《数据结构与算法之美》06~10笔记
文章目录
- 关于我的仓库
- 前言
- 06讲链表(上):如何实现LRU缓存淘汰算法
- 实现LRU缓存淘汰算法
- 课后题:如何判断一个字符串是否是回文字符串的问题,我想你应该听过,我们今天的思题目就是基于这个问题的改造版本。如果字符串是通过单链表来存储的,那该如何来判断是一个回文串呢?你有什么好的解决思路呢?相应的时间空间复杂度又是多少呢?【LeetCode 234 回文链表】
- 07讲链表(下):如何轻松写出正确的链表代码
- 链表六技
- 技巧一:理解指针或引用的含义
- 技巧二:警惕指针丢失和内存泄漏
- 技巧三:利用哨兵简化实现难度
- 技巧四:重点留意边界条件处理
- 技巧五:举例画图,辅助思考
- 技巧六:多写多练,没有捷径
- 单链表反转【LeetCode 206 反转链表】
- 参考文章
- 题解
- 我的题解
- 参考题解
- 反思
- 链表中环的检测【LeetCode 141 环形链表】
- 参考文章
- 题解
- 我的题解
- 参考题解
- 反思
- 两个有序的链表合并【LeetCode 21 合并两个有序链表】
- 参考文章
- 题解
- 我的题解
- 参考题解
- 反思
- 删除链表倒数第n个结点【LeetCode 19 删除链表的倒数第N个节点】
- 参考文章
- 题解
- 我的题解
- 参考题解
- 反思
- 求链表的中间结点【LeetCode 876 链表的中间结点】
- 参考文章
- 题解
- 我的题解
- 参考题解
- 反思
- 课后题:今天我们讲到用哨兵来简化编码实现,你是否还能够想到其他场景,利用哨兵可以大大地简化编码难度?
- 08讲栈:如何实现浏览器的前进和后退功能
- 顺序栈的基本实现
- 支持动态扩容的顺序栈
- 典型使用
- 栈在函数调用中的应用【函数调用栈】
- 栈在表达式求值中的应用
- 栈在括号匹配中的应用
- 通过栈实现浏览器的前进和后退
- 课后题
- 我们在讲栈的应用时,讲到用函数调用栈来保存临时变量,为什么函数调用要用“栈”来保存临时变量呢?用其他数据结构 不行吗?
- 我们都知道,JVM内存管理中有个“堆栈”的概念。栈内存用来存储局部变量和方法调用,堆内存用来存储Java中的对象。 那JVM里面的“栈”跟我们这里说的“栈”是不是一回事呢?如果不是,那它为什么又叫作“栈”呢?
- 作业
- 09讲队列:队列在线程池等有限资源池中的应用
- 如何理解“队列”?
- 顺序队列和链式队列
- 顺序队列
- 链式队列
- 循环队列
- 阻塞队列和并发队列
- 线程池没有空闲线程时,新的任务请求线程资源时,线程池该如何处理?各种处理策略又是如何实现的呢?
- 课后题
- 除了线程池这种池结构会用到队列排队请求,你还知道有哪些类似的池结构或者场景中会用到队列的排队请求呢?
- 今天讲到并发队列,关于如何实现无锁并发队列,网上有非常多的讨论。对这个问题,你怎么看呢?
- 作业:循环队列【LeetCode 622. 设计循环队列】
- 10讲递归:如何用三行代码找到“最终推荐人”
- 如何理解“递归”?
- 递归需要满足的三个条件
- Leetcode 687. 最长同值路径
- 分析:
- 代码:
- 递归心法
- 警惕栈溢出
- 递归代码警惕重复计算
- 迭代法与递归相互转化
- 开篇解答:如何找到“最终推荐人”?
- 课后题:我们平时调试代码喜欢使用IDE的单步跟踪功能,像规模比较大、递归层次很深的递归代码,几乎无法使用这种调试方式。对于递归代码,你有什么好的调试方法呢?
关于我的仓库
- 这篇文章是我为面试准备的学习总结中的一篇
- 我将准备面试中找到的所有学习资料,写的Demo,写的博客都放在了这个仓库里iOS-Engineer-Interview
- 欢迎star??
- 其中的博客在简书,CSDN都有发布
- 博客中提到的相关的代码Demo可以在仓库里相应的文件夹里找到
前言
- 该系列为学习《数据结构与算法之美》的系列学习笔记
- 总结规律为一周一更,内容包括其中的重要知识带你,以及课后题的解答
- 算法的学习学与刷题并进,希望能真正养成解算法题的思维
- LeetCode刷题仓库:LeetCode-All-In
- 多说无益,你应该开始打代码了
06讲链表(上):如何实现LRU缓存淘汰算法
- 常见缓存淘汰策略:先进先出策略FIFO(First In,First Out)、最少使用策略LFU(Least Frequently Used)、最近最少使用策略LRU(Least Recently Used)。
- 删除指定节点:由于删除节点需要使用前一个节点的next指针,所以对于单链表,在执行这样的删除,插入【前一个插入】的时候,都需要遍历链表
- 而双向链表对此就很有优势,包括对于有序链表查找,由于可以判定往后还是往前【此处存疑,怎么从中间开始?】
- 对于执行较慢的程序,可以通过消耗更多的内存(空间换时间)来进行优化;而消耗过多内存的程序,可以 通过消耗更多的时间(时间换空间)来降低内存的消耗。

- 在实现上使用的是连续的内存空间,可以借助CPU的缓存机制,预读数组中的数据,所以访问效率更高。而 链表在内存中并不是连续存储,所以对CPU缓存不友好,没办法有效预读。CPU在从内存读取数据的时候,会先把读取到的数据加载到CPU的缓存中。而CPU每次从内存读取数据并不是只读取那个特定 要访问的地址,而是读取一个数据块并保存到CPU缓存中,然后下次访问内存数据的时候就会先从CPU缓存开始查找,如果找到就不需要再从内存中取。这样就实现了比内存访问速度更快的机制,也就是CPU缓存存在的意义:为了弥补内存访问速度过慢与CPU执行速度快之间的差异而引入。对于数组来说,存储空间是连续的,所以在加载某个下标的时候可以把以后的几个下标元素也加载到CPU缓存这样执行速度会 快于存储空间不连续的链表存储。
- 链表本身没有大小的限制,天然地支持动态扩容,我觉得这也是它与数组最大的区 别。如果我们用ArrayList存储了了1GB大小的数据,这个时候已经没有空闲空间了,当我们再插入数据 的时候,ArrayList会申请一个1.5GB大小的存储空间,并且把原来那1GB的数据拷⻉到新申请的空间上。听起来是不是就很耗时?
实现LRU缓存淘汰算法
- 维护一个单向链表,越靠近尾节点越是远古且不常用
- 插入数据时:
- 缓存已满,直接删除尾节点,将新数据插入头节点
- 缓存不满:
- 找到的该数据,删除原来的,在头节点加入
- 找不到,直接在头节点加入
课后题:如何判断一个字符串是否是回文字符串的问题,我想你应该听过,我们今天的思题目就是基于这个问题的改造版本。如果字符串是通过单链表来存储的,那该如何来判断是一个回文串呢?你有什么好的解决思路呢?相应的时间空间复杂度又是多少呢?【LeetCode 234 回文链表】
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {
return true;
}
ListNode *prev = NULL;
ListNode *slow = head;
ListNode *fast = head;
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
//pre:前一个
//slow:慢指针&&后一段链表的开头
//fast:快指针,边界工具人
//操作就是要把慢指针经过的逆置过来,所以让pre作为前一个,slow作为当前工具人,使用next去记录下一个,就是slow的下一位
//变换时,先把前面的逆过来,slow再往下走
fast = fast->next->next;
ListNode *next = slow->next;
slow->next = prev;
prev = slow;
slow = next;
}
if (fast != NULL) {
//!=NULL的这个情况就是奇数的情况,此时,slow工具人站在中间,pre就位,因此要让slow往前一个
slow = slow->next;
}
while (slow != NULL) {
if (slow->val != prev->val) {
return false;
}
slow = slow->next;
prev = prev->next;
}
return true;
}
};
- 先通过快慢指针找到中点,此时链表分为两部分,把前半部分逆置,然后比较两列
07讲链表(下):如何轻松写出正确的链表代码
链表六技
技巧一:理解指针或引用的含义
- 指针的作用就在于存储对象的内存地址
- 将某个变量赋值给指针,实际上就是将这个变量的地址赋值给指针,或者反过来说,指针中存储了这个变量的内存地址,指向了这个变量,通过指针就能找到这个变量。
- p->next=q:p结点中的next指针存储了q结点的内存地址
- p->next=p->next->next:p结点的next指针存储了p 结点的下下一个结点的内存地址。
技巧二:警惕指针丢失和内存泄漏
- 这一点其实就是由于链表单向性的特征,所以我们需要,我们一旦改变某一个节点的next指向,就会丢失掉原来那个
- 插入结点时,一定要注意操作的顺序
技巧三:利用哨兵简化实现难度
- 针对链表的插入,删除操作,需要对插入第一个节点和删除最后一个节点的情况进行特殊处理
- 一个使用哨兵的例子:
// 正常人写的代码
// 在数组a中,查找key,返回key所在的位置 // 其中,n表示数组a的⻓度
int find(char* a, int n, char key) {
// 边界条件处理,如果a为空,或者n<=0,说明数组中没有数据,就不用while循环比较了
if(a == null || n <= 0) {
return -1;
}
int i = 0;
// 这里有两个比较操作:i
while (i < n) {
if (a[i] == key) {
return i;
}
++i;
}
return -1;
}
// 憨憨哨兵代码
// 在数组a中,查找key,返回key所在的位置
// 其中,n表示数组a的⻓度
// 我举2个例子,你可以拿例子走一下代码 //a={4,2,3,5,9,6} n=6key=7 //a={4,2,3,5,9,6} n=6key=6
int find(char* a, int n, char key) {
if(a == null || n <= 0) {
return -1;
}
// 这里因为要将a[n-1]的值替换成key,所以要特殊处理这个值
if (a[n-1] == key) {
return n-1;
}
// 把a[n-1]的值临时保存在变量tmp中,以便之后恢复。tmp=6。
// 之所以这样做的目的是:希望find()代码不要改变a数组中的内容 char tmp = a[n-1];
// 把key的值放到a[n-1]中,此时a = {4, 2, 3, 5, 9, 7}
a[n-1] = key;
int i = 0;
// while 循环比起代码一,少了i
while (a[i] != key) {
++i;
}
// 恢复a[n-1]原来的值,此时a= {4, 2, 3, 5, 9, 6}
a[n-1] = tmp;
if (i == n-1) {
// 如果i == n-1说明,在0...n-2之间都没有key,所以返回-1
return -1;
} else {
// 否则,返回i,就是等于key值的元素的下标
return i;
}
}
- 简单来说,这么一整就可以使得少了i < n这个判断,??
- 当然,这只是为了举例说明哨兵的作用,你写代码的时候千万不要写第二段那样的代码,因为可读性太差了。大部分情况下, 我们并不需要如此追求极致的性能。【谁写谁憨说白了】
技巧四:重点留意边界条件处理
- 如果链表为空时,代码是否能正常工作?
- 如果链表仅包含一个结点时,代码是否能正常工作?
- 如果链表只包含两个结点时,代码是否能正常工作?
- 代码逻辑在处理头结点和尾结点的时候,是否能正常工作?
技巧五:举例画图,辅助思考
技巧六:多写多练,没有捷径
单链表反转【LeetCode 206 反转链表】
参考文章
- LeetCode官方题解
题解
我的题解
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *pre = NULL;
ListNode *next = NULL;
ListNode *pNode = head;
while (pNode != NULL) {
next = pNode->next;
pNode->next = pre;
pre = pNode;
pNode = next;
}
return pre;
}
};
参考题解
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;
ListNode *p = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return p;
}
};
反思
- 递归骚断腿,实在难悟
- 妙
链表中环的检测【LeetCode 141 环形链表】
参考文章
- LeetCode官方题解
题解
我的题解
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {
return false;
}
ListNode *slow = head;
ListNode *fast = head;
while (fast->next != NULL && fast->next->next != NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow->val == fast->val) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
参考题解
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
Set nodesSeen = new HashSet<>();
while (head != null) {
if (nodesSeen.contains(head)) {
return true;
} else {
nodesSeen.add(head);
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
反思
- 要想链表玩的溜,两根指针少不了
两个有序的链表合并【LeetCode 21 合并两个有序链表】
参考文章
- LeetCode官方题解
题解
我的题解
//这谁会呢
参考题解
//递归
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
if (l1 == NULL) {
//这一步不仅是一开始的判空,更是后面当一个链表已经遍历到结束了
//就一直使用另一个里面的节点
return l2;
}
else if (l2 == NULL) {
return l1;
}
else if (l1->val < l2->val) {
//由于从小到大,因此
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
}
else {
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
}
};
//迭代
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
//这等于就是添加哨兵的思想,使得不用考虑开头的数字,妙啊
ListNode *prehead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *prev = prehead;
while (l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL) {
if (l1->val <= l2->val) {
//把l1连上
prev->next = l1;
//接下来要做的仅仅是把l1指针指向下一个
l1 = l1->next;
} else {
prev->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = l1 == NULL ? l2 :l1;
return prehead->next;
}
};
反思
- 还是想太复杂了,其实只要进行一下链接就行,不用考虑辣么多
删除链表倒数第n个结点【LeetCode 19 删除链表的倒数第N个节点】
参考文章
- LeetCode官方题解
题解
我的题解
//这谁会呢
参考题解
//两次遍历算法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy->next = head;
int length = 0;
ListNode *first = head;
while (first != NULL) {
length++;
first = first->next;
}
length -= n;
first = dummy;
while (length > 0) {
length--;
first = first->next;
}
first->next = first->next->next;
return dummy->next;
}
};
//一次遍历法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode *first = dummy;
ListNode *second = dummy;
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
first = first->next;
}
while (first != NULL) {
first = first->next;
second = second->next;
}
second->next = second->next->next;
return dummy->next;
}
};
反思
- 这又啥难的,惊了
求链表的中间结点【LeetCode 876 链表的中间结点】
参考文章
- LeetCode官方题解
题解
我的题解
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *slowNode = head;
ListNode *fastNode = head;
while (fastNode->next != NULL && fastNode->next->next != NULL) {
fastNode = fastNode->next->next;
slowNode = slowNode->next;
}
if (fastNode->next != NULL) {
slowNode = slowNode->next;
}
return slowNode;
}
};
参考题解
//这要啥参考题解呢
反思
- 联动题目,回文链表
课后题:今天我们讲到用哨兵来简化编码实现,你是否还能够想到其他场景,利用哨兵可以大大地简化编码难度?
- 举例:iOS开发中,对于autoreleasing Pool那一块,在每个autoreleasingPool之间是靠哨兵对象nil隔开的
- 具体看我这篇博客从RunTime源码回看autoreleasepool
08讲栈:如何实现浏览器的前进和后退功能
- 后进者先出,先进者后出,这就是典型的**“栈”**结构
- 当某个数据集合只涉及在一端插入和删除数据,并且满足后进先出、先进后出的特性,我们就应该首选**“栈”**这种数据结构。
顺序栈的基本实现
- 存储数据需要一个长度为n的数组并不是说空间复杂度就是O(n),因为这n个空间是必须的,空间复杂度应该是算法所需要的额外存储空间
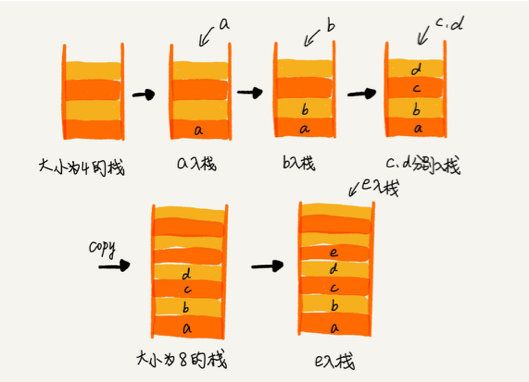
支持动态扩容的顺序栈
- 最好情况时间复杂度是O(1),最坏情况时间复杂度是O(n),使用摊还分析法分析
- 总共涉及了K个数据的搬移,以及K次simple-push操作。将K个数据搬移均摊到K次入栈 操作,那每个入栈操作只需要一个数据搬移和一个simple-push操作。以此类推,入栈操作的均摊时间复杂度就为O(1)。
- 因为在大部分情况下,入 栈操作的时间复杂度O都是O(1),只有在个别时刻才会退化为O(n),所以把耗时多的入栈操作的时间均摊到其他入栈操作上, 平均情况下的耗时就接近O(1)。
典型使用
栈在函数调用中的应用【函数调用栈】
- 作系统给每个线程分配了一块独立的内存空间,这块内存被组织成“栈”这种结构,用来存储函数调用时的临时变 量。每进入一个函数,就会将临时变量作为一个栈帧入栈,当被调用函数执行完成,返回之后,将这个函数对应的栈帧出栈。
- 【程序员的自我修养p.287】:每一次函数的调用,都会在调用栈(call stack)上维护一个独立的栈帧(stack frame).每个独立的栈帧一般包括函数的返回地址和参数, 临时变量: 包括函数的非静态局部变量以及编译器自动生成的其他临时变量, 保存的上下文【包括在函数调用前后需要不变的寄存器】
//
// main.cpp
// stack-Test
//
// Created by Kevin.J on 2019/9/11.
// Copyright © 2019 姜凯文. All rights reserved.
//
#include
int add(int x, int y) {
int sum = 0;
sum = x + y;
return sum;
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
// insert code here...
std::cout << "Hello, World!\n";
int a = 1;
int ret = 0;
int res = 0;
ret = add(3, 5);
res = a + ret;
printf("%d", res);
return 0;
}
- 我们在add中打上一个断电,通过Xcode自带的LLDB来查看下栈帧
//输入 thread backtrace
* thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = breakpoint 2.1
* frame #0: 0x00000001000011d1 stack-Test`add(x=3, y=5) at main.cpp:13:11
frame #1: 0x0000000100001234 stack-Test`main(argc=1, argv=0x00007ffeefbff5f0) at main.cpp:24:11
frame #2: 0x00007fff6bf9f3d5 libdyld.dylib`start + 1
//当前顶上的就是add
栈在表达式求值中的应用
- 编译器就是通过两个栈来实现的。其中一个保存操作数的栈,另一个是保存运算符的栈。我们从左向右遍历表达式, 当遇到数字,我们就直接压入操作数栈;当遇到运算符,就与运算符栈的栈顶元素进行比较。
- 这里还是要借助下西邮的数据结构课来说明比较妥当表达式求值问题
- 数据优先级:
- 这里的图画的不清楚,实际上在计算完8 * 5后得到40,会把40这个数重新压入数据栈,接下来也不会急着读取下一位,而是继续比较,发现减号优先级大于栈顶的加号,那就在处理加法,这时在比较遇到的是#,优先级比减号大了,此时才会把减号压入
栈在括号匹配中的应用
- 这个没什么好说的,就是遇到做括号入栈,遇到右括号出栈
通过栈实现浏览器的前进和后退
- 我们使用两个栈,X和Y,我们把首次浏览的⻚面依次压入栈X,当点击后退按钮时,再依次从栈X中出栈,并将出栈的数据依 次放入栈Y。当我们点击前进按钮时,我们依次从栈Y中取出数据,放入栈X中。当栈X中没有数据时,那就说明没有⻚面可以 继续后退浏览了。当栈Y中没有数据,那就说明没有⻚面可以点击前进按钮浏览了。
- 当你通过浏览器的后退按钮,从⻚面c后退到⻚面a之后,我们就依次把c和b从栈X中弹出,并且依次放入到栈Y。这个时候, 两个栈的数据就是这个样子:
- 这个时候你又想看⻚面b,于是你又点击前进按钮回到b⻚面,我们就把b再从栈Y中出栈,放入栈X中。此时两个栈的数据是这 个样子:
课后题
我们在讲栈的应用时,讲到用函数调用栈来保存临时变量,为什么函数调用要用“栈”来保存临时变量呢?用其他数据结构 不行吗?
-
其实,我们不一定非要用栈来保存临时变量,只不过如果这个函数调用符合后进先出的特性,用栈这种数据结构来实现,是最顺理成章的选择。
从调用函数进入被调用函数,对于数据来说,变化的是什么呢?是作用域。所以根本上,只要能保证每进入一个新的函数,都是一个新的作用域就可以。而要实现这个,用栈就非常方便。在进入被调用函数的时候,分配一段栈空间给这个函数的变量,在函数结束的时候,将栈顶复位,正好回到调用函数的作用域内。
我们都知道,JVM内存管理中有个“堆栈”的概念。栈内存用来存储局部变量和方法调用,堆内存用来存储Java中的对象。 那JVM里面的“栈”跟我们这里说的“栈”是不是一回事呢?如果不是,那它为什么又叫作“栈”呢?
- JVM里面的栈和我们这里说的是一回事,被称为方法栈。和前面函数调用的作用是一致的,用来存储方法中的局部变量。
作业
- leetcode上关于栈的题目大家可以先做20,155,232,844,224,682,496
- 我就不贴过来了,在我的LeetCode仓库里有
09讲队列:队列在线程池等有限资源池中的应用
- 这一节没啥新东西,完全是数据结构课上的知识,咱就总结总结过去
如何理解“队列”?
- 队列跟栈非常相似,支持的操作也很有限,最基本的操作也是两个:入队enqueue(),放一个数据到队列尾部;出队dequeue(),从队列头部取一个元素。
- 队列的应用也非常广泛,特别是一些具有某些额外特性的队列,比如循环队列、阻塞队列、并发队列。它们在很多偏底层系统、框架、中间件的开发中,起着关键性的作用。比如高性能队列Disruptor、Linux环形缓存,都用到了循环并发队列;Java concurrent并发包利用ArrayBlockingQueue来实现公平锁等。
顺序队列和链式队列
- 用数组实现的队列叫作顺序队列,用链表实现的队列叫作链式队列。
顺序队列
// 顺序队列的实现
// 用数组实现的队列
public class ArrayQueue {
// 数组:items,数组大小:n
private String[] items;
private int n = 0;
// head表示队头下标,tail表示队尾下标
private int head = 0;
private int tail = 0;
// 申请一个大小为capacity的数组
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
items = new String[capacity];
n = capacity;
}
// 入队
public boolean enqueue(String item) {
// 如果tail == n 表示队列已经满了
if (tail == n) return false;
items[tail] = item;
++tail;
return true;
}
// 出队
public String dequeue() {
// 如果head == tail 表示队列为空
if (head == tail) return null;
// 为了让其他语言的同学看的更加明确,把--操作放到单独一行来写了
String ret = items[head];
++head;
return ret;
}
}
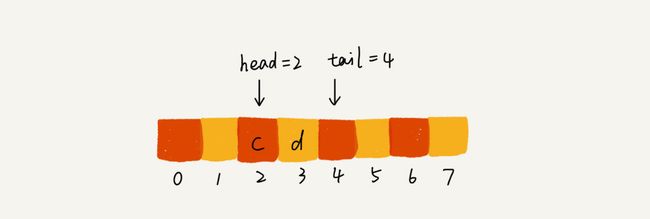
- 当a、b、c、d依次入队之后,队列中的head指针指向下标为0的位置,tail指针指向下标为4的位置。
- 当我们调用两次出队操作之后,队列中head指针指向下标为2的位置,tail指针仍然指向下标为4的位置。
- 解决顺序队列浪费空间的缺点:数据搬移【改写入队函数】
// 入队操作,将item放入队尾
public boolean enqueue(String item) {
// tail == n表示队列末尾没有空间了
if (tail == n) {
// tail ==n && head==0,表示整个队列都占满了
if (head == 0) return false;
// 数据搬移
for (int i = head; i < tail; ++i) {
items[i-head] = items[i];
}
// 搬移完之后重新更新head和tail
tail -= head;
head = 0;
}
items[tail] = item;
++tail;
return true;
}
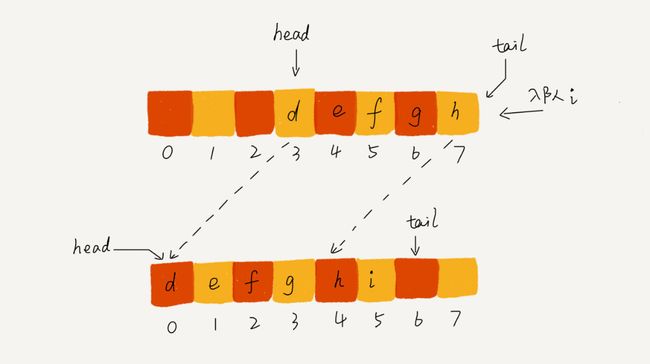
- 从代码中我们看到,当队列的tail指针移动到数组的最右边后,如果有新的数据入队,我们可以将head到tail之间的数据,整体搬移到数组中0到tail-head的位置。
- 这里入队的时间复杂度,使用均摊计算法,肯定还是O(1)
链式队列
循环队列
- 循环队列,顾名思义,它长得像一个环。原本数组是有头有尾的,是一条直线。现在我们把首尾相连,扳成了一个环。我画了一张图,你可以直观地感受一下。
- 队列空的条件还是head = tail,满的条件是**(tail+1)%n=head**
- tail=3,head=4,n=8,所以总结一下规律就是:(3+1)%8=4
- 此时tail不存放数据,浪费一个空间
public class CircularQueue {
// 数组:items,数组大小:n
private String[] items;
private int n = 0;
// head表示队头下标,tail表示队尾下标
private int head = 0;
private int tail = 0;
// 申请一个大小为capacity的数组
public CircularQueue(int capacity) {
items = new String[capacity];
n = capacity;
}
// 入队
public boolean enqueue(String item) {
// 队列满了
if ((tail + 1) % n == head) return false;
items[tail] = item;
tail = (tail + 1) % n;
return true;
}
// 出队
public String dequeue() {
// 如果head == tail 表示队列为空
if (head == tail) return null;
String ret = items[head];
head = (head + 1) % n;
return ret;
}
}
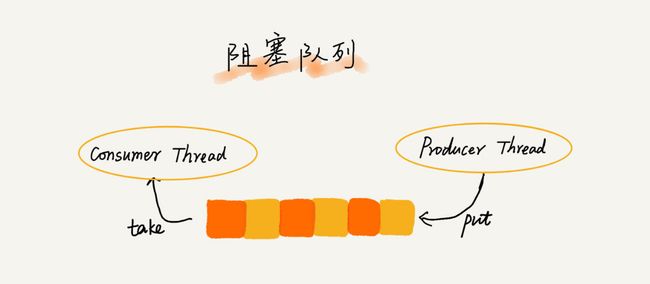
阻塞队列和并发队列
- 阻塞队列其实就是在队列基础上增加了阻塞操作。简单来说,就是在队列为空的时候,从队头取数据会被阻塞。因为此时还没有数据可取,直到队列中有了数据才能返回;如果队列已经满了,那么插入数据的操作就会被阻塞,直到队列中有空闲位置后再插入数据,然后再返回。
- 这就涉及到“生产者-消费者模型”【在实际的软件开发过程中,经常会碰到如下场景:某个模块负责产生数据,这些数据由另一个模块来负责处理(此处的模块是广义的,可以是类、函数、线程、进程等)。产生数据的模块,就形象地称为生产者;而处理数据的模块,就称为消费者】
- 这种基于阻塞队列实现的“生产者-消费者模型”,可以有效地协调生产和消费的速度。当“生产者”生产数据的速度过快,“消费者”来不及消费时,存储数据的队列很快就会满了。这个时候,生产者就阻塞等待,直到“消费者”消费了数据,“生产者”才会被唤醒继续“生产”。
- 线程安全的队列我们叫作并发队列。最简单直接的实现方式是直接在enqueue()、dequeue()方法上加锁,但是锁粒度大并发度会比较低,同一时刻仅允许一个存或者取操作。实际上,基于数组的循环队列,利用CAS原子操作,可以实现非常高效的并发队列。这也是循环队列比链式队列应用更加广泛的原因。
线程池没有空闲线程时,新的任务请求线程资源时,线程池该如何处理?各种处理策略又是如何实现的呢?
- 我们一般有两种处理策略。第一种是非阻塞的处理方式,直接拒绝任务请求;另一种是阻塞的处理方式,将请求排队,等到有空闲线程时,取出排队的请求继续处理。
- 基于链表的实现方式,可以实现一个支持无限排队的无界队列(unbounded queue),但是可能会导致过多的请求排队等待,请求处理的响应时间过长。所以,针对响应时间比较敏感的系统,基于链表实现的无限排队的线程池是不合适的。
- 而基于数组实现的有界队列(bounded queue),队列的大小有限,所以线程池中排队的请求超过队列大小时,接下来的请求就会被拒绝,这种方式对响应时间敏感的系统来说,就相对更加合理。不过,设置一个合理的队列大小,也是非常有讲究的。队列太大导致等待的请求太多,队列太小会导致无法充分利用系统资源、发挥最大性能。
- 实际上,对于大部分资源有限的场景,当没有空闲资源时,基本上都可以通过“队列”这种数据结构来实现请求排队。
课后题
除了线程池这种池结构会用到队列排队请求,你还知道有哪些类似的池结构或者场景中会用到队列的排队请求呢?
- iOS:GCD就是通过队列的应用进行的线程管理
- 分布式应用中的消息队列,也是一种队列结构
今天讲到并发队列,关于如何实现无锁并发队列,网上有非常多的讨论。对这个问题,你怎么看呢?
- 考虑使用CAS实现无锁队列,则在入队前,获取tail位置,入队时比较tail是否发生变化,如果否,则允许入队,反之,本次入队失败。出队则是获取head位置,进行cas。
作业:循环队列【LeetCode 622. 设计循环队列】
- 我感觉我这代码没有任何问题呀,就是过不了
class MyCircularQueue {
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */
MyCircularQueue(int k) {
size = k;
head = 0;
tail = 0;
data.resize(k);
}
/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
bool enQueue(int value) {
if ((tail + 1) % size == head) {
return false;
}
data[tail] = value;
tail = (tail + 1) % size;
return true;
}
/** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
bool deQueue() {
if (head == tail) {
return false;
}
head = (head + 1) % size;
return true;
}
/** Get the front item from the queue. */
int Front() {
if (head == tail) {
return -1;
}
return data[head];
}
/** Get the last item from the queue. */
int Rear() {
if (head == tail) {
return -1;
}
return data[(tail - 1 + size) % size];
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */
bool isEmpty() {
if (head == tail) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */
bool isFull() {
if ((tail + 1) % size == head) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private:
vector data;
int size, head, tail;
};
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularQueue* obj = new MyCircularQueue(k);
* bool param_1 = obj->enQueue(value);
* bool param_2 = obj->deQueue();
* int param_3 = obj->Front();
* int param_4 = obj->Rear();
* bool param_5 = obj->isEmpty();
* bool param_6 = obj->isFull();
*/
10讲递归:如何用三行代码找到“最终推荐人”
如何理解“递归”?
- 去的过程要将递,来的过程叫归
- 关键在与找出递归推导式
递归需要满足的三个条件
- 一个问题的解可以分解为几个子问题的解
- 这个问题与分解之后的子问题,除了数据规模不同,求解思路完全一样
- 存在递归终止条件
- 这里我们用一个Leetcode上的简单递归题来总结下:
Leetcode 687. 最长同值路径
给定一个二叉树,找到最长的路径,这个路径中的每个节点具有相同值。 这条路径可以经过也可以不经过根节点。
注意:两个节点之间的路径长度由它们之间的边数表示。
示例 1:
输入:
5
/ \
4 5
/ \ \
1 1 5
输出:
2
示例 2:
输入:
1
/ \
4 5
/ \ \
4 4 5
输出:
2
注意: 给定的二叉树不超过10000个结点。 树的高度不超过1000。
分析:
- 一个问题的解可以分解为几个子问题的解
- 首先对于树形结构,我们肯定是从根结点往下遍历,对于每个结点,我们的长度本质是对其在左结点以及右结点路径和上在+1
- 当然还是很难懂,怪不得说递归是最难的了,虾米玩意
- 这个问题与分解之后的子问题,除了数据规模不同,求解思路完全一样
- 这个在第一点也说明的很清楚了
- 存在递归终止条件
- 这个很简单,对与树形结构,在碰到结点为NULL肯定终止了
- 好难,感觉自己做还是整不出来
- 只能理解下
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int ans;
int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode* root) {
ans = 0;
arrowLength(root);
return ans;
}
int arrowLength(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int left = arrowLength(node->left);
int right = arrowLength(node->right);
int arrowLeft = 0, arrowRight = 0;
if (node->left != NULL && node->left->val == node->val) {
arrowLeft += left + 1;
}
if (node->right != NULL && node->right->val == node->val) {
arrowRight += right + 1;
}
ans = max(ans, arrowLeft + arrowRight);
return max(arrowLeft, arrowRight);
}
};
递归心法
- 写递归代码的关键就是找到如何将大问题分解为小问题的规律,并且基于此写出递推公式,然后再推敲终止条件,最后将递推公式和终止条件翻译成代码
- 下面这一点我觉得说的很有道理,对于递归,关键在于不要纠结,想着吧所有代码铺开去思考整个过程,比如说对于上面这道题,我们在计算f(n)的时候,就假设n-1结果已经出来,直接用就完了,只思考一次的调用去写我们的递归代码,可能是个比较好的习惯
- 编写递归代码的关键是,只要遇到递归,我们就把它抽象成一个递推公式,不用想一层层的调用关系,不要试图用人脑去分解递归的每个步骤
警惕栈溢出
- 这一段在讲了函数调用栈之后应该已经很好理解了,其实就是说由于在递归时,我们时函数套函数,导致函数调用栈被占用很多内存,会出现溢出风险
- 这里通常做法是设置一下递归深度最大值
递归代码警惕重复计算
- 我们看到为了计算一个f(6),我们计算了好几次f(3),这就是重复计算
- 解决方法一般是使用一个哈希表来存储值,下次用到的时候直接查询使用就行
- 另外由于递归调用一次就会在内存栈中保存一次现场数据所以空间复杂度基本上不会是O(1)
迭代法与递归相互转化
- 基本上所有递归代码都可以转化,由于递归的本质上是使用栈来实现的,只是他的使用是依靠系统做的,我们无法感知到
- 所以可以使用迭代法,手动实现出入栈
开篇解答:如何找到“最终推荐人”?
- 给定一个用户ID,如何查找这个用户的“最终推荐人”?
long findRootReferrerId(long actorId) {
Long referrerId = select referrer_id from [table] where actor_id = actorId;
if (referrerId == null) return actorId;
return findRootReferrerId(referrerId);
}
- 上述代码的漏洞:
- 如果递归很深,可能会有堆栈溢出的问题
- 如果数据库里存在脏数据,我们还需要处理由此产生的无限递归问题。比如demo环境下数据库中,测试工程师为了方便测试,会人为地插入一些数据,就会出现脏数据。如果A的推荐人是B,B的推荐人是C,C的推荐人是A,这样就会发生死循环
课后题:我们平时调试代码喜欢使用IDE的单步跟踪功能,像规模比较大、递归层次很深的递归代码,几乎无法使用这种调试方式。对于递归代码,你有什么好的调试方法呢?
- 打印日志发现,递归值;结合条件断点进行调试