Java后端架构师的成长之路(一)——数据结构与算法(2)
数据结构与算法
- 栈
- 简介
- 栈的应用场景
- 栈的快速入门
- 数组实现栈
- 链表实现栈
- 前缀、中缀、后缀表达式(逆波兰表达式)
- 前缀表达式
- 中缀表达式
- 后缀表达式
- 中缀表达式转后缀表达式
- 举例
- 栈实现计算器
- 整数计数
- 计算器升级版
- 递归
- 简介
- 递归的概念
- 递归能解决的问题
- 递归需要遵守的规则
- 迷宫问题
- 代码实现
- 八皇后问题
- 思路分析
- 代码实现
- 哈希表
- 基本介绍
- 思路分析
- 代码实现
栈
- 先看一个实际需求:输入一个表达式(例如:7 * 2 * 2 -5+1-5+3-3),计算该表达式的值。
- 请问: 计算机底层是如何运算得到结果的? 注意不是简单的把算式列出运算,因为我们看这个算式 7 * 2 * 2 - 5,但是计算机怎么理解这个算式的(对计算机而言,它接收到的就是一个字符串)。==>> 栈
简介
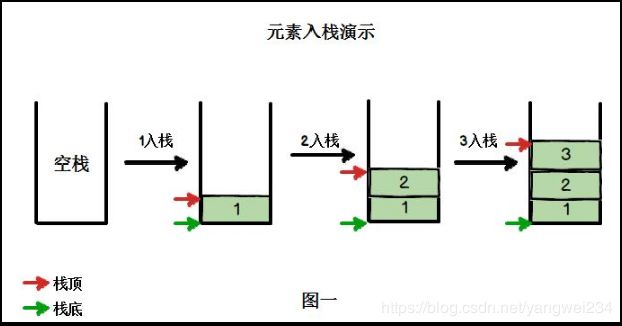
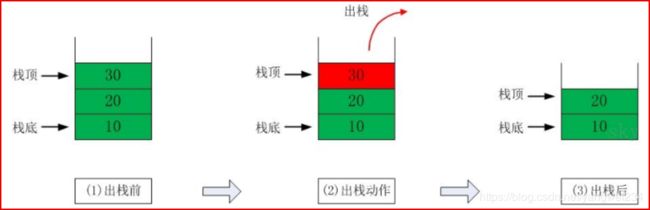
- 栈的英文为 stack,是一个先入后出(FILO-First In Last Out)的有序列表。
- 栈(stack)是限制线性表中元素的插入和删除只能在线性表的同一端进行的一种特殊线性表。允许插入和删除的一端,为变化的一端,称为栈顶(Top),另一端为固定的一端,称为栈底(Bottom)。
- 根据栈的定义可知,最先放入栈中元素在栈底,最后放入的元素在栈顶,而删除元素刚好相反,最后放入的元素最先删除,最先放入的元素最后删除。
- 出栈(pop)和入栈(push)的概念,如下图所示:
栈的应用场景
- 子程序的调用:在跳往子程序前,会先将下个指令的地址存到堆栈中,直到子程序执行完后再将地址取出,以回到原来的程序中。
- 处理递归调用:和子程序的调用类似,只是除了储存下一个指令的地址外,也将参数、区域变量等数据存入堆栈中。
- 表达式的转换:中缀表达式转后缀表达式 与求值(实际解决)。
- 二叉树的遍历。
- 图形的深度优先(depth一first)搜索法。
栈的快速入门
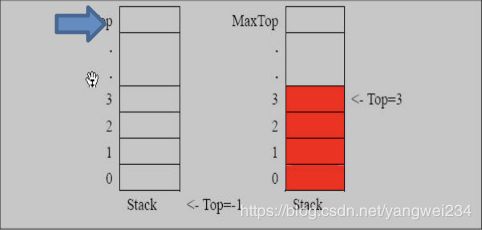
- 需求:用数组模拟栈的使用,由于栈是一种有序列表,当然可以使用数组的结构来储存栈的数据内容,下面我们就用数组模拟栈的出栈,入栈等操作。
- 思路分析:① 定义一个 top 来表示栈顶,初始化 为 -1;② 入栈的操作,当有数据加入到栈时,top++; stack[top] = data;③ 出栈的操作,int value = stack[top]; top–, return value;
数组实现栈
- 代码实现:
/**
* 定义栈接口
*/
public interface Stack {
/**
* 判断栈满
*
* @return
*/
boolean isFull();
/**
* 判断栈空
*
* @return
*/
boolean isEmpty();
/**
* 入栈-push
*/
void push(int value);
/**
* 出栈-pop
*/
int pop();
/**
* 查看栈顶的元素
*/
int peek();
/**
* 遍历栈
*/
void show();
}
/**
* 数组实现栈
*/
class ArrayStack implements Stack {
/**
* 栈的大小
*/
private int maxSize;
/**
* 数组模拟栈
*/
private int[] stack;
/**
* 栈顶,初始化为-1
*/
private int top = -1;
public ArrayStack(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize <= 0 ? 0 : maxSize;
stack = new int[this.maxSize];
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return top == maxSize - 1;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
@Override
public void push(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈满了~~");
}
top++;
stack[top] = value;
}
@Override
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈空,没有数据~~");
}
int value = stack[top];
top--;
return value;
}
@Override
public int peek() {
return stack[top];
}
@Override
public void show() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空,没有数据~~");
return;
}
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n", i, stack[i]);
}
}
}
- 测试:
public class StackApp {
public static void play(Stack stack, String subject) {
System.out.println(subject);
// 菜单
System.out.println("show:显示栈");
System.out.println("exit:退出程序");
System.out.println("push[空格][number]:添加数据到栈(入栈)");
System.out.println("pop:从栈获取数据(出栈)");
System.out.println("peek:查看栈顶的数据");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
while (loop) {
// 接收一个字符
String command = scanner.nextLine().trim();
String[] commands = command.split(" ");
switch (commands[0]) {
case "show":
stack.show();
break;
case "exit":
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
case "push":
try {
int value = Integer.parseInt(commands[1]);
stack.push(value);
System.out.printf("%d入栈成功!\n", value);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage() + " 入栈失败!");
}
break;
case "pop":
try {
int value = stack.pop();
System.out.printf("出栈的数据是%d\n", value);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case "peek":
try {
int value = stack.peek();
System.out.printf("栈顶的数据是%d\n", value);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
public class ArrayStackDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StackApp.play(new ArrayStack(4), "数组实现栈功能演示~~");
}
}
数组实现栈功能演示~~
show:显示栈
exit:退出程序
push[空格][number]:添加数据到栈(入栈)
pop:从栈获取数据(出栈)
peek:查看栈顶的数据
show
栈空,没有数据~~
push 1
1入栈成功!
push 2
2入栈成功!
push 3
3入栈成功!
push 5
5入栈成功!
push 8
栈满了~~ 入栈失败!
peek
栈顶的数据是5
pop
出栈的数据是5
pop
出栈的数据是3
pop
出栈的数据是2
pop
出栈的数据是1
pop
栈空,没有数据~~
peek
-1
exit
链表实现栈
- 代码实现:
/**
* 链表实现栈
*/
class LinkedListStack implements Stack {
/**
* 定义一个双向链表
*/
static class LinkedNode {
private Integer value;
private LinkedNode next;
private LinkedNode pre;
public LinkedNode(Integer value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
/**
* 栈的大小
*/
private int maxSize;
/**
* 记录链表有效数据长度
*/
private int counter = 0;
/**
* 链表模拟栈
*/
private LinkedNode head;
/**
* 栈顶
*/
private LinkedNode top;
public LinkedListStack(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
// 初始化头结点和栈顶
head = new LinkedNode(null);
top = head.next;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return counter == maxSize;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head.next == null;
}
@Override
public void push(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈满了~~");
}
LinkedNode node = new LinkedNode(value);
node.pre = top;
if (top == null) {
head.next = node;
node.pre = head;
} else {
top.next = node;
}
top = node;
counter++;
}
@Override
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈空,没有数据~~");
}
int value = top.value;
LinkedNode pre = top.pre;
top.pre = null;
top = pre;
top.next = null;
counter--;
return value;
}
@Override
public int peek() {
return top.value;
}
@Override
public void show() {
LinkedNode cursor = head.next;
while (cursor != null) {
System.out.printf("%d -> ", cursor.value);
cursor = cursor.next;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
}
- 测试:
public class LinkedListStackDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StackApp.play(new LinkedListStack(4), "链表实现栈功能演示~~");
}
}
链表实现栈功能演示~~
show:显示栈
exit:退出程序
push[空格][number]:添加数据到栈(入栈)
pop:从栈获取数据(出栈)
peek:查看栈顶的数据
show
null
push 1
1入栈成功!
push 2
2入栈成功!
push 3
3入栈成功!
show
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> null
push 4
4入栈成功!
push 5
栈满了~~ 入栈失败!
pop
出栈的数据是4
pop
出栈的数据是3
peek
栈顶的数据是2
pop
出栈的数据是2
pop
出栈的数据是1
pop
栈空,没有数据~~
show
null
exit
前缀、中缀、后缀表达式(逆波兰表达式)
前缀表达式
- 前缀表达式又称波兰表达式,运算符位于操作数之前,例如: (3+4)×5-6 对应的前缀表达式就是 - × + 3 4 5 6
- 前缀表达式的计算机求值过程:从右至左扫描表达式,遇到数字时,将数字压入堆栈,遇到运算符时,弹出栈顶的两个数,用运算符对它们做相应的计算(栈顶元素 和 次顶元素),并将结果入栈;重复上述过程直到表达式最左端,最后运算得出的值即为表达式的结果。
- 例如: (3+4)×5-6 对应的前缀表达式就是 - × + 3 4 5 6 , 针对前缀表达式求值步骤如下:
* 从右至左扫描,将6、5、4、3压入堆栈
* 遇到+运算符,因此弹出3和4(3为栈顶元素,4为次顶元素),计算出3+4的值,得7,再将7入栈
* 接下来是×运算符,因此弹出7和5,计算出7×5=35,将35入栈
* 最后是-运算符,计算出35-6的值,即29,由此得出最终结果
中缀表达式
- 中缀表达式就是常见的运算表达式,如(3+4)×5-6
- 中缀表达式的求值是我们人最熟悉的,但是对计算机来说却不好操作。因此,在计算结果时,往往会将中缀表达式转成其它表达式来操作(一般转成后缀表达式)。
后缀表达式
- 后缀表达式又称逆波兰表达式,与前缀表达式相似,只是运算符位于操作数之后。
- 举例:(3+4)×5-6 对应的后缀表达式就是 3 4 + 5 × 6 –
- 再比如:

- 后缀表达式的计算机求值过程:从左至右扫描表达式,遇到数字时,将数字压入堆栈,遇到运算符时,弹出栈顶的两个数,用运算符对它们做相应的计算(次顶元素 和 栈顶元素),并将结果入栈;重复上述过程直到表达式最右端,最后运算得出的值即为表达式的结果。
- 例如: (3+4)×5-6 对应的后缀表达式就是 3 4 + 5 × 6 - , 针对后缀表达式求值步骤如下:
* 从左至右扫描,将3和4压入堆栈
* 遇到+运算符,因此弹出4和3(4为栈顶元素,3为次顶元素),计算出3+4的值,得7,再将7入栈
* 将5入栈
* 接下来是×运算符,因此弹出5和7,计算出7×5=35,将35入栈
* 将6入栈
* 最后是-运算符,计算出35-6的值,即29,由此得出最终结果
中缀表达式转后缀表达式
后缀表达式适合计算式进行运算,但是人却不太容易写出来,尤其是表达式很长的情况下,因此在开发中,我们需要将 中缀表达式转成后缀表达式。具体步骤如下:
- ① 初始一个栈(stack)用于存放运算符,和一个队列(queue)用于结果输出,并从左至右开始读取中缀表达式;
- ② 当读到一个操作数时,立即把它放到输出队列中;
- ③ 当读到一个运算符时,比较其与栈顶运算符的优先级:
1. 若栈为空,或栈顶运算符为左括号“(”,则直接将此运算符入栈
2. 否则,若优先级比栈顶运算符的高,也将运算符压入栈中
3. 否则,栈顶的运算符弹出,并加入到输出队列中,再次转到步骤(③-1)与stack中新的栈顶运算符相比较
- ④ 遇到括号时:
4. 若是左括号"(",则直接压入栈中;
5. 若是右括号")",则依次弹出栈顶的运算符,并加入到输出队列中,直至遇到左括号,此时将这一对括号丢弃
- ⑤ 重复步骤②至④ ,直到表达式的最右边;
- ⑥ 将栈中剩余的运算符依次弹出,并加入到输出队列中,此时输出队列queue的值即为后缀表达式的值
举例
- 求解中缀表达式 a + b * c + (d * e + f) * g 的后缀表达式
- 过程如下:
| 序号 | 元素 | 栈stack | 输出队列queue(头->尾) | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a | 空 | a | 数字a,直接入队列 |
| 2 | + | + | a | 栈空,运算符+直接入栈 |
| 3 | b | + | a b | 数字b,直接入队列 |
| 4 | * | + * | a b | 运算符*优先级高于+,直接入栈 |
| 5 | c | + * | a b c | 数字c,直接入队列 |
| 6 | + | + | a b c * + | +优先级不大于 *、+,则*、+依次入队,再将+入栈 |
| 7 | ( | + ( | a b c * + | 左括号,直接入栈 |
| 8 | d | + ( | a b c * + d | 数字d,直接入队列 |
| 9 | * | + ( * | a b c * + d | 栈顶为左括号,运算符直接入栈 |
| 10 | e | + ( * | a b c * + d e | 数字e,直接入队列 |
| 11 | + | + ( + | a b c * + d e * | 同第6步 |
| 12 | f | + ( + | a b c * + d e * f | 数字f,直接入队列 |
| 13 | ) | + | a b c * + d e * f + | 栈顶为右括号,弹出运算符直至遇到"(" |
| 14 | * | + * | a b c * + d e * f + | 同第4步 |
| 15 | g | + * | a b c * + d e * f + g | 数字g,直接入队列 |
| 16 | 空 | a b c * + d e * f + g * + | 栈中剩余的操作数依次出栈,并入队列 |
栈实现计算器
整数计数
- 代码实现:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Calculator {
private static final String ADD = "+";
private static final String SUB = "-";
private static final String MUL = "*";
private static final String DIV = "/";
private static final String LEFT = "(";
private static final String RIGHT = ")";
private static final int PRIORITY_ZERO = 0;
private static final int PRIORITY_LOW = 1;
private static final int PRIORITY_HIGH = 2;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个中缀表达式:");
String infixExp = (sc.nextLine()).trim();
String suffixExp = parseSuffixExp(infixExp);
System.out.printf("对应的后缀表达式:%s\n", suffixExp);
System.out.printf("后缀表达式计算结果:%s\n", calculate(suffixExp));
}
/**
* 解析中缀表达式为后缀表达式
*/
private static String parseSuffixExp(String infixExp) {
if (infixExp == null || "".equals(infixExp)) {
return infixExp;
}
// 定义一个栈用于存放运算符
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
// 定义一个StringBuffer用于拼接后缀表达式
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
String[] elements = infixExp.split(" ");
for (String ele : elements) {
parseElement(ele, stack, sb);
}
// 栈中剩余的操作数依次出栈,并进行结果拼接
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
sb.append(stack.pop()).append(" ");
}
return sb.toString();
}
private static void parseElement(String ele, Stack<String> stack, StringBuffer sb) {
if (isNumber(ele)) {
// 如果是数字,直接sb拼接(多位数也一样)
sb.append(ele).append(" ");
} else if (isSymbol(ele)) {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
// 如果栈空,则运算符直接入栈
stack.push(ele);
} else {
// 否则,比较栈顶的元素运算符的优先级
while (!stack.isEmpty() && getPriority(stack.peek()) >= getPriority(ele)) {
sb.append(stack.pop()).append(" ");
}
// 最后还得将当前的运算符入栈
stack.push(ele);
}
} else if (LEFT.equals(ele)) {
// 如果是左括号,则直接入栈
stack.push(ele);
} else if (RIGHT.equals(ele)) {
// 如果是右括号,则依次弹出栈顶的运算符,并加入到输出队列中(进行sb拼接),直至遇到"("
while (!stack.peek().equals(LEFT)) {
sb.append(stack.pop()).append(" ");
}
// 最后消除左括号,将"("弹出
stack.pop();
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("未知符号:" + ele);
}
}
/**
* 根据后缀表达式计算
*/
private static int calculate(String suffixExp) {
if (suffixExp == null || "".equals(suffixExp)) {
throw new RuntimeException("运算表达式空~~");
}
// 创建一个栈,用于后缀表达式的计算
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
// 按空格拆分表达式
String[] elements = suffixExp.split(" ");
// 遍历
for (String ele : elements) {
// 如果是数字,则直接入栈
if (isNumber(ele)) {
stack.push(ele);
} else {
// 否则,弹出两个数,进行运算后,结果再入栈
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
stack.push(String.valueOf(doCalculate(num1, num2, ele)));
}
}
// 最后留在 stack 中的数据就是运算结果
return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
}
private static int doCalculate(int num1, int num2, String symbol) {
switch (symbol) {
case ADD:
return num1 + num2;
case SUB:
return num1 - num2;
case MUL:
return num1 * num2;
case DIV:
return num1 / num2;
default:
throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误");
}
}
/**
* 判断是否为整数
*/
private static boolean isNumber(String ele) {
return ele.matches("\\d+");
}
/**
* 判断是否为(+-*\)运算符
*/
private static boolean isSymbol(String ele) {
return Arrays.asList(ADD, SUB, MUL, DIV).contains(ele);
}
private static int getPriority(String s) {
if (ADD.equals(s) || SUB.equals(s)) {
return PRIORITY_LOW;
}
if (MUL.equals(s) || DIV.equals(s)) {
return PRIORITY_HIGH;
}
return PRIORITY_ZERO;
}
}
- 测试:
请输入一个中缀表达式:4 * 5 - 8 + 60 + 8 / 2
对应的后缀表达式:4 5 * 8 - 60 + 8 2 / +
后缀表达式计算结果:76
计算器升级版
- 抽象类:
public abstract class Calculator {
protected static final String ADD = "+";
protected static final String SUB = "-";
protected static final String MUL = "*";
protected static final String DIV = "/";
private static final String LEFT = "(";
private static final String RIGHT = ")";
private static final int PRIORITY_ZERO = 0;
private static final int PRIORITY_LOW = 1;
private static final int PRIORITY_HIGH = 2;
public void play() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个中缀表达式:");
String infixExp = (sc.nextLine()).trim();
String suffixExp = parseSuffixExp(infixExp);
System.out.printf("对应的后缀表达式:%s\n", suffixExp);
System.out.printf("后缀表达式计算结果:%s\n", calculate(suffixExp));
}
/**
* 解析中缀表达式为后缀表达式
*/
private String parseSuffixExp(String infixExp) {
if (infixExp == null || "".equals(infixExp)) {
return infixExp;
}
// 定义一个栈用于存放运算符
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
// 定义一个StringBuffer用于拼接后缀表达式
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
String[] elements = infixExp.split(" ");
for (String ele : elements) {
parseElement(ele, stack, sb);
}
// 栈中剩余的操作数依次出栈,并进行结果拼接
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
sb.append(stack.pop()).append(" ");
}
return sb.toString();
}
private void parseElement(String ele, Stack<String> stack, StringBuffer sb) {
if (isNumber(ele)) {
// 如果是数字,直接sb拼接(多位数也一样)
sb.append(ele).append(" ");
} else if (isSymbol(ele)) {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
// 如果栈空,则运算符直接入栈
stack.push(ele);
} else {
// 否则,比较栈顶的元素运算符的优先级
while (!stack.isEmpty() && getPriority(stack.peek()) >= getPriority(ele)) {
sb.append(stack.pop()).append(" ");
}
// 最后还得将当前的运算符入栈
stack.push(ele);
}
} else if (LEFT.equals(ele)) {
// 如果是左括号,则直接入栈
stack.push(ele);
} else if (RIGHT.equals(ele)) {
// 如果是右括号,则依次弹出栈顶的运算符,并加入到输出队列中(进行sb拼接),直至遇到"("
while (!stack.peek().equals(LEFT)) {
sb.append(stack.pop()).append(" ");
}
// 最后消除左括号,将"("弹出
stack.pop();
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("未知符号:" + ele);
}
}
/**
* 根据后缀表达式计算
*/
private String calculate(String suffixExp) {
if (suffixExp == null || "".equals(suffixExp)) {
throw new RuntimeException("运算表达式空~~");
}
// 创建一个栈,用于后缀表达式的计算
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
// 按空格拆分表达式
String[] elements = suffixExp.split(" ");
// 遍历
for (String ele : elements) {
// 如果是数字,则直接入栈
if (isNumber(ele)) {
stack.push(ele);
} else {
// 否则,弹出两个数,进行运算后,结果再入栈
String pop2 = stack.pop();
String pop1 = stack.pop();
stack.push(doCalculate(pop1, pop2, ele));
}
}
// 最后留在 stack 中的数据就是运算结果
return stack.pop();
}
/**
* 具体计算
*/
public abstract String doCalculate(String ele1, String ele2, String symbol);
/**
* 判断是否为整数
*/
protected boolean isNumber(String ele) {
return ele.matches("^[-\\+]?[.\\d]+$");
}
/**
* 判断是否为(+-*\)运算符
*/
protected boolean isSymbol(String ele) {
return Arrays.asList(ADD, SUB, MUL, DIV).contains(ele);
}
/**
* 获取运算符优先级
*/
protected int getPriority(String symbol) {
if (ADD.equals(symbol) || SUB.equals(symbol)) {
return PRIORITY_LOW;
}
if (MUL.equals(symbol) || DIV.equals(symbol)) {
return PRIORITY_HIGH;
}
return PRIORITY_ZERO;
}
}
- 整数计算器
public class IntegerCalculatorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new IntegerCalculator().play();
}
}
class IntegerCalculator extends Calculator {
@Override
public String doCalculate(String ele1, String ele2, String symbol) {
Integer num1 = Integer.parseInt(ele1);
Integer num2 = Integer.parseInt(ele2);
switch (symbol) {
case ADD:
return String.valueOf(num1 + num2);
case SUB:
return String.valueOf(num1 - num2);
case MUL:
return String.valueOf(num1 * num2);
case DIV:
return String.valueOf(num1 / num2);
default:
throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误");
}
}
}
- 小数计算器
public class DoubleCalculatorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new DoubleCalculator().play();
}
}
class DoubleCalculator extends Calculator {
@Override
public String doCalculate(String ele1, String ele2, String symbol) {
Double num1 = Double.parseDouble(ele1);
Double num2 = Double.parseDouble(ele2);
switch (symbol) {
case ADD:
return String.valueOf(num1 + num2);
case SUB:
return String.valueOf(num1 - num2);
case MUL:
return String.valueOf(num1 * num2);
case DIV:
return String.valueOf(num1 / num2);
default:
throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误");
}
}
}
递归
- 实际应用场景:迷宫问题(回溯)——递归(Recursion)
简介
递归的概念
- 简单的说:递归就是方法自己调用自己,每次调用时传入不同的变量。递归有助于编程者解决复杂的问题,同时可以让代码变得简洁。
- 案例回归递归
- ① 打印问题
public class RecursionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("打印问题");
test(4);
}
private static void test(int n) {
if (n > 2) {
test(n - 1);
}
System.out.println("n = " + n);
}
}
- ② 阶乘问题:
public class RecursionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.printf("阶乘计算:%d\n", factorial(4));
}
private static int factorial(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return factorial(n - 1) * n;
}
}
}
递归能解决的问题
- 各种数学问题:8皇后问题 , 汉诺塔, 阶乘问题, 迷宫问题, 球和篮子的问题(google编程大赛)
- 各种算法中也会使用到递归,比如快排,归并排序,二分查找,分治算法等
- 将用栈解决的问题–>递归代码比较简洁
递归需要遵守的规则
- 执行一个方法时,就创建一个新的受保护的独立空间(栈空间)
- 方法的局部变量是独立的,不会相互影响, 比如n变量
- 如果方法中使用的是引用类型变量(比如数组),就会共享该引用类型的数据
- 递归必须向退出递归的条件逼近,否则就是无限递归,出现StackOverflowError,死龟了:)
- 当一个方法执行完毕,或者遇到return,就会返回。遵守谁调用,就将结果返回给谁,同时当方法执行完毕或者返回时,该方法也就执行完毕。
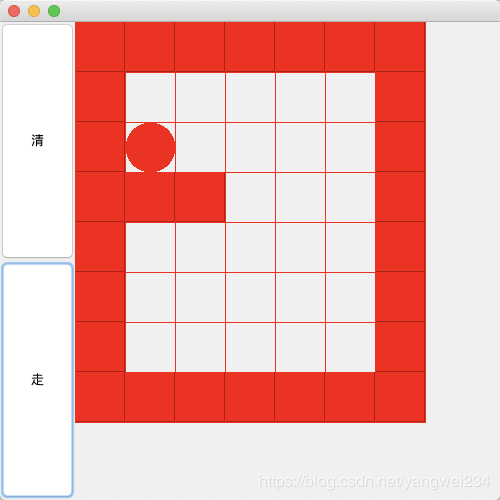
迷宫问题
- 小球得到的路径,和程序员设置的找路策略有关,即找路的上下左右的顺序相关
- 在得到小球路径时,可以先 使用(下右上左),再改成(上 右下左),看看路径是不是有变化
- 如何测试回溯现象?
- 如何求出最短路径?
代码实现
public class MazeDemo {
/**
* 迷宫类
* 约定:map[i][j] = 0:该点没有走过, 1:墙, 2:通路可以走, 3:已经走过但走不通
*/
private static class Maze {
private int[][] map;
private static final int WALL = 1;
private static final int ROUTE = 2;
private static final int NO_ROUTE = 3;
/**
* 起点x y坐标
*/
private int startX;
private int startY;
/**
* 终点x y坐标
*/
private int endX;
private int endY;
public Maze(int[][] map, int startX, int startY, int endX, int endY) {
this.map = map;
this.startX = startX;
this.startY = startY;
this.endX = endX;
this.endY = endY;
}
private void printMap() {
for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < map[i].length; j++) {
System.out.printf("%d ", map[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
private void findWay() {
boolean result = findWayDRUL(startX, startY);
if (result) {
System.out.println("找到一条出迷宫的路~~");
} else {
System.out.println("没有找到出迷宫的路");
}
}
/**
* 需要确定一个策略(方法) 下(D)->右(R)->上(U)->左(L) , 如果该点走不通,再回溯
* @param x
* @param y
* @return
*/
private boolean findWayDRUL(int x, int y) {
if (map[endX][endY] == ROUTE) {
return true;
} else {
if (map[x][y] == 0) {
// 当前这个点还没有走过
// 假定该点是可以走通的
map[x][y] = ROUTE;
if (findWayDRUL(x + 1, y)) { // 向下走
return true;
} else if (findWayDRUL(x, y +1)) { // 向右走
return true;
} else if (findWayDRUL(x - 1, y)) { // 向上走
return true;
} else if (findWayDRUL(x, y - 1)) { // 向左走
return true;
} else {
// 说明该点走不通,是死路
map[x][y] = NO_ROUTE;
return false;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义迷宫地图
int[][] map = {
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}
};
// 创建迷宫
Maze maze = new Maze(map, 1, 1, 6, 5);
// 打印地图
System.out.println("地图的情况:");
maze.printMap();
System.out.println("输出新的地图的情况:");
maze.findWay();
maze.printMap();
}
}
- 结果输出
地图的情况:
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 1 1 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
输出新的地图的情况:
找到一条出迷宫的路~~
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 2 0 0 0 0 1
1 2 2 2 0 0 1
1 1 1 2 0 0 1
1 0 0 2 0 0 1
1 0 0 2 0 0 1
1 0 0 2 2 2 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
八皇后问题
- 八皇后问题,是一个古老而著名的问题,是回溯算法的典型案例。该问题是国际西洋棋棋手马克斯·贝瑟尔于1848年提出:在8×8格的国际象棋上摆放八个皇后,使其不能互相攻击,即:任意两个皇后都不能处于同一行、同一列或同一斜线上,问有多少种摆法。例如:
思路分析
- ① 第一个皇后先放第一行第一列。
- ② 第二个皇后放在第二行第一列、然后判断是否OK;如果不OK,继续放在第二列、第三列、依次把所有列都放完,找到一个合适
- ③ 继续第三个皇后,还是第一列、第二列……直到第8个皇后也能放在一个不冲突的位置,算是找到了一个正确解。
- ④ 当得到一个正确解时,在栈回退到上一个栈时,就会开始回溯,即将第一个皇后,放到第一列的所有正确解,全部得到。
- ⑤ 然后回头继续第一个皇后放第二列,后面继续循环执行 ①②③④ 的步骤。
- 理论上应该创建一个二维数组来表示棋盘,但是实际上可以通过算法,用一个一维数组即可解决问题。
- 例如:arr[8] = {0 , 4, 7, 5, 2, 6, 1, 3} —— 对应 arr 下标表示第几行,即第几个皇后,arr[i] = val , val 表示第 i+1 个皇后,放在第 i+1 行的第 val+1 列。
代码实现
- 八皇后问题求解:
class EightQueen {
/**
* 定义有多少个皇后
*/
private int size;
/**
* 定义数组,保存皇后摆放位置的结果,如array = {0, 4, 7, 5, 2, 6, 1, 3}
*/
private int[] array;
/**
* 统计有多少种解法
*/
private List<int[]> schemes = new ArrayList<>(128);
/**
* 冲突次数统计
*/
private int conflictCount = 0;
public EightQueen(int size) {
this.size = size;
this.array = new int[this.size];
}
/**
* 得到所有解
*/
public List<int[]> getAllScheme() {
settingQueen(0);
return schemes;
}
/**
* 获取冲突判断次数
*/
public int getConflictCount() {
return conflictCount;
}
/**
* 放置第n个皇后
* 每一次递归进入到settingQueen,都有for (int i = 0; i < size; i++),因此会有回溯
* @param n 表示第n个皇后
*/
private void settingQueen(int n) {
if (n == size) {
// 得到一个解
print();
return;
}
// 依次放置皇后,并判断是否冲突
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
// 先把当前的皇后n,放置到该行的第i列
array[n] = i;
if (!isConflict(n)) {
// 不冲突,则接着放n+1个皇后
settingQueen(n + 1);
}
// 如果冲突,就继续执行array[n] = i
// 即将第n个皇后,放置到本行的 后移的一个位置
}
}
/**
* 当放置第n个皇后时,就去检测该皇后和前面已摆放的皇后是否冲突
* @param n 表示第n个皇后
* @return true 表示冲突 false 表示不冲突
*/
private boolean isConflict(int n) {
conflictCount++;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 同一列,同一行不需要判断(n==i)
boolean isSameColumn = array[i] == array[n];
// 同一斜线
boolean isSameSlash = Math.abs(n - i) == Math.abs(array[n] - array[i]);
if (isSameColumn || isSameSlash) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 打印皇后摆放的位置输出
*/
private void print() {
schemes.add(array);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
- 测试:
public class EightQueenDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EightQueen eightQueen = new EightQueen(8);
// 得到所有解
List<int[]> allScheme = eightQueen.getAllScheme();
System.out.printf("一共有 %d 种解法\n", allScheme.size());
System.out.printf("一共有判断冲突 %d 次\n", eightQueen.getConflictCount());
}
}
- 输出:
0 4 7 5 2 6 1 3
0 5 7 2 6 3 1 4
0 6 3 5 7 1 4 2
0 6 4 7 1 3 5 2
1 3 5 7 2 0 6 4
1 4 6 0 2 7 5 3
1 4 6 3 0 7 5 2
1 5 0 6 3 7 2 4
1 5 7 2 0 3 6 4
1 6 2 5 7 4 0 3
1 6 4 7 0 3 5 2
1 7 5 0 2 4 6 3
2 0 6 4 7 1 3 5
2 4 1 7 0 6 3 5
2 4 1 7 5 3 6 0
2 4 6 0 3 1 7 5
2 4 7 3 0 6 1 5
2 5 1 4 7 0 6 3
2 5 1 6 0 3 7 4
2 5 1 6 4 0 7 3
2 5 3 0 7 4 6 1
2 5 3 1 7 4 6 0
2 5 7 0 3 6 4 1
2 5 7 0 4 6 1 3
2 5 7 1 3 0 6 4
2 6 1 7 4 0 3 5
2 6 1 7 5 3 0 4
2 7 3 6 0 5 1 4
3 0 4 7 1 6 2 5
3 0 4 7 5 2 6 1
3 1 4 7 5 0 2 6
3 1 6 2 5 7 0 4
3 1 6 2 5 7 4 0
3 1 6 4 0 7 5 2
3 1 7 4 6 0 2 5
3 1 7 5 0 2 4 6
3 5 0 4 1 7 2 6
3 5 7 1 6 0 2 4
3 5 7 2 0 6 4 1
3 6 0 7 4 1 5 2
3 6 2 7 1 4 0 5
3 6 4 1 5 0 2 7
3 6 4 2 0 5 7 1
3 7 0 2 5 1 6 4
3 7 0 4 6 1 5 2
3 7 4 2 0 6 1 5
4 0 3 5 7 1 6 2
4 0 7 3 1 6 2 5
4 0 7 5 2 6 1 3
4 1 3 5 7 2 0 6
4 1 3 6 2 7 5 0
4 1 5 0 6 3 7 2
4 1 7 0 3 6 2 5
4 2 0 5 7 1 3 6
4 2 0 6 1 7 5 3
4 2 7 3 6 0 5 1
4 6 0 2 7 5 3 1
4 6 0 3 1 7 5 2
4 6 1 3 7 0 2 5
4 6 1 5 2 0 3 7
4 6 1 5 2 0 7 3
4 6 3 0 2 7 5 1
4 7 3 0 2 5 1 6
4 7 3 0 6 1 5 2
5 0 4 1 7 2 6 3
5 1 6 0 2 4 7 3
5 1 6 0 3 7 4 2
5 2 0 6 4 7 1 3
5 2 0 7 3 1 6 4
5 2 0 7 4 1 3 6
5 2 4 6 0 3 1 7
5 2 4 7 0 3 1 6
5 2 6 1 3 7 0 4
5 2 6 1 7 4 0 3
5 2 6 3 0 7 1 4
5 3 0 4 7 1 6 2
5 3 1 7 4 6 0 2
5 3 6 0 2 4 1 7
5 3 6 0 7 1 4 2
5 7 1 3 0 6 4 2
6 0 2 7 5 3 1 4
6 1 3 0 7 4 2 5
6 1 5 2 0 3 7 4
6 2 0 5 7 4 1 3
6 2 7 1 4 0 5 3
6 3 1 4 7 0 2 5
6 3 1 7 5 0 2 4
6 4 2 0 5 7 1 3
7 1 3 0 6 4 2 5
7 1 4 2 0 6 3 5
7 2 0 5 1 4 6 3
7 3 0 2 5 1 6 4
一共有 92 种解法
一共判断冲突 15720 次
哈希表
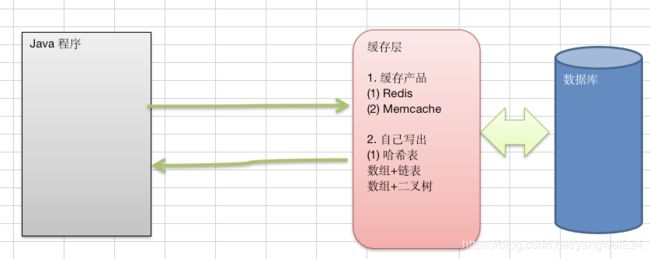
- 看一个实际需求,google公司的一个上机题:有一个公司,当有新的员工来报道时,要求将该员工的信息加入(id、性别、年龄、住址…),当输入该员工的id时,要求查找到该员工的所有信息。要求:不使用数据库,尽量节省内存,速度越快越好=>哈希表(散列)。
基本介绍
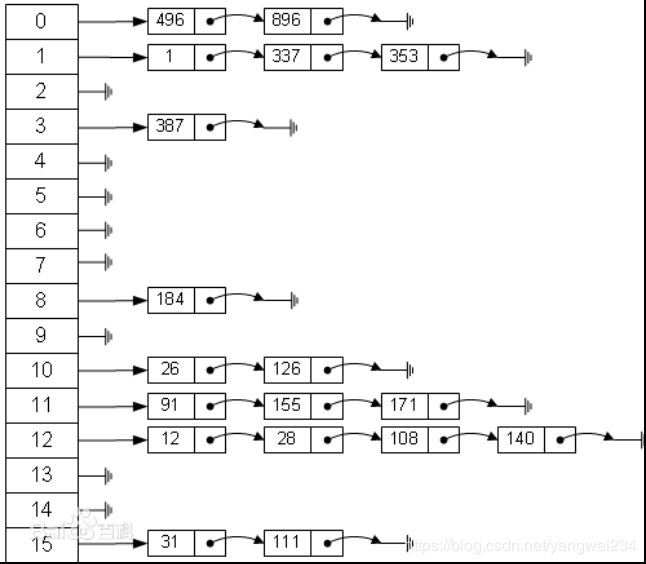
- 散列表(Hash table,也叫哈希表),是根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构。也就是说,它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表。
思路分析
代码实现
- Demo:
/**
* 需求:
* 有一个公司,当有新的员工来报道时,要求将该员工的信息加入(id,性别,年龄,住址..),
* 当输入该员工的id时,要求查找到该员工的 所有信息.
*
* @author yangwei
* @date 2020-05-18 23:16
*/
public class HashTabDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final HashTab hashTab = new HashTab(7);
//写一个简单的菜单
String key = "";
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("add: 添加雇员");
System.out.println("list: 显示雇员");
System.out.println("find: 查找雇员");
System.out.println("exit: 退出系统");
while (true) {
key = scanner.next();
switch (key) {
case "add":
System.out.println("输入 id");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入名字");
//创建 雇员
String name = scanner.next();
Emp emp = new Emp(id, name);
hashTab.add(emp);
break;
case "list":
hashTab.list();
break;
case "find":
System.out.println("请输入要查找的 id");
id = scanner.nextInt();
hashTab.findById(id);
break;
case "exit":
scanner.close();
System.exit(0);
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 哈希表
*/
class HashTab {
private int size;
private EmpLinkedList[] empLinkedLists;
/**
* 构造器
*
* @param size
*/
public HashTab(int size) {
this.size = size;
// 初始化
empLinkedLists = new EmpLinkedList[size];
// 这时不要忘了分别初始化每个链表
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
empLinkedLists[i] = new EmpLinkedList();
}
}
/**
* 添加
*/
public void add(Emp emp) {
// 根据员工的 id ,得到该员工应当添加到哪条链表
int hashVal = hash(emp.id);
empLinkedLists[hashVal].add(emp);
System.out.println("添加 " + emp.toString() + " 成功");
}
/**
* 遍历
*/
public void list() {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
empLinkedLists[i].list(i+1);
}
}
/**
* 根据id查找
*/
public void findById(int id) {
int hashVal = hash(id);
Emp emp = empLinkedLists[hashVal].findById(hashVal);
if (emp != null) {
System.out.printf("在第 %d 条链表中找到 雇员 id = %d\n", (hashVal + 1), id);
} else {
System.out.println("在哈希表中,没有找到该雇员~");
}
}
private int hash(int id) {
return id % size;
}
}
/**
* EmpLinkedList
*/
class EmpLinkedList {
/**
* 头指针,指向第一个Emp,因此我们这个链表的head是直接指向第一个Emp
*/
private Emp head;
/**
* 添加:假定,当添加雇员时,id 是自增长,即 id 的分配总是从小到大
* 因此我们将该雇员直接加入到本链表的最后即可
*/
public void add(Emp emp) {
if (head == null) {
head = emp;
return;
}
Emp curEmp = head;
while (curEmp.next != null) {
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
curEmp.next = emp;
}
/**
* 遍历
*/
public void list(int no) {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("第" + no + "条链表空~~");
return;
}
System.out.print("第" + no + "条链表的信息为:");
Emp curEmp = head;
while (curEmp != null) {
System.out.printf("=> id=%d name=%s\t", curEmp.id, curEmp.name);
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 根据 id 查找雇员
* 如果查找到,就返回 Emp, 如果没有找到,就返回 null
*/
public Emp findById(int id) {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空~~");
return null;
}
Emp curEmp = head;
while (curEmp.next != null) {
if (curEmp.id == id) {
// 找到了,此时 curEmp 就指向要查找的雇员
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
return curEmp;
}
}
/**
* 雇员类
*/
class Emp {
public int id;
public String name;
public Emp next;
public Emp(int id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "}";
}
}
- 测试:
add: 添加雇员
list: 显示雇员
find: 查找雇员
exit: 退出系统
add
输入 id
1
输入名字
Tom
添加 Emp{id=1, name=Tom} 成功
add
输入 id
2
输入名字
Jack
添加 Emp{id=2, name=Jack} 成功
add
输入 id
3
输入名字
Simith
添加 Emp{id=3, name=Simith} 成功
list
第1条链表空~~
第2条链表的信息为:=> id=1 name=Tom
第3条链表的信息为:=> id=2 name=Jack
第4条链表的信息为:=> id=3 name=Simith
第5条链表空~~
第6条链表空~~
第7条链表空~~
add
输入 id
10
输入名字
zhangsan
添加 Emp{id=10, name=zhangsan} 成功
list
第1条链表空~~
第2条链表的信息为:=> id=1 name=Tom
第3条链表的信息为:=> id=2 name=Jack
第4条链表的信息为:=> id=3 name=Simith => id=10 name=zhangsan
第5条链表空~~
第6条链表空~~
第7条链表空~~
find
请输入要查找的 id
10
在第 4 条链表中找到 雇员 id = 10
exit