手指在指纹传感器上摸一下就能解锁,Keyguard是怎么做到的呢?
下面我们就跟着源码,解析这整个过程。
何时开始监听指纹传感器?
先来看下IKeyguardService这个binder接口有哪些回调吧
// 当另一个窗口使用FLAG_SHOW_ON_LOCK_SCREEN解除Keyguard时PhoneWindowManager调用
public void setOccluded(boolean isOccluded, boolean animate) throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 添加锁屏状态回调
public void addStateMonitorCallback(com.android.internal.policy.IKeyguardStateCallback callback) throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 核验解锁(用于快捷启动)
public void verifyUnlock(com.android.internal.policy.IKeyguardExitCallback callback) throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 解除锁屏
public void dismiss(com.android.internal.policy.IKeyguardDismissCallback callback) throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 屏保开始(Intent.ACTION_DREAMING_STARTED)
public void onDreamingStarted() throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 屏保结束(Intent.ACTION_DREAMING_STOPPED)
public void onDreamingStopped() throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 设备开始休眠 reason:OFF_BECAUSE_OF_USER/OFF_BECAUSE_OF_ADMIN/OFF_BECAUSE_OF_TIMEOUT
public void onStartedGoingToSleep(int reason) throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 休眠完成
public void onFinishedGoingToSleep(int reason, boolean cameraGestureTriggered) throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 设备开始唤醒
public void onStartedWakingUp() throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 唤醒完成
public void onFinishedWakingUp() throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 正在亮屏
public void onScreenTurningOn(com.android.internal.policy.IKeyguardDrawnCallback callback) throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 已经亮屏完成
public void onScreenTurnedOn() throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 正在灭屏
public void onScreenTurningOff() throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 灭屏完成
public void onScreenTurnedOff() throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 外部应用取消Keyguard接口
public void setKeyguardEnabled(boolean enabled) throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 开机系统准备完成回调
public void onSystemReady() throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 延时锁屏 (用于自动休眠)
public void doKeyguardTimeout(android.os.Bundle options) throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 切换用户中
public void setSwitchingUser(boolean switching) throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 设置当前用户
public void setCurrentUser(int userId) throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 系统启动完成回调
public void onBootCompleted() throws android.os.RemoteException;
// Keyguard后面的activity已经绘制完成,可以开始移除壁纸和Keyguard flag
public void startKeyguardExitAnimation(long startTime, long fadeoutDuration) throws android.os.RemoteException;
// 通知Keyguard对power键做特殊处理,使设备不进行休眠或唤醒而是启动Home(目前是空实现)
public void onShortPowerPressedGoHome() throws android.os.RemoteException;
在这么多接口里,有
onStartedGoingToSleep/
onFinishedGoingToSleep/
onScreenTurningOff/
onScreenTurnedOff
这四个接口是在power键按下后触发,其中onStartedGoingToSleep最先被触发,他们的
调用顺序我会在后文里讲解。
而我们的指纹传感器监听,就是在onStartedGoingToSleep时开始的。
代码逻辑由在KeyguardService中由中间类KeyguardMediator调用到KeyguardUpdateMonitor
android/frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/keyguard/KeyguardUpdateMonitor.java
protected void handleStartedGoingToSleep(int arg1) {
...
updateFingerprintListeningState();
}
private void updateFingerprintListeningState() {
// If this message exists, we should not authenticate again until this message is
// consumed by the handler
if (mHandler.hasMessages(MSG_FINGERPRINT_AUTHENTICATION_CONTINUE)) {
return;
}
mHandler.removeCallbacks(mRetryFingerprintAuthentication);
boolean shouldListenForFingerprint = shouldListenForFingerprint();
if (mFingerprintRunningState == FINGERPRINT_STATE_RUNNING && !shouldListenForFingerprint) {
stopListeningForFingerprint();
} else if (mFingerprintRunningState != FINGERPRINT_STATE_RUNNING
&& shouldListenForFingerprint) {
startListeningForFingerprint();
}
}
在同时判断mFingerprintRunningState和shouldListenForFingerprint后,
Keyguard在startListeningForFingerprint中真正使用FingerprintManager监听指纹传感器
指纹传感器的监听方法
private void startListeningForFingerprint() {
if (mFingerprintRunningState == FINGERPRINT_STATE_CANCELLING) {
setFingerprintRunningState(FINGERPRINT_STATE_CANCELLING_RESTARTING);
return;
}
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "startListeningForFingerprint()");
int userId = ActivityManager.getCurrentUser();
if (isUnlockWithFingerprintPossible(userId)) {
if (mFingerprintCancelSignal != null) {
mFingerprintCancelSignal.cancel();
}
mFingerprintCancelSignal = new CancellationSignal();
mFpm.authenticate(null, mFingerprintCancelSignal, 0, mAuthenticationCallback, null, userId);
setFingerprintRunningState(FINGERPRINT_STATE_RUNNING);
}
}
真正到了使用指纹识别功能的时候,你会发现其实很简单,只是调用 FingerprintManager 类的的方法authenticate()而已,然后系统会有相应的回调反馈给我们,该方法如下:
public void authenticate(CryptoObject crypto, CancellationSignal cancel, int flags, AuthenticationCallback callback, Handler handler, int userId)
该方法的几个参数解释如下:
- 第一个参数是一个加密对象。目前为null
- 第二个参数是一个 CancellationSignal 对象,该对象提供了取消操作的能力。创建该对象也很简单,使用 new CancellationSignal() 就可以了。
- 第三个参数是一个标志,默认为0。
- 第四个参数是 AuthenticationCallback 对象,它本身是 FingerprintManager 类里面的一个抽象类。该类提供了指纹识别的几个回调方法,包括指纹识别成功、失败等。需要我们重写。
- 最后一个 Handler,可以用于处理回调事件,可以传null。
- 用户id
下面只需要在mAuthenticationCallback继承AuthenticationCallback这个抽象方法,重写回调接口
private FingerprintManager.AuthenticationCallback mAuthenticationCallback
= new AuthenticationCallback() {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailed() {
handleFingerprintAuthFailed();
};
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSucceeded(AuthenticationResult result) {
Trace.beginSection("KeyguardUpdateMonitor#onAuthenticationSucceeded");
handleFingerprintAuthenticated(result.getUserId());
Trace.endSection();
}
@Override
// 指纹验证
public void onAuthenticationHelp(int helpMsgId, CharSequence helpString) {
handleFingerprintHelp(helpMsgId, helpString.toString());
}
@Override
// 指纹验证时回调
public void onAuthenticationError(int errMsgId, CharSequence errString) {
}
@Override
// 获取到指纹时回调
public void onAuthenticationAcquired(int acquireInfo) {
handleFingerprintAcquired(acquireInfo);
}
};
获取指纹后,Keyguard做了哪些事?
从AuthenticationCallback里可以看出,获取指纹回调首先发生在 onAuthenticationAcquired 中, 我们先看代码
private void handleFingerprintAcquired(int acquireInfo) {
if (acquireInfo != FingerprintManager.FINGERPRINT_ACQUIRED_GOOD) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < mCallbacks.size(); i++) {
KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback cb = mCallbacks.get(i).get();
if (cb != null) {
cb.onFingerprintAcquired();
}
}
}
首先用acquireInfo参数判断是否正确获取指纹,之后遍历KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback,进行回调。
重写onFingerprintAcquired方法的只有FingerprintUnlockController,FingerprintUnlockController就是
用于协调UI的所有指纹解锁操作的控制器。
@Override
public void onFingerprintAcquired() {
...
mWakeLock = mPowerManager.newWakeLock(
PowerManager.PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK, FINGERPRINT_WAKE_LOCK_NAME);
mWakeLock.acquire();
mHandler.postDelayed(mReleaseFingerprintWakeLockRunnable,
FINGERPRINT_WAKELOCK_TIMEOUT_MS);
}
...
}
onFingerprintAcquired的核心逻辑全部是和WakeLock相关的,
获取WakeLock,并发送一条延时消息,15秒后,释放WakeLock。
下一步就发生在,onFingerprintAuthenticated回调中了,实现onFingerprintAuthenticated接口的不止一处,但真正实现解锁的还是在FingerprintUnlockController中
@Override
public void onFingerprintAuthenticated(int userId) {
...
startWakeAndUnlock(calculateMode());
}
private int calculateMode() {
boolean unlockingAllowed = mUpdateMonitor.isUnlockingWithFingerprintAllowed();
boolean deviceDreaming = mUpdateMonitor.isDreaming();
if (!mUpdateMonitor.isDeviceInteractive()) {
if (!mStatusBarKeyguardViewManager.isShowing()) {
return MODE_ONLY_WAKE;
} else if (mDozeScrimController.isPulsing() && unlockingAllowed) {
return MODE_WAKE_AND_UNLOCK_PULSING;
} else if (unlockingAllowed || !mUnlockMethodCache.isMethodSecure()) {
return MODE_WAKE_AND_UNLOCK;
} else {
return MODE_SHOW_BOUNCER;
}
}
if (unlockingAllowed && deviceDreaming) {
return MODE_WAKE_AND_UNLOCK_FROM_DREAM;
}
if (mStatusBarKeyguardViewManager.isShowing()) {
if (mStatusBarKeyguardViewManager.isBouncerShowing() && unlockingAllowed) {
return MODE_DISMISS_BOUNCER;
} else if (unlockingAllowed) {
return MODE_UNLOCK;
} else if (!mStatusBarKeyguardViewManager.isBouncerShowing()) {
return MODE_SHOW_BOUNCER;
}
}
return MODE_NONE;
}
这段代码逻辑很清晰,就是根据锁屏的状态计算指纹解锁的模式
public void startWakeAndUnlock(int mode) {
...
boolean wasDeviceInteractive = mUpdateMonitor.isDeviceInteractive();
mMode = mode;
if (!wasDeviceInteractive) {
mPowerManager.wakeUp(SystemClock.uptimeMillis(), "android.policy:FINGERPRINT");
}
releaseFingerprintWakeLock();
switch (mMode) {
...
}
}
startWakeAndUnlock中的代码经过简化后,只剩三部分:
1.先判断设备唤醒状态,是用PowerManager的wakeUp接口点亮屏幕
2.然后释放在acquire阶段获取的WakeLock
3.最后在根据上面calculateMode得出的解锁模式,进行真正的解锁动作,这在之前的解锁流程中已经分析过,这里不再做分析。
这里面值得我们注意的是wakeUp接口, 下面我们稍微对该接口进行一点探究
PowerManager的wakeUp接口
我们知道上层应用要唤醒系统一般只能依靠两种方式:
1.在应用启动Activity时候设置相应的window的flags,通过WMS来唤醒系统;
即通过WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON
2.在应用申请wakelock锁时附带ACQUIRE_CAUSES_WAKEUP标志
PowerManager的wakeup接口属性是@hide的,对一般应用是不可见的,而我们的SystemUI就不存在调用问题。
SystemUI通过调用第三种方式:PowerManager的wakeup接口,来强制唤醒系统,如果该设备处于睡眠状态,调用该接口会立即唤醒系统,比如按Power键,来电,闹钟等场景都会调用该接口。唤醒系统需要android.Manifest.permission#DEVICE_POWER的权限,我们可以看到SystemUI的Manifest文件里已经添加了该权限。
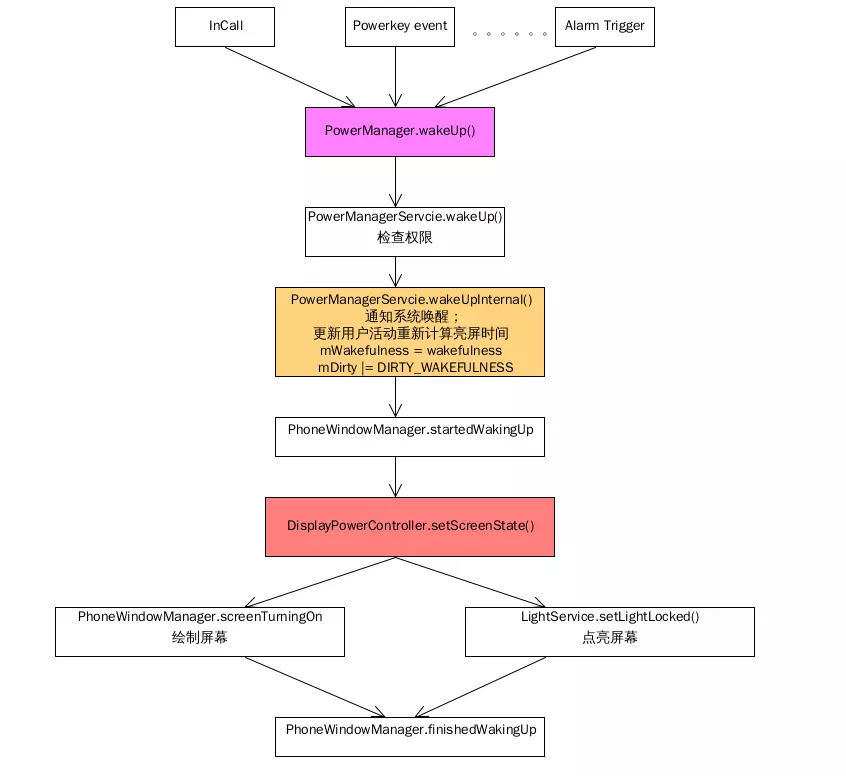
PowerManagerService唤醒的流程请看流程图:
PMS的wakeUp流程
从流程可以看到,亮屏流程可以和KeyguardService中的回调对应上了。
总结
其实指纹解锁的本质是在KeyguardService收到从PMS到WMS的调用中,在StartedGoingToSleep时就开始使用FingerprintManager的authticate开始监听感器,在FIngerManager验证成功时,使用PowerManagerService点亮屏幕,进行解锁流程。