【LOG2】【专业笔记】MySQL复习笔记
MySQL
复习笔记
一.复习前的准备
1:确认你已安装wamp
2:确认你已安装ecshop,并且ecshop的数据库名为shop
二.基础知识
1.数据库的连接
mysql -u -p -h
-u 用户名
-p 密码
-h host主机
2.库级知识
2.1 显示数据库: show databases;
2.2 选择数据库: use dbname;
2.3 创建数据库: create database dbname charset utf8;
2.3 删除数据库: drop database dbname;
3.表级操作
3.1 显示库下面的表
show tables;
3.2 查看表的结构:
desc tableName;
3.3 查看表的创建过程:
show create table tableName;
3.4 创建表:
create table tbName (
列名称1 列类型 [列参数] [not null default ],
....列2...
....
列名称N 列类型 [列参数] [not null default ]
)engine myisam/innodb charset utf8/gbk
3.4的例子:
create table user (
id int auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null default '',
age tinyint unsigned not null default 0,
index id (id)
)engine=innodb charset=utf8;
注:innodb是表引擎,也可以是myisam或其他,但最常用的是myisam和innodb,
charset 常用的有utf8,gbk;
3.5 修改表
3.5.1 修改表之增加列:
alter table tbName
add 列名称1 列类型 [列参数] [not null default ] #(add之后的旧列名之后的语法和创建表时的列声明一样)
3.5.2 修改表之修改列
alter table tbName
change 旧列名 新列名 列类型 [列参数] [not null default ]
(注:旧列名之后的语法和创建表时的列声明一样)
3.5.3 修改表之减少列:
alter table tbName
drop 列名称;
3.5.4 修改表之增加主键
alter table tbName add primary key(主键所在列名);
例:alter table goods add primary key(id)
该例是把主键建立在id列上
3.5.5 修改表之删除主键
alter table tbName drop primary key;
3.5.6 修改表之增加索引
alter table tbName add [unique|fulltext] index 索引名(列名);
3.5.7 修改表之删除索引
alter table tbName drop index 索引名;
3.5.8 清空表的数据
truncate tableName;
4.列类型讲解
MySQL支持多种类型,大致可以分为三类:数值、日期/时间和字符串(字符)类型。
5.增删改查基本操作
5.1 插入数据
insert into 表名(col1,col2,……) values(val1,val2……); -- 插入指定列
insert into 表名 values (,,,,); -- 插入所有列
insert into 表名 values -- 一次插入多行
(val1,val2……),
(val1,val2……),
(val1,val2……);
5.3 修改数据
update tablename
set
col1=newval1,
col2=newval2,
...
...
colN=newvalN
where 条件;
5.4 删除数据
delete from tablenaeme where 条件;
5.5 select 查询
(1) 条件查询 where
a. 条件表达式的意义,表达式为真,则该行取出
b. 比较运算符 = ,!=,< > <= >=
c. like , not like ('%'匹配任意多个字符,'_'匹配任意单个字符),
in , not in , between and
d. is null , is not null
(2) 分组 group by
一般要配合5个聚合函数使用:max,min,sum,avg,count
(3) 筛选 having
(4) 排序 order by
(5) 限制 limit
6.连接查询
6.1 左连接
.. left join .. on
table A left join table B on tableA.col1 = tableB.col2 ;
例句:
select 列名 from table A left join table B on tableA.col1 = tableB.col2
2. 右链接: right join
3. 内连接: inner join
左右连接都是以在左边的表的数据为准,沿着左表查右表.
内连接是以两张表都有的共同部分数据为准,也就是左右连接的数据之交集.
7.子查询
where 型子查询:内层sql的返回值在where后作为条件表达式的一部分
例句: select * from tableA where colA = (select colB from tableB where ...);
from 型子查询:内层sql查询结果,作为一张表,供外层的sql语句再次查询
例句:select * from (select * from ...) as tableName where ....
8.字符集
客服端sql编码 character_set_client
服务器转化后的sql编码 character_set_connection
服务器返回给客户端的结果集编码 character_set_results
快速把以上3个变量设为相同值: set names 字符集
9.存储引擎 engine=1或2
1 Myisam 速度快 不支持事务 回滚
2 Innodb 速度慢 支持事务,回滚
①开启事务 start transaction
②运行sql;
③提交,同时生效\回滚 commit\rollback
10.触发器 trigger
监视地点:表
监视行为:增 删 改
触发时间:after\before
触发事件:增 删 改
创建触发器语法
create trigger tgName
after/before insert/delete/update
on tableName
for each row
sql; -- 触发语句
删除触发器:
drop trigger tgName;
11.索引
提高查询速度,但是降低了增删改的速度,所以使用索引时,要综合考虑.
索引不是越多越好,一般我们在常出现于条件表达式中的列加索引.
值越分散的列,索引的效果越好
索引类型
primary key主键索引
index 普通索引
unique index 唯一性索引
fulltext index 全文索引
三.综合练习
连接上数据库服务器
创建一个gbk编码的数据库
建立商品表和栏目表,字段如下:
|
商品表:goods
|
栏目表:category
|
建表完成后,作以下操作:
删除goods表的goods_desc 字段,及货号字段
并增加字段:click_count -- 点击量
在goods_name列上加唯一性索引
在shop_price列上加普通索引
在clcik_count列上加普通索引
删除click_count列上的索引
注
:以下查询基于ecshop网站的商品表(ecs_goods),
在练习时可以只取部分列,方便查看
|
|
goods_id --主键,
goods_name -- 商品名称
cat_id -- 栏目id
brand_id -- 品牌id
goods_sn -- 货号
goods_number -- 库存量
shop_price -- 价格
goods_desc --商品详细描述
|
cat_id --主键
cat_name -- 栏目名称
parent_id -- 栏目的父id
|
1.基础查询 where的练习
1.1:主键为32的商品
select goods_id,goods_name,shop_price
from ecs_goods
where goods_id=32;
1.2:不属第3栏目的所有商品
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods
where cat_id!=3;
1.3:本店价格高于3000元的商品
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods
where shop_price >3000;
1.4:本店价格低于或等于100元的商品
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods where shop_price <=100;
1.5:取出第4栏目或第11栏目的商品(不许用or)
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods
where cat_id in (4,11);
1.6:取出100<=价格<=500的商品(不许用and)
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods
where shop_price between 100 and 500;
1.7:取出不属于第3栏目且不属于第11栏目的商品(and,或not in分别实现)
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods where cat_id!=3 and cat_id!=11;
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods where cat_id not in (3,11);
1.8:取出价格大于100且小于300,或者大于4000且小于5000的商品()
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods where shop_price>100 and shop_price <300 or shop_price >4000 and shop_price <5000;
1.9:取出第3个栏目下面价格<1000或>3000,并且点击量>5的系列商品
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price,click_count from ecs_goods where
cat_id=3 and (shop_price <1000 or shop_price>3000) and click_count>5;
1.10:取出第1个栏目下面的商品(注意:1栏目下面没商品,但其子栏目下有)
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price,click_count from ecs_goods
where cat_id in (2,3,4,5);
1.11:取出名字以"诺基亚"开头的商品
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods where goods_name like '诺基亚%';
1.12:取出名字为"诺基亚Nxx"的手机
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods
where goods_name like '诺基亚N__';
1.13:取出名字不以"诺基亚"开头的商品
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goos
where goods_name not like '诺基亚%';
1.14:取出第3个栏目下面价格在1000到3000之间,并且点击量>5 "诺基亚"开头的系列商品
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods where
cat_id=3 and shop_price>1000 and shop_price <3000 and click_count>5 and goods_name like '诺基亚%';
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods where
shop_price between 1000 and 3000 and cat_id=3 and click_count>5 and goods_name like '诺基亚%';
2.分组查询group
把good表中商品名为'诺基亚xxxx'的商品,改为'HTCxxxx',
提示:大胆的把列看成变量,参与运算,甚至调用函数来处理 .
substring(),concat()
2.1:查出最贵的商品的价格
select max(shop_price) from ecs_goods;
2.2:查出最大(最新)的商品编号
select max(goods_id) from ecs_goods;
2.3:查出最便宜的商品的价格
select min(shop_price) from ecs_goods;
2.4:查出最旧(最小)的商品编号
select min(goods_id) from ecs_goods;
2.5:查询该店所有商品的库存总量
select sum(goods_number) from ecs_goods;
2.6:查询所有商品的平均价
select avg(shop_price) from ecs_goods;
2.7:查询该店一共有多少种商品
select count(*) from ecs_goods;
2.8:查询每个栏目下面
最贵商品价格
最低商品价格
商品平均价格
商品库存量
商品种类
提示:(5个聚合函数,sum,avg,max,min,count与group综合运用)
select cat_id,max(shop_price) from ecs_goods group by cat_id;
3.having与group综合运用查询:
3.1:查询该店的商品比市场价所节省的价格
select goods_id,goods_name,market_price-shop_price as j
from ecs_goods ;
3.2:查询每个商品所积压的货款(提示:库存*单价)
select goods_id,goods_name,goods_number*shop_price from ecs_goods;
3.3:查询该店积压的总货款
select sum(goods_number*shop_price) from ecs_goods;
3.4:查询该店每个栏目下面积压的货款.
select cat_id,sum(goods_number*shop_price) as k from ecs_goods group by cat_id;
3.5:查询比市场价省钱200元以上的商品及该商品所省的钱(where和having分别实现)
select goods_id,goods_name,market_price-shop_price as k from ecs_goods
where market_price-shop_price >200;
select goods_id,goods_name,market_price-shop_price as k from ecs_goods
having k >200;
3.6:查询积压货款超过2W元的栏目,以及该栏目积压的货款
select cat_id,sum(goods_number*shop_price) as k from ecs_goods group by cat_id
having k>20000
3.7:where-having-group综合练习题
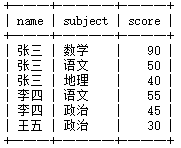
有如下表及数据(
要求:查询出2门及2门以上不及格者的平均成绩
)
|
## 一种错误做法(用的count)
mysql> select name,count(score<60) as k,avg(score) from stu group by name having k>=2;
#再多加些信息,加上赵六后错误暴露
mysql> insert into stu
-> values
-> ('赵六','A',100),
-> ('赵六','B',99),
-> ('赵六','C',98);
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.05 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
#错误显现(为什么会筛选出分数大于60分的,我很好奇)
mysql> select name,count(score<60) as k,avg(score) from stu group by name having k>=2;
##
正确思路(用的sum)
(1)
先查看每个人的平均成绩
mysql> select name,avg(score) from stu group by name;
(2)mysql> # 看每个人挂科情况
mysql> select name,score < 60 from stu;
(3)mysql> #计算每个人的挂科科目
mysql> select name,sum(score < 60) from stu group by name;
(4)#同时计算每人的平均分
mysql> select name,sum(score < 60),avg(score) as pj from stu group by name;
(5)#利用having筛选挂科2门以上的.
mysql> select name,sum(score < 60) as gk ,avg(score) as pj from stu group by name having gk >=2;
|
4. order by 与 limit查询
4.1:按价格由高到低排序
select goods_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods order by shop_price desc;
4.2:按发布时间由早到晚排序
select goods_id,goods_name,add_time from ecs_goods order by add_time;
4.3:接栏目由低到高排序,栏目内部按价格由高到低排序
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods
order by cat_id ,shop_price desc;
4.4:取出价格最高的前三名商品
select goods_id,goods_name,shop_price from ecs_goods order by shop_price desc limit 3;
4.5:取出点击量前三名到前5名的商品
select goods_id,goods_name,click_count from ecs_goods order by click_count desc limit 2,3;
5.连接查询
5.1:取出所有商品的商品名,栏目名,价格
select goods_name,cat_name,shop_price from
ecs_goods left join ecs_category
on ecs_goods.cat_id=ecs_category.cat_id;
5.2:取出第4个栏目下的商品的商品名,栏目名,价格
select goods_name,cat_name,shop_price from
ecs_goods left join ecs_category
on ecs_goods.cat_id=ecs_category.cat_id
where ecs_goods.cat_id = 4;
5.3:取出第4个栏目下的商品的商品名,栏目名,与品牌名
select goods_name,cat_name,brand_name from
ecs_goods left join ecs_category
on ecs_goods.cat_id=ecs_category.cat_id
left join ecs_brand
on ecs_goods.brand_id=ecs_brand.brand_id
where ecs_goods.cat_id = 4;
5.4: 用友面试题
(1)根据给出的表结构;
Match表的hostTeamID与guestTeamID都与Team表中的teamID关联
(2)按要求写出SQL语句。
查出 2006-6-1 到2006-7-1之间举行的所有比赛,并且用以下形式列出:
拜仁 2:0 不来梅 2006-6-21
Match 赛程表
|
字段名称
|
字段类型
|
描述
|
|
matchID
|
int
|
主键
|
|
hostTeamID
|
int
|
主队的ID
|
|
guestTeamID
|
int
|
客队的ID
|
|
matchResult
|
varchar(20)
|
比赛结果,如(2:0)
|
|
matchTime
|
date
|
比赛开始时间
|
Team 参赛队伍表
|
字段名称
|
字段类型
|
描述
|
|
teamID
|
int
|
主键
|
|
teamName
|
varchar(20)
|
队伍名称
|
|
参考答案:
mysql> select hid,t1.tname as hname ,mres,gid,t2.tname as gname,matime
-> from
-> m left join t as t1
-> on m.hid = t1.tid
-> left join t as t2
-> on m.gid = t2.tid;
|
6.union查询
6.1:把ecs_comment,ecs_feedback两个表中的数据,各取出4列,并把结果集union成一个结果集.
6.2:3期学员碰到的一道面试题
|
mysql> # 合并 ,注意all的作用
mysql> select * from ta
-> union all
-> select * from tb;
要求查询出以下效果:
参考答案:
mysql> # sum,group求和
mysql> select id,sum(num) from (select * from ta union all select * from tb) as tmp group by id;
|
7.子查询
7.1:查询出最新一行商品(以商品编号最大为最新,用子查询实现)
select goods_id,goods_name from
ecs_goods where goods_id =(select max(goods_id) from ecs_goods);
7.2:查询出编号为19的商品的栏目名称(用左连接查询和子查询分别)
7.3:用where型子查询把ecs_goods表中的每个栏目下面最新的商品取出来
select goods_id,goods_name,cat_id from ecs_goods where goods_id in (select max(goods_id) from ecs_goods group by cat_id);
7.4:用from型子查询把ecs_goods表中的每个栏目下面最新的商品取出来
select * from (select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name from ecs_goods order by goods_id desc) as t group by cat_id;
8.创建触发器
CREATE trigger tg2
after insert on ord
for each row
update goods set goods_number=goods_number-new.num where id=new.gid
CREATE trigger tg3
after delete on ord
for each row
update goods set goods_number=good_number+old.num where id=old.gid
CREATE trigger tg4
after update on ord
for each row
update goods set goods_number=goods_number+old.num-new.num where id=old.gid
9.常用函数
一、数学函数
abs(x) 返回x的绝对值
bin(x) 返回x的二进制(oct返回八进制,hex返回十六进制)
ceiling(x) 返回大于x的最小整数值
exp(x) 返回值e(自然对数的底)的x次方
floor(x) 返回小于x的最大整数值
greatest(x1,x2,...,xn)返回集合中最大的值
least(x1,x2,...,xn) 返回集合中最小的值
ln(x) 返回x的自然对数
log(x,y)返回x的以y为底的对数
mod(x,y) 返回x/y的模(余数)
pi()返回pi的值(圆周率)
rand()返回0到1内的随机值,可以通过提供一个参数(种子)使rand()随机数生成器生成一个指定的值。
round(x,y)返回参数x的四舍五入的有y位小数的值
sign(x) 返回代表数字x的符号的值
sqrt(x) 返回一个数的平方根
truncate(x,y) 返回数字x截短为y位小数的结果
二、聚合函数(常用于group by从句的select查询中)
avg(col)返回指定列的平均值
count(col)返回指定列中非null值的个数
min(col)返回指定列的最小值
max(col)返回指定列的最大值
sum(col)返回指定列的所有值之和
group_concat(col) 返回由属于一组的列值连接组合而成的结果
三、字符串函数
ascii(char)返回字符的ascii码值
bit_length(str)返回字符串的比特长度
concat(s1,s2...,sn)将s1,s2...,sn连接成字符串
concat_ws(sep,s1,s2...,sn)将s1,s2...,sn连接成字符串,并用sep字符间隔
insert(str,x,y,instr) 将字符串str从第x位置开始,y个字符长的子串替换为字符串instr,返回结果
find_in_set(str,list)分析逗号分隔的list列表,如果发现str,返回str在list中的位置
lcase(str)或lower(str) 返回将字符串str中所有字符改变为小写后的结果
left(str,x)返回字符串str中最左边的x个字符
length(s)返回字符串str中的字符数
ltrim(str) 从字符串str中切掉开头的空格
position(substr,str) 返回子串substr在字符串str中第一次出现的位置
quote(str) 用反斜杠转义str中的单引号
repeat(str,srchstr,rplcstr)返回字符串str重复x次的结果
reverse(str) 返回颠倒字符串str的结果
right(str,x) 返回字符串str中最右边的x个字符
rtrim(str) 返回字符串str尾部的空格
strcmp(s1,s2)比较字符串s1和s2
trim(str)去除字符串首部和尾部的所有空格
ucase(str)或upper(str) 返回将字符串str中所有字符转变为大写后的结果
四、日期和时间函数
curdate()或current_date() 返回当前的日期
curtime()或current_time() 返回当前的时间
date_add(date,interval int keyword)返回日期date加上间隔时间int的结果(int必须按照关键字进行格式化),如:selectdate_add(current_date,interval 6 month);
date_format(date,fmt) 依照指定的fmt格式格式化日期date值
date_sub(date,interval int keyword)返回日期date加上间隔时间int的结果(int必须按照关键字进行格式化),如:selectdate_sub(current_date,interval 6 month);
dayofweek(date) 返回date所代表的一星期中的第几天(1~7)
dayofmonth(date) 返回date是一个月的第几天(1~31)
dayofyear(date) 返回date是一年的第几天(1~366)
dayname(date) 返回date的星期名,如:select dayname(current_date);
from_unixtime(ts,fmt) 根据指定的fmt格式,格式化unix时间戳ts
hour(time) 返回time的小时值(0~23)
minute(time) 返回time的分钟值(0~59)
month(date) 返回date的月份值(1~12)
monthname(date) 返回date的月份名,如:select monthname(current_date);
now() 返回当前的日期和时间
quarter(date) 返回date在一年中的季度(1~4),如select quarter(current_date);
week(date) 返回日期date为一年中第几周(0~53)
year(date) 返回日期date的年份(1000~9999)
一些示例:
获取当前系统时间:select from_unixtime(unix_timestamp());
select extract(year_month from current_date);
select extract(day_second from current_date);
select extract(hour_minute from current_date);
返回两个日期值之间的差值(月数):select period_diff(200302,199802);
在mysql中计算年龄:
select date_format(from_days(to_days(now())-to_days(birthday)),'%y')+0 as age from employee;
这样,如果brithday是未来的年月日的话,计算结果为0。
下面的sql语句计算员工的绝对年龄,即当birthday是未来的日期时,将得到负值。
select date_format(now(), '%y') - date_format(birthday, '%y') -(date_format(now(), '00-%m-%d')
五、加密函数
aes_encrypt(str,key) 返回用密钥key对字符串str利用高级加密标准算法加密后的结果,调用aes_encrypt的结果是一个二进制字符串,以blob类型存储
aes_decrypt(str,key) 返回用密钥key对字符串str利用高级加密标准算法解密后的结果
decode(str,key) 使用key作为密钥解密加密字符串str
encrypt(str,salt) 使用unixcrypt()函数,用关键词salt(一个可以惟一确定口令的字符串,就像钥匙一样)加密字符串str
encode(str,key) 使用key作为密钥加密字符串str,调用encode()的结果是一个二进制字符串,它以blob类型存储
md5() 计算字符串str的md5校验和
password(str) 返回字符串str的加密版本,这个加密过程是不可逆转的,和unix密码加密过程使用不同的算法。
sha() 计算字符串str的安全散列算法(sha)校验和
示例:
select encrypt('root','salt');
select encode('xufeng','key');
select decode(encode('xufeng','key'),'key');#加解密放在一起
select aes_encrypt('root','key');
select aes_decrypt(aes_encrypt('root','key'),'key');
select md5('123456');
select sha('123456');
六、控制流函数
mysql有4个函数是用来进行条件操作的,这些函数可以实现sql的条件逻辑,允许开发者将一些应用程序业务逻辑转换到数据库后台。
mysql控制流函数:
case when[test1] then [result1]...else [default] end如果testn是真,则返回resultn,否则返回default
case [test] when[val1] then [result]...else [default]end 如果test和valn相等,则返回resultn,否则返回default
if(test,t,f) 如果test是真,返回t;否则返回f
ifnull(arg1,arg2) 如果arg1不是空,返回arg1,否则返回arg2
nullif(arg1,arg2) 如果arg1=arg2返回null;否则返回arg1
这些函数的第一个是ifnull(),它有两个参数,并且对第一个参数进行判断。如果第一个参数不是null,函数就会向调用者返回第一个参数;如果是null,将返回第二个参数。
如:select ifnull(1,2), ifnull(null,10),ifnull(4*null,'false');
nullif()函数将会检验提供的两个参数是否相等,如果相等,则返回null,如果不相等,就返回第一个参数。
如:select nullif(1,1),nullif('a','b'),nullif(2+3,4+1);
和许多脚本语言提供的if()函数一样,mysql的if()函数也可以建立一个简单的条件测试,这个函数有三个参数,第一个是要被判断的表达式,如果表达式为真,if()将会返回第二个参数,如果为假,if()将会返回第三个参数。
如:selectif(1<10,2,3),if(56>100,'true','false');
if()函数在只有两种可能结果时才适合使用。然而,在现实世界中,我们可能发现在条件测试中会需要多个分支。在这种情况下,mysql提供了case函数,它和php及perl语言的switch-case条件例程一样。
case函数的格式有些复杂,通常如下所示:
case [expression to be evaluated]
when [val 1] then [result 1]
when [val 2] then [result 2]
when [val 3] then [result 3]
......
when [val n] then [result n]
else [default result]
end
这里,第一个参数是要被判断的值或表达式,接下来的是一系列的when-then块,每一块的第一个参数指定要比较的值,如果为真,就返回结果。所有的when-then块将以else块结束,当end结束了所有外部的case块时,如果前面的每一个块都不匹配就会返回else块指定的默认结果。如果没有指定else块,而且所有的when-then比较都不是真,mysql将会返回null。
case函数还有另外一种句法,有时使用起来非常方便,如下:
case
when [conditional test 1] then [result 1]
when [conditional test 2] then [result 2]
else [default result]
end
这种条件下,返回的结果取决于相应的条件测试是否为真。
示例:
mysql>select case 'green'
when 'red' then 'stop'
when 'green' then 'go' end;
select case 9 when 1 then 'a' when 2 then 'b' else 'n/a' end;
select case when (2+2)=4 then 'ok' when(2+2)<>4 then 'not ok' end asstatus;
select name,if((isactive = 1),'已激活','未激活') as result fromuserlogininfo;
select fname,lname,(math+sci+lit) as total,
case when (math+sci+lit) < 50 then 'd'
when (math+sci+lit) between 50 and 150 then 'c'
when (math+sci+lit) between 151 and 250 then 'b'
else 'a' end
as grade from marks;
select if(encrypt('sue','ts')=upass,'allow','deny') as loginresultfrom users where uname = 'sue';#一个登陆验证
七、格式化函数
date_format(date,fmt) 依照字符串fmt格式化日期date值
format(x,y) 把x格式化为以逗号隔开的数字序列,y是结果的小数位数
inet_aton(ip) 返回ip地址的数字表示
inet_ntoa(num) 返回数字所代表的ip地址
time_format(time,fmt) 依照字符串fmt格式化时间time值
其中最简单的是format()函数,它可以把大的数值格式化为以逗号间隔的易读的序列。
示例:
select format(34234.34323432,3);
select date_format(now(),'%w,%d %m %y %r');
select date_format(now(),'%y-%m-%d');
select date_format(19990330,'%y-%m-%d');
select date_format(now(),'%h:%i %p');
select inet_aton('10.122.89.47');
select inet_ntoa(175790383);
八、类型转化函数
为了进行数据类型转化,mysql提供了cast()函数,它可以把一个值转化为指定的数据类型。类型有:binary,char,date,time,datetime,signed,unsigned
示例:
select cast(now() as signed integer),curdate()+0;
select 'f'=binary 'f','f'=cast('f' as binary);
九、系统信息函数
database() 返回当前数据库名
benchmark(count,expr) 将表达式expr重复运行count次
connection_id() 返回当前客户的连接id
found_rows() 返回最后一个select查询进行检索的总行数
user()或system_user() 返回当前登陆用户名
version() 返回mysql服务器的版本
示例:
select database(),version(),user();
selectbenchmark(9999999,log(rand()*pi()));#该例中,mysql计算log(rand()*pi())表达式9999999次。