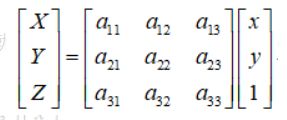Python+OpenCV实现图像的全景拼接
Python+OpenCV实现图像的全景拼接
- 实现结果
环境:python3.5.2 + openCV3.4
1.算法目的
将两张相同场景的场景图片进行全景拼接。
2.算法步骤
本算法基本步骤有以下几步:
步骤1:将图形先进行桶形矫正
图片越多拼接可能就会越夸张。

本算法是将图片进行桶形矫正。目的就是来缩减透视变换(Homography)之后图片产生的变形,从而使拼接图片变得畸形。
步骤2:特征点匹配
本算法使用的sift算法匹配,它具有旋转不变性和缩放不变性,具体原理在之后会补上一篇关于sift算法的文章,这里就不做详细介绍。
在匹配特征点的过程中,透视矩阵选取了4对特征点计算,公式为
点的齐次坐标依赖于其尺度定义,因此矩阵H也仅依赖尺度定义,所以,单应性矩阵具有8个独立的自由度。
如果在选取的不正确的特征点,那么透视矩阵就可能计算错误,所以为了提高结果的鲁棒性,就要去除这些错误的特征点,而RANSAC方法就是用来删除这些错误的特征点。
**RANSAC:**用来找到正确模型来拟合带有噪声数据的迭代方法。基本思想:数据中包含正确的点和噪声点,合理的模型应该能够在描述正确数据点的同时摈弃噪声点。
RANSAC方法随机获取4对不同的特征匹配坐标,计算出透视矩阵H1,再将第二张图的特征匹配点经过这个矩阵H1映射到第一张图的坐标空间里,通过计算来验证这个H1矩阵是否满足绝大部分的特征点。
通过迭代多次,以满足最多特征匹配点的特征矩阵H作为结果。
这样正常情况就可以去除错误的特征点了,除非匹配错误的特征点比正确的还多。
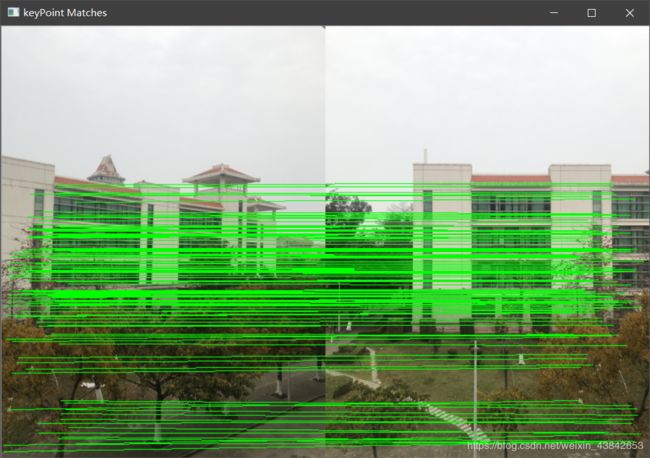
下图是我在嘉庚图书馆旁拍摄的照片的特征点匹配。
步骤三利用得到的变换矩阵进行图片的拼接。
可以看出基本做到了无缝拼接。只是在色差上还是看得出衔接的部分存在。

实现结果
我在宿舍里又多照了几组照片来实验:
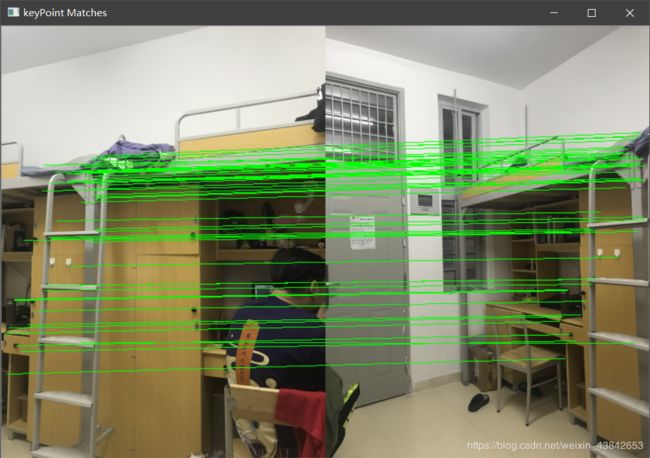
室内宿舍场景的特征点匹配:
拼接结果:
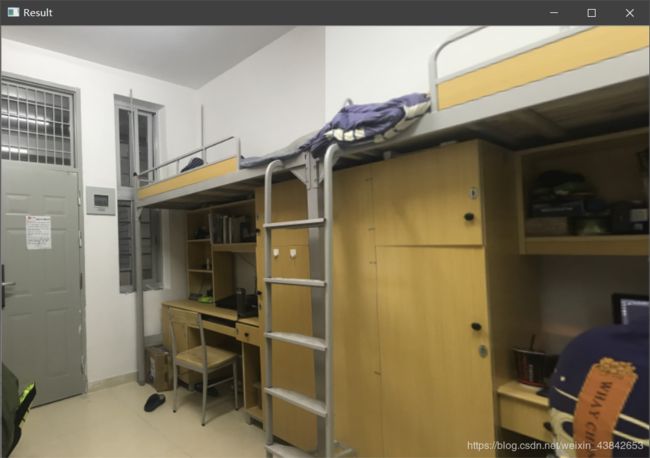

在室内的效果根据结果来看效果也还可以。
我测试了宿舍里景深落差较大的两张图片:
特征点匹配:

虽然距离较远,但是还是可以粗略的匹配到特征点。
拼接结果:

从结果上来看可以看得出来,两张图片依然可以正确而粗略地拼接再一起,可以看得出是同一个区域。只是由于特征点不够,在细节上景深落差较大的还是没办法完美地拼接。
import numpy as np
import cv2 as cv
import imutils
class Stitcher:
def __init__(self):
self.isv3 = imutils.is_cv3()
def stitch(self,imgs, ratio = 0.75, reprojThresh = 4.0, showMatches = False):
print('A')
(img2, img1) = imgs
#获取关键点和描述符
(kp1, des1) = self.detectAndDescribe(img1)
(kp2, des2) = self.detectAndDescribe(img2)
print(len(kp1),len(des1))
print(len(kp2), len(des2))
R = self.matchKeyPoints(kp1, kp2, des1, des2, ratio, reprojThresh)
#如果没有足够的最佳匹配点,M为None
if R is None:
return None
(good, M, mask) = R
print(M)
#对img1透视变换,M是ROI区域矩阵, 变换后的大小是(img1.w+img2.w, img1.h)
result = cv.warpPerspective(img1, M, (img1.shape[1] + img2.shape[1], img1.shape[0]))
#将img2的值赋给结果图像
result[0:img2.shape[0], 0:img2.shape[1]] = img2
#是否需要显示ROI区域
if showMatches:
vis = self.drawMatches1(img1, img2, kp1, kp2, good, mask)
return (result, vis)
return result
def detectAndDescribe(self,img):
print('B')
gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#检查我们使用的是否是penCV3.x
if self.isv3:
sift = cv.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
(kps, des) = sift.detectAndCompute(img, None)
else:
sift = cv.FastFeatureDetector_create('SIFT')
kps = sift.detect(gray)
des = sift.compute(gray, kps)
kps = np.float32([kp.pt for kp in kps]) # **********************************
#返回关键点和描述符
return (kps, des)
def matchKeyPoints(self,kp1, kp2, des1, des2, ratio, reprojThresh):
print('C')
#初始化BF,因为使用的是SIFT ,所以使用默认参数
matcher = cv.DescriptorMatcher_create('BruteForce')
# bf = cv.BFMatcher()
# matches = bf.knnMatch(des1, des2, k=2)
matches = matcher.knnMatch(des1, des2, 2) #***********************************
#获取理想匹配
good = []
for m in matches:
if len(m) == 2 and m[0].distance < ratio * m[1].distance:
good.append((m[0].trainIdx, m[0].queryIdx))
print(len(good))
#最少要有四个点才能做透视变换
if len(good) > 4:
#获取关键点的坐标
# src_pts = np.float32([kp1[m.queryIdx].pt for m in good]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
# dst_pts = np.float32([kp2[m.trainIdx].pt for m in good]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
src_pts = np.float32([kp1[i] for (_, i) in good])
dst_pts = np.float32([kp2[i] for (i, _) in good])
#通过两个图像的关键点计算变换矩阵
(M, mask) = cv.findHomography(src_pts, dst_pts, cv.RANSAC, reprojThresh)
#返回最佳匹配点、变换矩阵和掩模
return (good, M, mask)
#如果不满足最少四个 就返回None
return None
def drawMatches(img1, img2, kp1, kp2, matches, mask, M):
# 获得原图像的高和宽
h, w = img1.shape[:2]
# 使用得到的变换矩阵对原图像的四个角进行变换,获得目标图像上对应的坐标
pts = np.float32([[0, 0], [0, h-1], [w-1, h-1], [w-1, 0]]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
dst = cv.perspectiveTransform(pts, M)
matchesMask = mask.ravel().tolist()
draw_params = dict(matchColor = (0, 255, 0),
singlePointColor = None,
matchesMask = matchesMask,
flags = 2)
img = cv.drawMatches(img1, kp1, img2, kp2, matches, None, **draw_params)
return img
def drawMatches1(self,img1, img2, kp1, kp2, metches,mask):
print('D')
(hA,wA) = img1.shape[:2]
(hB,wB) = img2.shape[:2]
vis = np.zeros((max(hA,hB), wA+wB, 3), dtype='uint8')
vis[0:hA, 0:wA] = img1
vis[0:hB, wA:] = img2
for ((trainIdx, queryIdx),s) in zip(metches, mask):
if s == 1:
ptA = (int(kp1[queryIdx][0]), int(kp1[queryIdx][1]))
ptB = (int(kp2[trainIdx][0])+wA, int(kp2[trainIdx][1]))
cv.line(vis, ptA, ptB, (0, 255, 0), 1)
return vis
# def show():
# img1 = cv.imread('image/sedona_left_01.png')
# img2 = cv.imread('image/sedona_right_01.png')
# img1 = imutils.resize(img1, width=400)
# img2 = imutils.resize(img2, width=400)
#
# stitcher = cv.Stitcher()
# (result, vis) = stitcher.stitch([img1, img2])
# # (result, vis) = stitch([img1,img2], showMatches=True)
#
# cv.imshow('image A', img1)
# cv.imshow('image B', img2)
# cv.imshow('keyPoint Matches', vis)
# cv.imshow('Result', result)
#
# cv.waitKey(0)
# cv.destroyAllWindows()
# show()