lua 协程 | 协程实现消息机制(事件队列轮询处理机制)
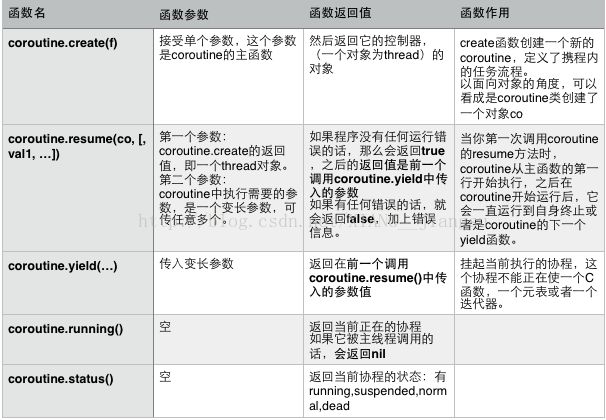
1 协程基础知识
Lua 协同程序(coroutine)与线程比较类似:拥有独立的堆栈,独立的局部变量,独立的指令指针,同时又与其它协同程序共享全局变量和其它大部分东西。
协程有三种状态:挂起,运行,停止。创建后是挂起状态,即不自动运行。status函数可以查看当前状态。协程可通过yield函数将一段正在运行的代码挂起。
lua的resume-yield可以互相交换数据。如果没有对应的yield,传递给resume的额外参数将作为参数传递给协程主函数:
co = coroutine.create(function (a, b, c)
print("co", a, b, c)
end)
coroutine.resume(co, 1, 2, 3)
运行结果: co 1 2 3co = coroutine.create(function (a, b)
coroutine.yield(a+b, a-b)
end)
print(coroutine.resume(co, 3, 8))
运行结果: true 11 5
co = coroutine.create (function ()
print("begin coroutine")
print("co", coroutine.yield())
end)
coroutine.resume(co) -- 遇到coroutine.yield()挂起
coroutine.resume(co, 4, 5) -- 完成第二个print过程
运行结果: begin coroutine
co 4 5
co = coroutine.create(function (a)
return 6, 7, coroutine.yield(a-1)
end)
print(coroutine.resume(co,5)) -- 输出true与coroutine.yield()运行参数
print(coroutine.resume(co,5)) -- 输出协程主函数返回值
运行结果: true 4
true 6 7 5下面用协同程序实现一个典型的生产者-消费者模式。
function receive(prod)
local status,value = coroutine.resume(prod)
return value
end
function send( x )
coroutine.yield(x) -- 挂起,返回当前协同程序 供resume调用
end
function produce() -- 生产者
return coroutine.create(function ()
while true do -- 该循环保证了生产者被无限驱动
local x = io.read()
send(x)
end
end)
end
function consume(prod) -- 消费者
while true do
local x = receive(prod) -- 消费者驱动生产者的执行
print(x)
end
end
function filter( prod ) -- 用过滤器处理生产者数据
return coroutine.create(function ()
while true do
local x = receive(prod) -- 驱动生产者生成数据
x = doSomeProcess(x)
send(x)
end
end)
end
consume(filter(produce()))我们尝试用协程来实现一些算法和应用级的效果。
1)用生产者-消费者模式实现迭代器,该迭代器能输出一个数组的全排列。
function permgen( a,n ) -- 生产者
if n <= 0 then
coroutine.yield(a)
else
for i=1,n do
a[i],a[n] = a[n],a[i]
permgen(a,n-1)
a[i],a[n] = a[n],a[i]
end
end
end
function perm( a ) -- 迭代器 消费者
return coroutine.wrap(function ()
permgen(a,#a)
end)
--[[
-- 与上面代码效果相同
local prod = coroutine.create(function ()
permgen(a,#a)
end)
return function ()
local code,rt = coroutine.resume(prod)
return rt
end
]]
end
local a = {1,2,3}
for v in perm(a) do
local st = ""
for i,v in ipairs(v) do
st = st .. v .. " "
end
print(st)
end2)用协程实现一个多文件下载分发器
有多个文件需要下载,如果采用顺序排队方式,那么大量时间将浪费在 请求下载-下载完成反馈之间的等待过程中。我们用协程解决这一效率问题:请求下载后,如果超时则yield挂起当前协程,并有分发器调用其他协程。
download = function (host,file)
local c = socket.connect(host,80)
c:send("GET " .. file .. "HTTP/1.0\r\n") -- 发送请求
while true do
local s,status = receive(c) -- 接收
if status == "closed" then
-- 当前协程的下载过程已完成
break
end
end
end
receive = function (connection)
local s,status = connection:receive()
if status == "timeout" then
coroutine.yield(connection)
end
return s,status
end
dispatch = function ()
while true do
if #loadLst <= 0 then
-- 所有下载器均完成 结束分发
break
end
for i,v in ipairs(loadLst) do
local status,res = coroutine.resume(v)
if not res then
table.remove(loadLst,i) -- 当前下载器完成
break
end
end
end
end2 协同实现消息机制(不同场景等待式消息处理)
游戏中,有时在处理消息时,希望一条一条消息独立处理(独立堆栈),且希望每条消息在不同场景内等待式逐步进行(如一个场景消息处理完,挂起,经过100ms再进行当前消息下一场景的处理),协程能够完成这一过程。下面提供一种实现方案。
local msgLst = {} -- 存储
local curMsgCor = nil -- 当前消息对应的协程
function insertPerMsg( msg )
table.insert(msgLst,msg)
scheduleScript(processMsg) -- -- 定时器中循环执行函数
end
function processMsg( )
if #msgLst <= 0 then
unScheduleScript(processPerMsgCor)
else
if not curMsgCor then
local curMsg = table.remove(msgLst,1)
curMsgCor = coroutine.create(function () processPerMsgCor(curMsg) end) -- 创建coroutine
end
if curMsgCor then
local state,errMsg = coroutine.resume(curMsgCor) -- 重启coroutine
local status = coroutine.status(curMsgCor) -- 查看coroutine状态: dead,suspend,running
-- 启动失败
if not state then
curMsgCor = nil
local debugInfo = debug.traceback(curMsgCor)
print(debugInfo)
end
-- coroutine消亡
if status == "dead" then
curMsgCor = nil
end
end
end
end
function processPerMsgCor( curMsg )
processForTalk()
coroutine.yield() -- 挂起coroutine
processForSpecialRoom()
coroutine.yield()
processForOtherWay()
end3 事件队列轮询处理机制
游戏场景经常需要一次执行一系列事件,每个事件的完成均需要一定时间。如需要在奔跑至指定区域后释放技能或攻击某一对象。可通过事件队列方式完成这一过程。
local Event = class("Event")
Event.State = {
None = 1,
Doing = 2,
Done = 3,
}
function Event:ctor()
self.state = self.State.None
end
function Event:isNotStart()
return self.state == self.State.None
end
function Event:setDoing()
self.state = self.State.Doing
end
function Event:setFunc( func,... )
self.func = func
self.funcParams = {...}
end
function Event:doFunc()
self.func(self,unpack(self.funcParams))
end
-- Func完成后调用
function Event:setDone()
self.state = self.State.Done
end
function Event:isDone()
return self.state == self.State.Done
end
function Test:ctor( )
-- 创建事件队列
self.eventQueue = Queue:create()
-- 定时器轮询时间事件队列
local schedule = cc.Director:getInstance():getScheduler()
self.scheduleId = schedule:scheduleScriptFunc(handler(self,self.runEventQueue),1,false)
-- 添加几个事件
local deltaTime = cc.DelayTime:create(5)
local event = Event:create()
-- func中的参数event在执行doFunc时传入
local func = function (event)
local f1 = function()
-- 5秒后输出
print("print this after 5 sec")
event:setDone()
end
self:runAction(cc.Sequence:create(deltaTime,cc.CallFunc:create(f1)))
end
event:setFunc(func)
self:addEvent(event)
event = Event:create()
func = function (event)
local f1 = function()
-- 10秒后输出
print("print this after 10 sec")
event:setDone()
end
self:runAction(cc.Sequence:create(deltaTime,cc.CallFunc:create(f1)))
end
event:setFunc(func)
self:addEvent(event)
event = Event:create()
func = function (event)
local f1 = function()
-- 15秒后输出
print("print this after 15 sec")
event:setDone()
end
self:runAction(cc.Sequence:create(deltaTime,cc.CallFunc:create(f1)))
end
event:setFunc(func)
self:addEvent(event)
end
function Test:addEvent(event)
self.eventQueue:push_back(event)
end
function Test:runEventQueue()
if self.eventQueue:size() <= 0 then
return
end
-- 两种写法
--[[ 第一种写法:完成当前事件后等待计时器执行下一个事件,事件之间存在时间间隙
local curEvent = self.eventQueue:front()
if curEvent and not curEvent:isDoing() then
if curEvent:isNotStart() then
-- 执行事件
curEvent:setDoing()
curEvent:doFunc()
elseif curEvent:isDone() then
-- 事件已完成,删除并转至下个事件
self.eventQueue:pop_front()
curEvent = nil
if self.eventQueue:size() > 0 then
curEvent = self.eventQueue:front()
end
end
end
]]
-- 第二种写法:当前时间完成即刻执行下一时间
while curEvent and not curEvent:isDoing() do
if curEvent:isNotStart() then
-- 执行事件
curEvent:setDoing()
curEvent:doFunc()
elseif curEvent:isDone() then
-- 事件已完成,删除并转至下个事件
self.eventQueue:pop_front()
curEvent = nil
if self.eventQueue:size() > 0 then
curEvent = self.eventQueue:front()
end
end
end
end