java8新日期时间类使用
java8之后提供了新的日期和时间相关类,接口和枚举,放在了java.time包下(之前旧的日期时间类放在java.util包),使设置日期时间更加方便。java8的新日期时间类的设计,借鉴了joda-time时间库。
ISO-8601日历系统是当今世界大多数国家/地区使用的现代民用日历系统。在闰年等规则方面和格里高利历系统(阳历)相同,该系统一直沿用至今。java8之前的日期显示是使用的CST(中央标准时间)标准。有个网站可以查看各种时间标准(例如CST,UTC等):http://zh.thetimenow.com/
| 包 |
描述 |
| java.time |
包含最常使用的类,基于ISO-8601标准 |
| java.time.chrono |
支持非ISO日历 |
| java.time.format |
包含日期和时间的解析与格式化 |
| java.time.temporal |
包含访问日期时间的信息与调整 |
| java.time.zone |
支持时区 |
java8提供了3个新的完整日期时间类:LocalDte,LocalTime和LocalDateTime,位于java.time包中,LocalDate表示一个不可变的日期对象,LocalTime表示一个不可对的时间对象;LocalDateTime表示一个不可变的日期和时间,此外还可以创建部分日期时间对象,如Year对象,YearMonth对象,MonthDay对象。
这些类都有类似的方法。这三个类没有提供共有的构造方法,创建对象需要使用静态工厂方法,主要有now()和of()方法。
目录
1.获取日期时间实例
2. 日期时间的格式化和解析
3.日期时间修改
4、时间日期相关
1.获取日期时间实例
1.1 now()方法:
public static LocalDate now() {
return now(Clock.systemDefaultZone());
}LocalDte的静态工厂方法,该方法使用默认时区获得当前日期,返回LocalDte对象。
public static LocalTime now() {
return now(Clock.systemDefaultZone());
}LocalTime的静态工厂方法,该方法使用默认时区获得当前时间,返回LocalTime对象。
public static LocalDateTime now() {
return now(Clock.systemDefaultZone());
}LocalDateTime的静态工厂方法,该方法使用默认时区获得当前日期时间,返回LocalDateTime对象。
1.2 of()方法有很多重载的方法,说明如下:
public static LocalDateTime of(int year, int month, int dayOfMonth, int hour, int minute, int second, int nanoOfSecond) {
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(year, month, dayOfMonth);
LocalTime time = LocalTime.of(hour, minute, second, nanoOfSecond);
return new LocalDateTime(date, time);
}按照指定的年、月、日、时、分、秒、纳秒获得LocalDateTime实例,秒之后直接设置纳秒。当纳秒为0是,重载方法如下:
public static LocalDateTime of(int year, int month, int dayOfMonth, int hour, int minute, int second) {
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(year, month, dayOfMonth);
LocalTime time = LocalTime.of(hour, minute, second);
return new LocalDateTime(date, time);
}同理LocalDte和LocalTime也是类似的of()方法
public static LocalTime of(int hour, int minute, int second) {
HOUR_OF_DAY.checkValidValue(hour);
if ((minute | second) == 0) {
return HOURS[hour]; // for performance
}
MINUTE_OF_HOUR.checkValidValue(minute);
SECOND_OF_MINUTE.checkValidValue(second);
return new LocalTime(hour, minute, second, 0);
}按照指定的时、分、秒获取一个LocalTime实例。
public static LocalDate of(int year, int month, int dayOfMonth) {
YEAR.checkValidValue(year);
MONTH_OF_YEAR.checkValidValue(month);
DAY_OF_MONTH.checkValidValue(dayOfMonth);
return create(year, month, dayOfMonth);
}按照指定的年、月、日获得一个LocalDate实例,日期中的年月日必须有效,否则会抛出异常。
日期时间参数取值范围:
| 参数 | 说明 |
| year | 从-999 999 999到999 999 999的年份 |
| month | 一年中的月份,从1到12 |
| dayOfMonth | 月中的天,从1到31 |
| hour | 从0到23表示的时 |
| minute | 从0到59表示的分 |
| second | 从0到59表示的秒 |
1.3 参考实例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
// 获取当前日期
System.out.println("now()方法创建的当前日期:"+LocalDate.now());
// 设置日期
System.out.println("of()方法设置的日期:"+LocalDate.of(2020,8,18));
// 获取当前时间(包含毫秒)
System.out.println("now()方法创建的当前时间:"+LocalTime.now());
// 设置时间(时,分,秒)
System.out.println("of()方法设置的时间:"+LocalTime.of(16,14,12));
// 获取当前日期和时间
System.out.println("now()方法创建的当前日期时间:"+LocalDateTime.now());
// 设置日期和时间(秒之后设置的是纳秒)
System.out.println("of()方法设置的日期时间:"+LocalDateTime.of(2020,2,29,12,24,35,1000));
// 只显示年和月
YearMonth yearMonth=YearMonth.of(2020,3);
YearMonth now=YearMonth.now();
// 只显示月和天
MonthDay monthday=MonthDay.of(3,7);
MonthDay nowMonthDay=MonthDay.now();
}运行之后输出在控制台的结果:
2. 日期时间的格式化和解析
java提供的日期格式化类时java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter, DateTimeFormatter中本身没有提供日期格式化和日期的解析方法,这些方法还是有LocalTime,LocalDate和LocalDateTime提供的。
2.1 日期格式化
日期格式化方法是format(),这三个类都有String format(DateTimeFormatter formatter),参数是 DateTimeFormatter类型。
2.2 日期解析
日期解析方法是parse(),这三个类每一个都有两个版本的parse方法,具体如下:
public static LocalDateTime parse(CharSequence text) {
return parse(text, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME);
}使用默认格式,从一个文本字符串获取LocalDateTime实例,如:2020-03-07T17:25:30.
public static LocalDateTime parse(CharSequence text, DateTimeFormatter formatter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(formatter, "formatter");
return formatter.parse(text, LocalDateTime::from);
}使用指定格式化,从文本字符串获取LocalDateTime实例。
public static LocalDate parse(CharSequence text) {
return parse(text, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE);
}使用默认格式,从一个文本字符串获取LocalDate实例。如:2020-03-07
public static LocalDate parse(CharSequence text, DateTimeFormatter formatter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(formatter, "formatter");
return formatter.parse(text, LocalDate::from);
}使用指定格式化,从文字符串获取LocalDate实例。
public static LocalTime parse(CharSequence text) {
return parse(text, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_TIME);
}使用默认格式,从一个文本字符串获取LocalTime实例。
public static LocalTime parse(CharSequence text, DateTimeFormatter formatter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(formatter, "formatter");
return formatter.parse(text, LocalTime::from);
}使用指定格式化,从文本字符串获取LocalTime实例
2.3 参考实例:
package com.xiaomifeng1010.rbacboot.common.util;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
/**
* @author xiaomifeng1010
* @version 1.0
* @date: 2020/3/7 17:36
*/
public class DateTimeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建LocalDateTime对象
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
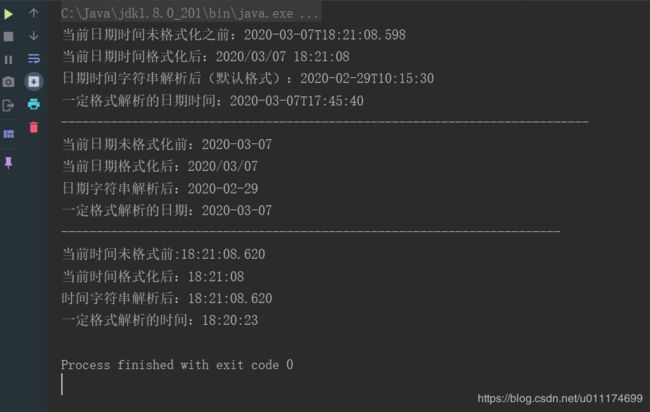
System.out.println("当前日期时间未格式化之前:"+localDateTime);
// 设置格式化类
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss");
String afterFormat=localDateTime.format(formatter);
System.out.println("当前日期时间格式化后:"+afterFormat);
// 格式化字符串"2020-02-29T12:24:23"(使用默认格式),返回localDateTime
LocalDateTime localDateTime1=LocalDateTime.parse("2020-02-29T10:15:30");
System.out.println("日期时间字符串解析后(默认格式):"+localDateTime1);
// 以指定格式("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss")解析日期字符串"2020/03/07 17:45:40",解析后输出的格式还是LocalDateTime默认的格式
LocalDateTime localDateTime2=LocalDateTime.parse("2020/03/07 17:45:40",formatter);
System.out.println("一定格式解析的日期时间:"+localDateTime2);
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------");
// 创建LocalDate对象
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println("当前日期未格式化前:"+localDate);
// 重新设置格式化类
DateTimeFormatter formatter1 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy/MM/dd");
String dateFormatAfter=localDate.format(formatter1);
System.out.println("当前日期格式化后:"+dateFormatAfter);
// 以默认格式解析日期字符串,返回LocalDate对象
LocalDate localDate1=LocalDate.parse("2020-02-29");
System.out.println("日期字符串解析后:"+localDate1);
// 以一定格式解析日期字符串
LocalDate localDate2=LocalDate.parse("2020/03/07",formatter1);
System.out.println("一定格式解析的日期:"+localDate2);
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------------------");
// 创建LocalTime
LocalTime localTime = LocalTime.now();
System.out.println("当前时间未格式前:"+localTime);
// 重新设置格式化类
DateTimeFormatter formatter2=DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("HH:mm:ss");
String timeFormatAfter= localTime.format(formatter2);
System.out.println("当前时间格式化后:"+timeFormatAfter);
// 以默认格式解析时间字符串
LocalTime localTime1=LocalTime.parse("18:18:23.089");
System.out.println("时间字符串解析后:"+localTime);
// 以一定格式解析时间字符串
LocalTime localTime2=LocalTime.parse("18:20:23",formatter2);
System.out.println("一定格式解析的时间:"+localTime2);
}
}
运行后,在控制台中输出:
格式化类DateTimeFormatter对象是通过ofPattern(String pattern)获得,其中patter是日期和时间格式。
注意事项,在parse方法中,即解析日期和时间字符串的时候,第一个参数传入的字符串的格式,一定要和pattern的格式模式匹配,比如LocalDate localDate2=LocalDate.parse("2020/03/07",formatter1);因为DateTimeFormatter中设置的格式是“yyyy/MM/dd”,即DateTimeFormatter formatter1 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy/MM/dd");所以如果LocalDate localDate2=LocalDate.parse("2020/3/7",formatter1)写成这样,也就是月份和日只写一位,是会抛出异常DateTimeParseException。
3.日期时间修改
日期时间相关枚举类
| 枚举 |
描述 |
| Month |
代表月份 |
| DayOfWeek |
代表星期几 |
| ChronoField |
代表时间字段 |
| ChronoUnit |
代表字段的单位 |
/**
* 测试修改日期时间
*/
@Test
public void modifyDateAndTimeTest(){
LocalDate localDate=LocalDate.of(2020,Month.MARCH,7);
LocalTime localTime = LocalTime.of(20,50,23);
// LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020,3,7,20,50,23);
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(localDate,localTime);
// 对已经创建好的日期时间localDateTime进行修改,可以链式调用对年月日时分秒进行修改
LocalDateTime modifyDatetime=localDateTime.withYear(2020).withMonth(5).withDayOfMonth(5).withHour(21).withMinute(10);
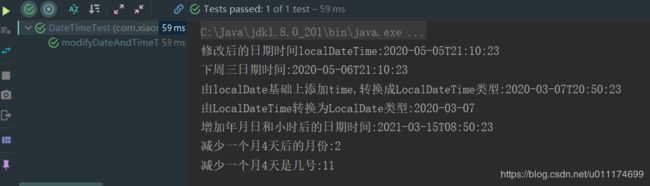
System.out.println("修改后的日期时间localDateTime:"+modifyDatetime);
// 将日期时间设置到下一个星期三(2020年5月5号是星期二,下个星期三,就是2020年5月6号),
// 不一定是下周,上边的日期是5月6日,则下个星期三,就在下周了
modifyDatetime=modifyDatetime.with(TemporalAdjusters.next(DayOfWeek.WEDNESDAY));
System.out.println("下一个星期三日期时间:"+modifyDatetime);
// 在已经创建好的日期localDate(日期)基础上添加时分秒(time),形成LocalDateTime类型。
LocalDateTime localDateTime1=localDate.atTime(localTime);
System.out.println("由localDate基础上添加time,转换成LocalDateTime类型:"+localDateTime1);
// 或者在已经创建好的日期localtime(时间)基础上添加日期,形成LocalDateTime类型。
LocalDateTime localDateTime2=localTime.atDate(localDate);
// 又或者将LocalDateTime转换成localDate类型
LocalDate localDate1=localDateTime2.toLocalDate();
System.out.println("由LocalDateTime转换为LocalDate类型:"+localDate1);
// 在原有日期时间基础上增加日期(年月日)或时间(时分秒)
LocalDateTime localDateTime3= localDateTime.plusYears(0).plusYears(1).plusDays(7).plusHours(12);
System.out.println("增加年月日和小时后的日期时间:"+localDateTime3);
// 在原有日期时间基础上减少一个月
localDateTime3=localDateTime3.minusMonths(1);
// 再减少4天,ChronoUnit表示时间单位,是一个枚举类
localDateTime3=localDateTime3.minus(4, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
System.out.println("减少一个月4天后的月份:"+localDateTime3.getMonthValue());
// 使用枚举类来设定获取日期(如获取月份中某一天)
System.out.println("减少一个月4天是几号:"+localDateTime3.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH));
}控制台输出:
4、时间日期相关
Instant类:instant表示瞬间,顾名思义,表示的是瞬时的时间点,时间线上的某个时点
Duration:时间点之间的持续时间,间隔时间
Period:ISO-8601日历系统中基于日期的时间量,表示的区间间隔显示更易读,更人性化(显示例如2年3个月4天),间隔可能会出现负值,此类不可变并且是线程安全的,
特点:适合机器处理,存储的是秒和纳秒
/**
* 测试时间点及时间区间间隔
*/
@Test
public void instantAndDurationTest(){
// 获取当前时刻
Instant nowInstant=Instant.now(Clock.systemDefaultZone());
// 获取当前时刻的秒数(时间戳)
long currentSeconds=nowInstant.getEpochSecond();
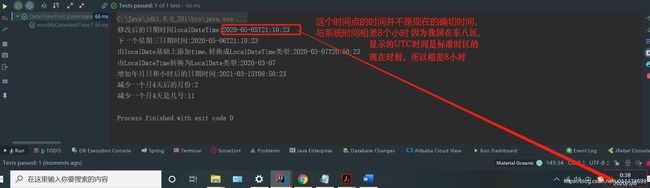
// 显示UTC(Coordinated Universal Time- 世界协调时间,格林威治时间)时间,对UTC时间最后加一个大写字母Z,
// 系统时间,我国在东八区,所以输出的时间距离现在相差八个小时
System.out.println("即刻时间:"+nowInstant);
Instant instant=Instant.ofEpochSecond(60);
Duration duration1 = Duration.ofDays(3);
Duration duration2=Duration.ofMinutes(20);
// 传入两个日期,比较间隔(注意比较的两个对象类型要一致,不能一个参数类型Localdate,一个参数类型LocalTime)
Duration duration3=Duration.between(LocalTime.of(12,5,1),LocalTime.of(22,5,5));
// 显示方式遵循iso-860标准,表示某一时间间隔,前面加一大写字母P,但时间段后都要加上相应的代表时间的大写字母(T表示time)
System.out.println(duration1);
System.out.println(duration2);
System.out.println(duration3);
// 两个时间相隔(可以使用ChronoUnit设置具体间隔年,月,日,或者时分秒的情况)
long intervalDays=ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(LocalDate.of(2020,5,1),LocalDate.of(2020,5,5));
System.out.println("相差天数:"+intervalDays);
Period period1=Period.between(LocalDate.of(2020,5,1),LocalDate.of(2020,5,5));
System.out.println("相差间隔:"+period1);
// 生成一个期间(1年2个月10天间隔)
Period period2=Period.of(1,2,10);
System.out.println("产生的期间:"+period2);
// 间隔时间减少20天(并不能只能计算真实间隔,只单纯对天数进行算数运算10-20=-10)
period2=period2.minusDays(20);
System.out.println("减少20天后的期间:"+period2);
}控制台输出结果: