TensorFlow Object Detection API 超详细教程和踩坑过程
安装Anacond:https://blog.csdn.net/ITLearnHall/article/details/81708148
安装Pycharm:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_15698613/article/details/86502371
一:MyQR 生成动态二维码100个
import random
from MyQR import myqr
import os
for i in range(1,101):
z=''.join(str(random.choice(range(10))) for _ in range(10))#生成长度为10的随机数
name=z+".png"#设置图片名字
myqr.run(
version=1, # 设置容错率
level='L',
brightness=1.0,
words=z,
save_name=name
)
二:下载图片,将图片和二维码大小进行修改
需要安装opencv参考
https://blog.csdn.net/iracer/article/details/80498732
import os
import cv2
#读取文件夹下文件
def read_directory(directory_name,save_img):
i=0
for fileName in os.listdir(directory_name):
#print(fileName)
obsPath=directory_name+"/"+fileName
obsSave_path=save_img+"/"+fileName
resize_img(obsPath,obsSave_path)
i+=1
if(i==100):
break
def resize_img(path_img,save_img):
im1 = cv2.imread(path_img)
im2 = cv2.resize(im1,(716,1000),) # 为图片重新指定尺寸
cv2.imwrite(save_img,im2)
read_directory("D:/pythonLearnDemo/AnacondaJqueryDemo/neg/neg","D:/pythonLearnDemo/AnacondaJqueryDemo/neg/resize_neg")
三:将照片和二维码进行随机合并
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
#读取照片
directory_name="D:/pythonLearnDemo/AnacondaJqueryDemo/neg/resize_neg"
myqrPaths=os.listdir("D:/pythonLearnDemo/AnacondaJqueryDemo/neg/myqrCode")
lens=len(os.listdir(directory_name))
for fileName in os.listdir(directory_name):
obsPathName=directory_name+"/"+fileName
yNum=0
xNum=0
for i in range(1,3):
dst = cv2.imread(obsPathName)#背景图
ranNum=random.randint(0,lens)
print("ranNum:",ranNum,"NAME:",myqrPaths[ranNum])
srcPath="D:/pythonLearnDemo/AnacondaJqueryDemo/neg/myqrCode"+"/"+myqrPaths[ranNum]
x_loc=0
y_loc=0
if(i==1):
y_loc=random.randint(141,350)
yNum=y_loc
x_loc=random.randint(141,260)
xNum=x_loc
else:
y_loc=random.randint(yNum+170,641)
x_loc=random.randint(xNum+141,500)
center = (x_loc,y_loc)
#dst = cv2.imread("D:/pythonLearnDemo/AnacondaJqueryDemo/neg/opencv-seamless-cloning-example.jpg.jpg")
print(srcPath)
src = cv2.imread(srcPath)
src_mask = np.zeros(src.shape, src.dtype)
poly = np.array([[0, 2], [258, 2], [258, 260], [0, 260]], np.int32)
cv2.fillPoly(src_mask, [poly], (255, 255, 255))
output = cv2.seamlessClone(src, dst, src_mask, center, cv2.NORMAL_CLONE)
mrgPath="D:/pythonLearnDemo/AnacondaJqueryDemo/neg/images"+"/"+fileName
obsPathName=mrgPath
cv2.imwrite(mrgPath, output);
下载安装Tensorflow object detection API :https://github.com/tensorflow/models下载到本地,解压放到需要使用的路径下
四:Protobuf 安装与配置
Protobuf(Google Protocol Buffers)是GG开发的的一套用于数据存储,网络通信时用于协议编解码的工具库。和XML,Json数据差不多,把数据按某种形式保存起来。相对与XML和Json的不同之处,它是一种二进制的数据格式,具有更高的传输,打包和解包效率。
在https://github.com/google/protobuf/releases 网站中选择windows 版本,解压后将bin文件夹中的【protoc.exe】放到models中的research目录下,执行下面的代码,将object_detection/protos下的.proto文件转换成.py文件
'''
需要到protoc所在的目录下执行protoc
'''
import os
os.chdir( 'models-master/research' )#可以写
for each in os.listdir( 'object_detection/protos' ):#可以写models-master(Tensorflow object detection API 解压后文件)可对路径
if each.endswith('proto'):
os.system('protoc object_detection/protos/%s --python_out=.' % each)
运行jupyter notebook,找到../models-master/research/object_detection下的
object_detection_tutorial.ipynb进行运行
demo结果
如果代码成功运行的话,运行结果如下图所示:
给图片打标签
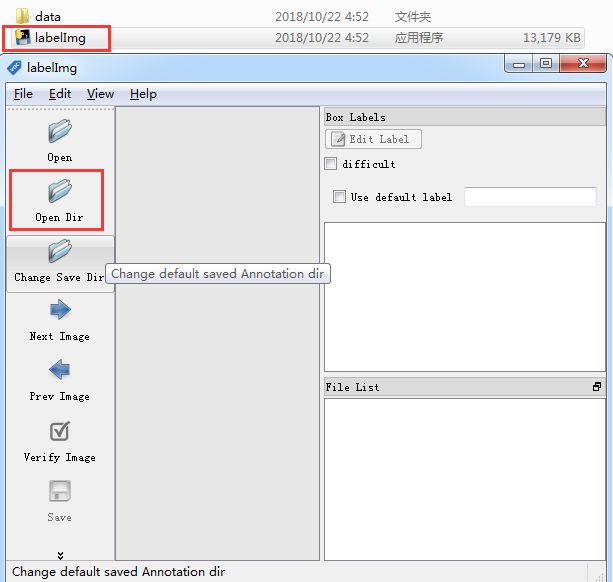
使用打标签工具LabelImg,下载页面链接:https://tzutalin.github.io/labelImg/
下载后解压,打开:
在输入法为英文输入的情况下,按键盘上的w键则可以开始绘制方框,方框会框住图片中的物体。完成绘制方框后,还需要为方框标上类别,如下图所示。
注意:每完成一张图的打标签,一定要记得保存!!!,初次使用可以在edit选项中设置正方形和矩形框:
每次打完标签,会生成对应的xml数据,感兴趣的可以查看一下某个xml文件,其中记录了标签及bounding box坐标:
xml转csv
xml转csv的意思是,将xml文件中的信息整合到csv文件中,其中利用的是xml模块
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@author: Zbb
将文件夹内所有XML文件的信息记录到CSV文件中
"""
import os
import pandas as pd
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
path = 'D:/pythonLearnDemo/saveLabels'
def xml_to_csv(path):
xml_list = []
for xml_file in glob.glob(path + '/*.xml'):
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
for member in root.findall('object'):
value = (root.find('filename').text,
int(root.find('size')[0].text),
int(root.find('size')[1].text),
member[0].text,
int(member[4][0].text),
int(member[4][1].text),
int(member[4][2].text),
int(member[4][3].text)
)
xml_list.append(value)
column_name = ['filename', 'width', 'height', 'class', 'xmin', 'ymin', 'xmax', 'ymax']
xml_df = pd.DataFrame(xml_list, columns=column_name)
return xml_df
def xmlPath_list_to_df(xmlPath_list):
xmlContent_list = []
for xmlPath in xmlPath_list:
print(xmlPath)
tree = ET.parse(xmlPath)
root = tree.getroot()
for member in root.findall('object'):
value = (root.find('filename').text, # 文件名
int(root.find('size')[0].text), # width
int(root.find('size')[1].text), # height
member[0].text, # 标签
int(member[4][0].text), # xmin
int(member[4][1].text), # ymin
int(member[4][2].text), # xmax
int(member[4][3].text) # ymax
)
xmlContent_list.append(value)
column_name = ['filename', 'width', 'height', 'class', 'xmin', 'ymin', 'xmax', 'ymax']
xmlContent_df = pd.DataFrame(xmlContent_list, columns=column_name)
return xmlContent_df
def main():
image_path = path
xml_df = xml_to_csv(image_path)
xml_df.to_csv('tv_vehicle_labels.csv', index=None)
print('Successfully converted xml to csv.')
def dirPath_to_csv(dirPath):
fileName_list = os.listdir(dirPath)
all_xmlPath_list = [os.path.join(dirPath, fileName) for fileName in fileName_list if '.xml' in fileName]
train_xmlPath_list, test_xmlPath_list = train_test_split(all_xmlPath_list, test_size=0.1, random_state=1)
train_df = xmlPath_list_to_df(train_xmlPath_list)
train_df.to_csv('train.csv')
print('成功产生文件train.csv,训练集共有%d张图片' % len(train_xmlPath_list))
test_df = xmlPath_list_to_df(test_xmlPath_list)
test_df.to_csv('test.csv')
print('成功产生文件test.csv,测试集共有%d张图片' % len(test_xmlPath_list))
#main()
dirPath_to_csv(path)
csv转tfrecord
由于下面的代码我们需要模块
| 1 |
|
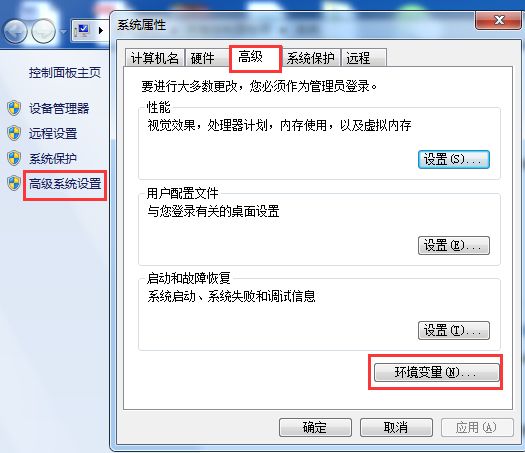
该模块是我们在Tensorflow object detection API中下载的,要想使用该模块,我们需要添加环境变量PATHPATH。方法如下:右键计算机->属性
其中变量值包含下载的objec_detection路径及slim路径,如E:\ML\models-master\research;E:\ML\models-master\research\slim
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@author: Zbb
将文件夹内所有XML文件的信息记录到CSV文件中
"""
import os
import io
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
from object_detection.utils import dataset_util
from collections import namedtuple, OrderedDict
import os
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from object_detection.utils import dataset_util
import shutil
def csv2tfrecord(csv_path, imageDir_path, tfrecord_path):
objectInfo_df = pd.read_csv(csv_path)
tfrecord_writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(tfrecord_path)
for filename, group in objectInfo_df.groupby('filename'):
height = group.iloc[0]['height']
width = group.iloc[0]['width']
filename_bytes = filename.encode('utf-8')
image_path = os.path.join(imageDir_path, filename)
with open(image_path, 'rb') as file:
encoded_jpg = file.read()
image_format = b'jpg'
xmin_list = list(group['xmin'] / width)
xmax_list = list(group['xmax'] / width)
ymin_list = list(group['ymin'] / height)
ymax_list = list(group['ymax'] / height)
classText_list = [classText.encode('utf-8') for classText in group['class']]
classLabel_list = [classText_to_classLabel(classText) for classText in group['class']]
tf_example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(
feature={
'image/height': dataset_util.int64_feature(height),
'image/width': dataset_util.int64_feature(width),
'image/filename': dataset_util.bytes_feature(filename_bytes),
'image/source_id': dataset_util.bytes_feature(filename_bytes),
'image/encoded': dataset_util.bytes_feature(encoded_jpg),
'image/format': dataset_util.bytes_feature(image_format),
'image/object/bbox/xmin': dataset_util.float_list_feature(xmin_list),
'image/object/bbox/xmax': dataset_util.float_list_feature(xmax_list),
'image/object/bbox/ymin': dataset_util.float_list_feature(ymin_list),
'image/object/bbox/ymax': dataset_util.float_list_feature(ymax_list),
'image/object/class/text': dataset_util.bytes_list_feature(classText_list),
'image/object/class/label': dataset_util.int64_list_feature(classLabel_list),
}))
tfrecord_writer.write(tf_example.SerializeToString())
tfrecord_writer.close()
print('成功产生tfrecord文件,保存在路径:%s' % tfrecord_path)
# 如果训练自己的模型,目标检测类别不同,需要修改此处
def classText_to_classLabel(row_label):
if row_label == 'fish':
return 1
elif row_label == 'human_face':
return 2
else:
return None
dir_name = 'training'
if not os.path.isdir(dir_name):
os.mkdir(dir_name)
csv2tfrecord('D:/pythonLearnDemo/train.csv', 'D:/pythonLearnDemo/AnacondaJqueryDemo/neg/images', 'D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/train.tfrecord')
csv2tfrecord('D:/pythonLearnDemo/test.csv', 'D:/pythonLearnDemo/AnacondaJqueryDemo/neg/images', 'D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/test.tfrecord')
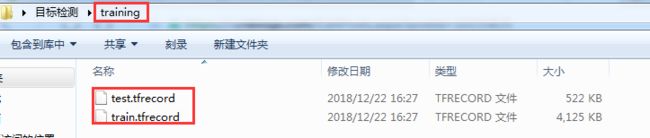
运行上面的代码,目标检测文件夹中会产生一个文件夹training,如下图所示:
编写pbtxt文件
在目标检测的文件夹training中,创建文本文件my_label_map.pbtxt。复制下面一段内容到文本文件my_label_map.pbtxt中:
item {
name : "qrCode"
id : 1
}
8)编写配置文件
可以在object_detection文件夹中的samples/config路径下,找到原生配置文件ssdlite_mobilenet_v2_coco.config,先复制1份到桌面文件目标检测的文件夹training中,并做如下修改:
- 第9行的num_classes,对于本文来说,此数设置为1
- 第141行的batch_size,对于本文来说,此数设置为
3,读者根据自己的电脑配置,可以调高或者调低 - 第177行input_path设置成
"D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/train.tfrecord"(我设置的为绝对路径) - 第179行label_map_path设置成
"D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/my_label_map.pbtxt" - 第191行input_path设置成
"D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/test.tfrecord" - 第193行label_map_path设置成
"D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/my_label_map.pbtxt" - 第158、159这2行需要删除
- 第二处为eval_config中的num_examples,它表示在验证阶段需要执行的图片数量,本次验证数量为10(可以在create_pascal_tf_record.py中,输出对应的examples_list长度,就可以知道这个大小)。
修改配置文件ssdlite_mobilenet_v2_coco.config并保存后,此时文件夹training中有4个文件,如下图所示:
# SSD with Mobilenet v1 configuration for MSCOCO Dataset.
# Users should configure the fine_tune_checkpoint field in the train config as
# well as the label_map_path and input_path fields in the train_input_reader and
# eval_input_reader. Search for "PATH_TO_BE_CONFIGURED" to find the fields that
# should be configured.
model {
ssd {
num_classes: 1
box_coder {
faster_rcnn_box_coder {
y_scale: 10.0
x_scale: 10.0
height_scale: 5.0
width_scale: 5.0
}
}
matcher {
argmax_matcher {
matched_threshold: 0.5
unmatched_threshold: 0.5
ignore_thresholds: false
negatives_lower_than_unmatched: true
force_match_for_each_row: true
}
}
similarity_calculator {
iou_similarity {
}
}
anchor_generator {
ssd_anchor_generator {
num_layers: 6
min_scale: 0.2
max_scale: 0.95
aspect_ratios: 1.0
aspect_ratios: 2.0
aspect_ratios: 0.5
aspect_ratios: 3.0
aspect_ratios: 0.3333
}
}
image_resizer {
fixed_shape_resizer {
height: 300
width: 300
}
}
box_predictor {
convolutional_box_predictor {
min_depth: 0
max_depth: 0
num_layers_before_predictor: 0
use_dropout: false
dropout_keep_probability: 0.8
kernel_size: 1
box_code_size: 4
apply_sigmoid_to_scores: false
conv_hyperparams {
activation: RELU_6,
regularizer {
l2_regularizer {
weight: 0.00004
}
}
initializer {
truncated_normal_initializer {
stddev: 0.03
mean: 0.0
}
}
batch_norm {
train: true,
scale: true,
center: true,
decay: 0.9997,
epsilon: 0.001,
}
}
}
}
feature_extractor {
type: 'ssd_mobilenet_v1'
min_depth: 16
depth_multiplier: 1.0
conv_hyperparams {
activation: RELU_6,
regularizer {
l2_regularizer {
weight: 0.00004
}
}
initializer {
truncated_normal_initializer {
stddev: 0.03
mean: 0.0
}
}
batch_norm {
train: true,
scale: true,
center: true,
decay: 0.9997,
epsilon: 0.001,
}
}
}
loss {
classification_loss {
weighted_sigmoid {
}
}
localization_loss {
weighted_smooth_l1 {
}
}
hard_example_miner {
num_hard_examples: 3000
iou_threshold: 0.99
loss_type: CLASSIFICATION
max_negatives_per_positive: 3
min_negatives_per_image: 0
}
classification_weight: 1.0
localization_weight: 1.0
}
normalize_loss_by_num_matches: true
post_processing {
batch_non_max_suppression {
score_threshold: 1e-8
iou_threshold: 0.6
max_detections_per_class: 100
max_total_detections: 100
}
score_converter: SIGMOID
}
}
}
train_config: {
batch_size: 3
optimizer {
rms_prop_optimizer: {
learning_rate: {
exponential_decay_learning_rate {
initial_learning_rate: 0.004
decay_steps: 800720
decay_factor: 0.95
}
}
momentum_optimizer_value: 0.9
decay: 0.9
epsilon: 1.0
}
}
#fine_tune_checkpoint: "PATH_TO_BE_CONFIGURED/model.ckpt"
#from_detection_checkpoint: true
# Note: The below line limits the training process to 200K steps, which we
# empirically found to be sufficient enough to train the pets dataset. This
# effectively bypasses the learning rate schedule (the learning rate will
# never decay). Remove the below line to train indefinitely.
num_steps: 200000
data_augmentation_options {
random_horizontal_flip {
}
}
data_augmentation_options {
ssd_random_crop {
}
}
}
train_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
input_path: "D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/train.tfrecord"
}
label_map_path: "D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/my_label_map.pbtxt"
}
eval_config: {
num_examples: 10
# Note: The below line limits the evaluation process to 10 evaluations.
# Remove the below line to evaluate indefinitely.
max_evals: 10
}
eval_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
input_path: "D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/test.tfrecord"
}
label_map_path: "D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/my_label_map.pbtxt"
shuffle: false
num_readers: 1
}
三、模型训练
1)错误一:
在桌面的目标检测文件夹中打开cmd,即在路径中输入cmd后按Enter键运行。在cmd中运行命令:
| 1 |
1. python D:/tensorflowObject/models-master/research/object_detection/model_main.py
2. python3 object_detection/model_main.py |
运行结果如下图所示:
可以看出缺少pycocotools库,在linux系统中安装pycocotools库只需要运行命令:pip install pycocotools,但是在Windows上安装则复杂得多:
首先下载Microsoft C++ build 14.0,链接:https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=691126,初始化安装程序->自定义->选择功能只勾选Windows 10 SDK 10.0.10240->安装,过程比较漫长,一般安装有VS完整版的,不会缺失
然后下载安装pycocotools,链接:https://github.com/philferriere/cocoapi,解压到当前文件夹,进入文件夹cocoapi-master中的文件夹PythonAPI,在此文件夹下打开cmd,输入:python setup.py build_ext install
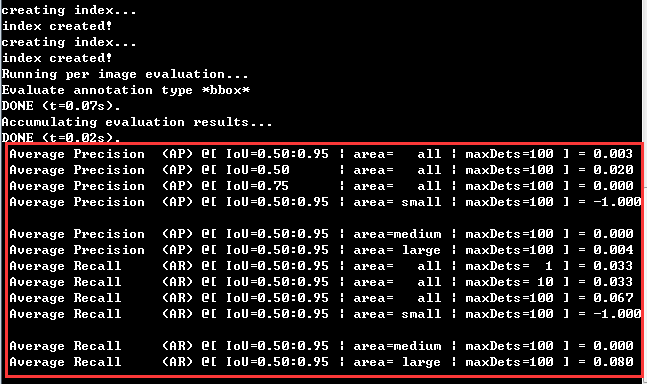
然后重新训练,模型训练稳定地进行一段时间后,会做一次模型评估,如下图所示。所以如果读者看到下图中的情况,则说明模型训练很顺利:
将训练模型导出
python D:/tensorflowObject/models-master/research/object_detection/export_inference_graph.py
--input_type=image_tensor
--pipeline_config_path=D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config
--trained_checkpoint_prefix=D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/model_training/model.ckpt-20000 #之前默认设置20000次
--output_directory=fish_inference_graph
3)查看模型训练状况
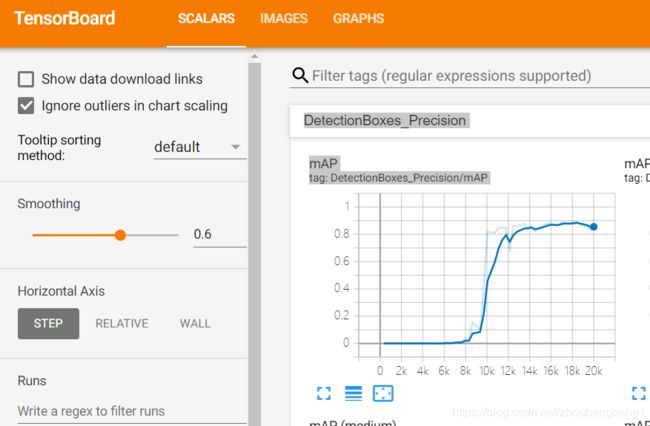
模型训练稳定地进行后,在桌面的目标检测文件夹中重新打开cmd。在cmd中运行命令:
D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/model_training(路径为之前保存训练模型的地方)--trained_checkpoint_prefix=D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/model_training/
tensorboard --logdir=D:/pythonLearnDemo/training/model_training --host=127.0.0.1
可查看数据
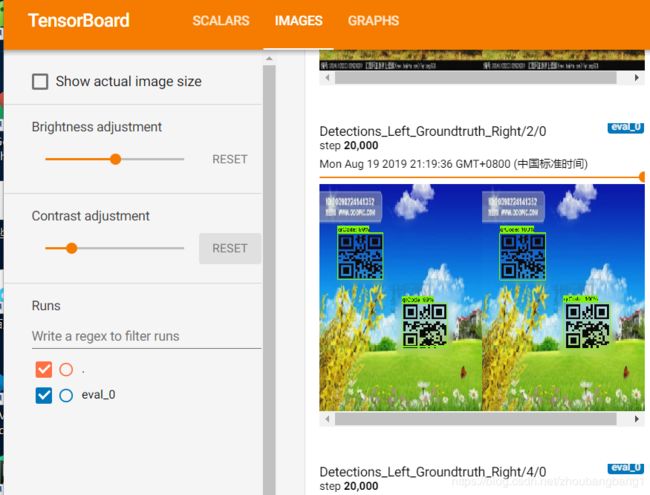
测试:
测试代码下载地址
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1kqFlP6vdsMgwyYRPFPmxnA
提取码:68rc
在测试过程中,出现不了展示图片大的效果,然后修改成了保存
训练结果: