX_VALUE
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
// 带参构造,直接指定长度
public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.capacity = capacity;
// 初始化 Head 节点
last = head = new Node(null);
} * LinkedBlockingQueue(Collection c)
public LinkedBlockingQueue(Collection c) {
// 初始化长度为默认长度
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 对写锁进行加锁,初始化参数集合到队列中
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock();
try {
// n表示元素数量
int n = 0;
// 遍历元素添加
for (E e : c) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (n == capacity)
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
// 写队列
enqueue(new Node(e));
++n;
}
// 最终添加到count中,count表示元素数量,通过AtomicInteger定义
count.set(n);
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
} 2,读源码分析
2.1,peek():取数据,不移除
public E peek() {
if (count.get() == 0)
return null;
// 对读锁加锁
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
// 获取头结点元素,并获取Node值
// 取下一个是因为head节点为包装的空节点
Node first = head.next;
if (first == null)
return null;
else
return first.item;
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
} 2.2,poll():取数据,移除
* poll()
public E poll() {
// 获取数量,为空直接返回null
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
if (count.get() == 0)
return null;
E x = null;
int c = -1;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
if (count.get() > 0) {
// 存在元素,直接获取并移除元素
x = dequeue();
// 并对count递减
c = count.getAndDecrement();
if (c > 1)
// 长度大于1,唤醒读线程
notEmpty.signal();
}
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
// 相等,表示已满,取出一个数据后,队列未满,直接唤醒写线程
if (c == capacity)
signalNotFull();
return x;
}* dequeue():线程出队列,公共方法
private E dequeue() {
// 把头结点直接移除,吧元素的首节点置空后替换为头结点,
// 并返回元素首节点
Node h = head;
Node first = h.next;
h.next = h; // help GC
head = first;
E x = first.item;
first.item = null;
return x;
} * signalNotFull()
private void signalNotFull() {
// 写线程加锁
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock();
try {
// 唤醒写数据线程
notFull.signal();
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
}2.3,take():取数据,阻塞,移除
* take()
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
E x;
int c = -1;
// 后去当前元素数量
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 元素数量为0,为空,非空Condition等待
while (count.get() == 0) {
notEmpty.await();
}
// 从链表中获取元素
x = dequeue();
// 数量递增
c = count.getAndDecrement();
// 此处可能适配多线程
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
// 如果原来数据量为最大长度,此时已经取出一个,则可以唤醒写线程
if (c == capacity)
signalNotFull();
return x;
}3,写源码分析
3.1,add(E e):添加元素,队列满后抛异常
* add(E e)
public boolean add(E e) {
// 直接调用offer保存数据,添加链表失败返回false后直接抛异常
if (offer(e))
return true;
else
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
}3.2,offer(E e):添加元素,队列满返回false
* offer(E e)
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 添加元素,如果数量为定长值,返回false
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
if (count.get() == capacity)
return false;
int c = -1;
// 包装Node节点
Node node = new Node(e);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock();
try {
// 队列未满,添加Node节点到队列中
if (count.get() < capacity) {
enqueue(node);
c = count.getAndIncrement();
// c + 1小于定长,说明当前链表长度未满,唤醒非满Condition
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
}
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
// c为0,表示原来链表为空,此时添加元素,唤醒非空Condition
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
return c >= 0;
} * enqueue(Node
private void enqueue(Node node) {
// 把当前节点挂在链表尾部
last = last.next = node;
} 3.3,put(E e):添加元素,队列满后阻塞
* put(E e)
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int c = -1;
Node node = new Node(e);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
putLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 如果链表已满,非满Condition等待
while (count.get() == capacity) {
notFull.await();
}
// 元素入链表
enqueue(node);
c = count.getAndIncrement();
// 链表未满,直接唤醒非满Condition
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
} 4,元素移除分析
* remove(Object o)
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
// 获取全部锁
fullyLock();
try {
// 从头节点开始遍历Node,判断元素是否相等
for (Node trail = head, p = trail.next;
p != null;
trail = p, p = p.next) {
// 元素相等,移除节点
if (o.equals(p.item)) {
unlink(p, trail);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
} * unlink(Node
// p:当前节点
// trail:上一个节点
void unlink(Node p, Node trail) {
// 置空当前节点,并把当前节点的下一个节点挂到trail的下一个节点
// 相当于把当前节点从列表中移除
p.item = null;
trail.next = p.next;
// 尾节点替换
if (last == p)
last = trail;
if (count.getAndDecrement() == capacity)
notFull.signal();
} 5,迭代器源码分析
5.1,迭代器初始化
* iterator()
// LinkedBlockingQueue 触发迭代
public Iterator iterator() {
return new Itr();
} * Itr()
Itr() {
// 迭代器处理对读锁和写锁全部加锁
fullyLock();
try {
// 初始化current参数,为头节点
current = head.next;
if (current != null)
currentElement = current.item;
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}5.2,判断下一个元素
* hasNext()
public boolean hasNext() {
// 判断current是否存在
return current != null;
}5.3,获取下一个元素
* next()
public E next() {
fullyLock();
try {
if (current == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// 表示返回元素
E x = currentElement;
// 此处初始化lastRet,表示上一个节点
lastRet = current;
// 重置当前元素为下一个节点
current = nextNode(current);
currentElement = (current == null) ? null : current.item;
return x;
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
} * nextNode(Node
private Node nextNode(Node p) {
for (;;) {
Node s = p.next;
// 表示最后一个节点,则返回头结点
if (s == p)
return head.next;
// 节点为有效节点,直接返回
if (s == null || s.item != null)
return s;
p = s;
}
} 5.4,移除当前元素
public void remove() {
// lastRet 在 next() 中初始化,表示当前迭代到的元素
if (lastRet == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
fullyLock();
try {
Node node = lastRet;
lastRet = null;
// 移除链表节点
for (Node trail = head, p = trail.next;
p != null;
trail = p, p = p.next) {
if (p == node) {
unlink(p, trail);
break;
}
}
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
} LinkedBlockingQueue的迭代器还行。。。