文章目录
- 0. 原始数据准备
- 1. Python原生实现
- 1.1 计算均方差
- 1.2 梯度下降
- 1.3 开始运行
- 1.4 回归最终结果作图
- 2. sklearn实现
- 2.1 导包
- 2.2 建模与训练
- 2.3 结果展示
- 2.4 回归最终结果作图
0. 原始数据准备
0.1 导包
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
0.2 数据
x_data = np.array(
[[100, 4],
[ 50, 1],
[100, 4],
[100, 3],
[ 50, 2],
[ 80, 2],
[ 75, 3],
[ 65, 4],
[ 90, 3],
[ 90, 2]])
y_data = np.array([9.3, 4.8, 8.9, 6.5, 4.2, 6.2, 7.4, 6.0, 7.6, 6.1])
print(x_data)
print(y_data)
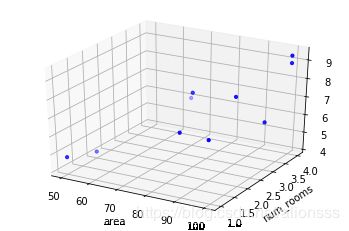
0.3 作图展示
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111, projection = "3d")
ax.scatter(x_data[:, 0], x_data[:, 1], y_data, c = "b", marker = 'o', s = 10)
ax.set_xlabel("area")
ax.set_ylabel("num_rooms")
plt.show()
1. Python原生实现
1.1 计算均方差
def compute_mse(b, w1, w2, x_data, y_data):
"""
求均方差
:param b: 截距
:param w1: 斜率1
:param w2: 斜率2
:param x_data: 特征数据
:param y_data: 标签数据
"""
total_error = 0.0
for i in range(0, len(x_data)):
total_error += (y_data[i] - (b + w1 * x_data[i, 0] + w2 * x_data[i, 1])) ** 2
return total_error / len(x_data)
1.2 梯度下降
def run_gradient_descent(x_data, y_data, b, w, learn_rate, epochs):
"""
运行梯度下降
:param x_data: 待训练的特征数据
:param y_data: 标签数据
:param b: 截距
:param w1: 斜率1
:param w2: 斜率2
:param learn_rate: 学习曲率
:param epochs: 训练次数
"""
m = float(len(x_data))
for i in range(epochs):
b_grad = 0
w1_grad = 0
w2_grad = 0
for j in range(0, len(x_data)):
b_grad += (1/m) * ((b + w1 * x_data[j, 0] + w2 * x_data[j, 1]) - y_data[j])
w1_grad += (1/m) * ((b + w1 * x_data[j, 0] + w2 * x_data[j, 1]) - y_data[j]) * x_data[j, 0]
w2_grad += (1/m) * ((b + w1 * x_data[j, 0] + w2 * x_data[j, 1]) - y_data[j]) * x_data[j, 1]
b -= learn_rate * b_grad
w1 -= learn_rate * w1_grad
w2 -= learn_rate * w2_grad
if i % 100 == 0:
print("epochs:", i)
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111, projection = "3d")
ax.scatter(x_data[:, 0], x_data[:, 1], y_data, c = "b", marker = 'o', s = 10)
x0 = x_data[:, 0]
x1 = x_data[:, 1]
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(x0, x1)
z = b + w1 * x0 + w2 * x1
ax.plot_surface(x0, x1, z, color = "r")
ax.set_xlabel("area")
ax.set_ylabel("num_rooms")
ax.set_zlabel("price")
plt.show()
print("mse: ", compute_mse(b, w1, w2, x_data, y_data))
print("------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------")
return b, w1, w2
1.3 开始运行
learn_rate = 0.0001
b = 0
w1 = 0
w2 = 0
epochs = 1000
print("Start args: b = {0}, w1 = {1}, w2 = {2}, mse = {3}".format(b, w1, w2, compute_mse(b, w1, w2, x_data, y_data)))
print("Running...")
b, w1, w2 = run_gradient_descent(x_data, y_data, b, w1, w2, learn_rate, epochs)
print("Finish args: iterations = {0} b = {1}, w1 = {2}, w2 = {3}, mse = {4}".format(epochs, b, w1, w2, compute_mse(b, w1, w2, x_data, y_data)))
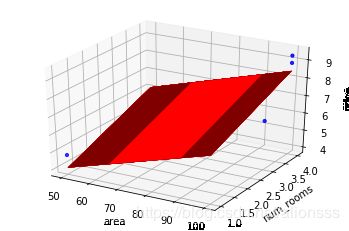
1.4 回归最终结果作图
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111, projection = "3d")
ax.scatter(x_data[:, 0], x_data[:, 1], y_data, c = "b", marker = 'o', s = 10)
x0 = x_data[:, 0]
x1 = x_data[:, 1]
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(x0, x1)
z = b + w1 * x0 + w2 * x1
ax.plot_surface(x0, x1, z, color = "r")
ax.set_xlabel("area")
ax.set_ylabel("num_rooms")
ax.set_zlabel("price")
plt.show()
2. sklearn实现
2.1 导包
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2.2 建模与训练
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(x_data, y_data)
2.3 结果展示
print("coefficients: ", model.coef_)
w1 = model.coef_[0]
w2 = model.coef_[1]
print("intercept: ", model.intercept_)
b = model.intercept_
x_test = [[90, 3]]
predict = model.predict(x_test)
print("predict: ", predict)
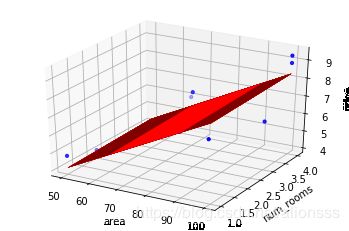
2.4 回归最终结果作图
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111, projection = "3d")
ax.scatter(x_data[:, 0], x_data[:, 1], y_data, c = "b", marker = 'o', s = 10)
x0 = x_data[:, 0]
x1 = x_data[:, 1]
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(x0, x1)
z = b + w1 * x0 + w2 * x1
ax.plot_surface(x0, x1, z, color = "r")
ax.set_xlabel("area")
ax.set_ylabel("num_rooms")
ax.set_zlabel("price")
plt.show()