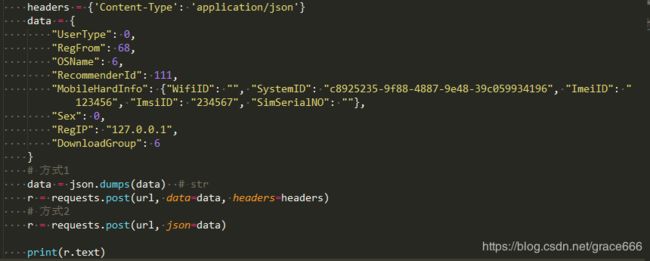
Python-Requests.post方法中,传参data与json的区别
Python3的requests.post()方法的源码:
def post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs):
r"""Sends a POST request.
:param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param data: (optional) Dictionary (will be form-encoded), bytes, or file-like object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param json: (optional) json data to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes.
:return: :class:`Response ` object
:rtype: requests.Response
"""
return request('post', url, data=data, json=json, **kwargs) 从上述源码中看出,参数中明确的参数是data和jsondata与json2个参数,类型既可以是str,也可以是dict
区别如下:
- 不管
json是str还是dict,如果不指定headers中的content-type,默认为application/json data参数为dict时,如果不指定content-type,默认为application/x-www-form-urlencoded,相当于普通form表单提交的形式,此时数据可以从request.POST里面获取,而request.body的内容则为a=1&b=2的这种形式,注意,即使指定content-type=application/json,request.body的值也是类似于a=1&b=2,所以并不能用json.loads(request.body.decode())得到想要的值data参数为str时,如果不指定content-type,默认为application/json- 用data参数提交数据时,
request.body的内容则为a=1&b=2的这种形式,用json参数提交数据时,request.body的内容则为'{"a": 1, "b": 2}'的这种形式
因此,拿注册接口来说明,有两种实现方式: