大家好,我系苍王。
以下是我这个系列的相关文章,有兴趣可以参考一下,可以给个喜欢或者关注我的文章。
[Android]如何做一个崩溃率少于千分之三噶应用app--章节列表
[Android]你不知道的Android进程化--进程信息
今天给大家分析一下OKhttp3拦截器的调度源码。
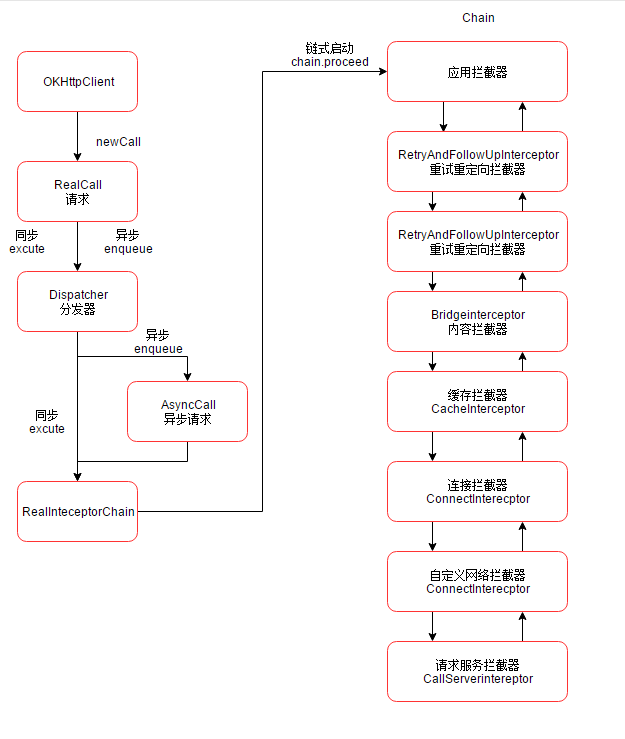
先来看看拦截器总流程图
下面是简单的一个okhttp3的get请求的例子。
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://www.baidu.com")
.build();
client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
Log.d("OkHttp", "Call Failed:" + e.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
Log.d("OkHttp", "Call succeeded:" + response.message());
}
});
(1)创建OkHttpClient的时候会初始化非常多的东西,分发器、协议、代理、拦截器、cookie、缓存、socket工厂等等一系列的东西
(2)Request是使用了建造者模式来设置一些请求参数,包括请求形式get/put、请求地址等
(3)OkHttpClient.newCall会调用RealCall.newRealCall
/**
* Prepares the {@code request} to be executed at some point in the future.
*/
@Override public Call newCall(Request request) {
return RealCall.newRealCall(this, request, false /* for web socket */);
}
(4)OKHttpClient里面dipatcher会调用enqueue
@Override public void enqueue(Callback responseCallback) {
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
captureCallStackTrace();
eventListener.callStart(this);
client.dispatcher().enqueue(new AsyncCall(responseCallback));
}
(5)Dispatcher会调用excute AsyncCall
synchronized void enqueue(AsyncCall call) {
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() < maxRequests && runningCallsForHost(call) < maxRequestsPerHost) {
runningAsyncCalls.add(call);
executorService().execute(call);
} else {
readyAsyncCalls.add(call);
}
}
(6)AsyncCall继承于Runnable,其主要调用在excute函数中
可以看到其主要是使用getResponseWithInterceptorChain()开始调用拦截链的
@Override protected void execute() {
boolean signalledCallback = false;
try {
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isCanceled()) {
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, new IOException("Canceled"));
} else {
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (signalledCallback) {
// Do not signal the callback twice!
Platform.get().log(INFO, "Callback failure for " + toLoggableString(), e);
} else {
eventListener.callFailed(RealCall.this, e);
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, e);
}
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
(7)拦截链包含多个不同的拦截器,构建一个ReaInterceptorChain,调用proceed执行链。
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor); //重试重定向拦截器
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar())); //内容桥接拦截
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache())); //缓存拦截器
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client)); //连接拦截器
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket)); //像服务器发送真正的访问
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, null, null, null, 0,
originalRequest, this, eventListener, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}
(8)这里会通过interceptor.intercept调用下一个调用链对象
public Response proceed(Request request, StreamAllocation streamAllocation, HttpCodec httpCodec,
RealConnection connection) throws IOException {
....
// Call the next interceptor in the chain.
RealInterceptorChain next = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, streamAllocation, httpCodec,
connection, index + 1, request, call, eventListener, connectTimeout, readTimeout,
writeTimeout);
Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.get(index);
Response response = interceptor.intercept(next);
....
return response;
}
(9)这里RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor拦截器,
重要功能在于
在网络请求失败后进行重试;
当服务器返回当前请求需要进行重定向时直接发起新的请求,并在条件允许情况下复用当前连接;
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Request request = chain.request();
RealInterceptorChain realChain = (RealInterceptorChain) chain;
Call call = realChain.call();
EventListener eventListener = realChain.eventListener();
//创建流分配
streamAllocation = new StreamAllocation(client.connectionPool(), createAddress(request.url()),
call, eventListener, callStackTrace);
int followUpCount = 0;
Response priorResponse = null;
while (true) {
if (canceled) {
streamAllocation.release();
throw new IOException("Canceled");
}
Response response;
boolean releaseConnection = true;
try {
response = realChain.proceed(request, streamAllocation, null, null); //获取下一个拦截器的响应
releaseConnection = false;
} catch (RouteException e) {
// The attempt to connect via a route failed. The request will not have been sent.
//通道失败,不会发送请求
if (!recover(e.getLastConnectException(), false, request)) {
throw e.getLastConnectException();
}
releaseConnection = false;
continue;
} catch (IOException e) {
// An attempt to communicate with a server failed. The request may have been sent.
boolean requestSendStarted = !(e instanceof ConnectionShutdownException);
if (!recover(e, requestSendStarted, request)) throw e;
releaseConnection = false;
continue;
} finally {
// We're throwing an unchecked exception. Release any resources.
if (releaseConnection) {
streamAllocation.streamFailed(null);
streamAllocation.release();
}
}
// Attach the prior response if it exists. Such responses never have a body.
if (priorResponse != null) {
response = response.newBuilder()
.priorResponse(priorResponse.newBuilder()
.body(null)
.build())
.build();
}
Request followUp = followUpRequest(response); //重定向和重试请求
if (followUp == null) {
if (!forWebSocket) {
streamAllocation.release();
}
return response;
}
closeQuietly(response.body());
if (++followUpCount > MAX_FOLLOW_UPS) {
streamAllocation.release();
throw new ProtocolException("Too many follow-up requests: " + followUpCount);
}
if (followUp.body() instanceof UnrepeatableRequestBody) {
streamAllocation.release();
throw new HttpRetryException("Cannot retry streamed HTTP body", response.code());
}
if (!sameConnection(response, followUp.url())) {
streamAllocation.release();
streamAllocation = new StreamAllocation(client.connectionPool(),
createAddress(followUp.url()), call, eventListener, callStackTrace);
} else if (streamAllocation.codec() != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Closing the body of " + response
+ " didn't close its backing stream. Bad interceptor?");
}
request = followUp;
priorResponse = response;
}
}
关键在于response = realChain.proceed(request, streamAllocation, null, null)调用下一个拦截器
(10)BridgeInterceptor主要作用
设置内容长度,内容编码
设置gzip压缩,并在接收到内容后进行解压。省去了应用层处理数据解压的麻烦
添加cookie
设置其他报头,如User-Agent,Host,Keep-alive等。其中Keep-Alive是实现多路复用的必要步骤
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Request userRequest = chain.request();
Request.Builder requestBuilder = userRequest.newBuilder();
RequestBody body = userRequest.body();
//构建报头Header内容
if (body != null) {
MediaType contentType = body.contentType();
if (contentType != null) {
requestBuilder.header("Content-Type", contentType.toString());
}
long contentLength = body.contentLength();
if (contentLength != -1) {
requestBuilder.header("Content-Length", Long.toString(contentLength));
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Transfer-Encoding");
} else {
requestBuilder.header("Transfer-Encoding", "chunked");
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Content-Length");
}
}
if (userRequest.header("Host") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("Host", hostHeader(userRequest.url(), false));
}
if (userRequest.header("Connection") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("Connection", "Keep-Alive");
}
// If we add an "Accept-Encoding: gzip" header field we're responsible for also decompressing
// the transfer stream.
boolean transparentGzip = false;
if (userRequest.header("Accept-Encoding") == null && userRequest.header("Range") == null) {
transparentGzip = true;
requestBuilder.header("Accept-Encoding", "gzip");
}
//构建Cookie内容
List cookies = cookieJar.loadForRequest(userRequest.url());
if (!cookies.isEmpty()) {
requestBuilder.header("Cookie", cookieHeader(cookies));
}
if (userRequest.header("User-Agent") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("User-Agent", Version.userAgent());
}
Response networkResponse = chain.proceed(requestBuilder.build()); //交托给下一个拦截器
HttpHeaders.receiveHeaders(cookieJar, userRequest.url(), networkResponse.headers());
Response.Builder responseBuilder = networkResponse.newBuilder()
.request(userRequest);
//gzip压缩内容
if (transparentGzip
&& "gzip".equalsIgnoreCase(networkResponse.header("Content-Encoding"))
&& HttpHeaders.hasBody(networkResponse)) {
GzipSource responseBody = new GzipSource(networkResponse.body().source());
Headers strippedHeaders = networkResponse.headers().newBuilder()
.removeAll("Content-Encoding")
.removeAll("Content-Length")
.build();
responseBuilder.headers(strippedHeaders);
String contentType = networkResponse.header("Content-Type");
responseBuilder.body(new RealResponseBody(contentType, -1L, Okio.buffer(responseBody)));
}
return responseBuilder.build();
}
(11)CacheInterceptor负责缓存管理
当网络请求有符合要求的Cache时直接返回Cache
当服务器返回内容有改变时更新当前cache
如果当前cache失效,删除。
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Response cacheCandidate = cache != null
? cache.get(chain.request())
: null;
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
CacheStrategy strategy = new CacheStrategy.Factory(now, chain.request(), cacheCandidate).get();
Request networkRequest = strategy.networkRequest;
Response cacheResponse = strategy.cacheResponse;
if (cache != null) {
cache.trackResponse(strategy);
}
if (cacheCandidate != null && cacheResponse == null) {
closeQuietly(cacheCandidate.body()); // The cache candidate wasn't applicable. Close it.
}
// If we're forbidden from using the network and the cache is insufficient, fail.
if (networkRequest == null && cacheResponse == null) {
return new Response.Builder()
.request(chain.request())
.protocol(Protocol.HTTP_1_1)
.code(504)
.message("Unsatisfiable Request (only-if-cached)")
.body(Util.EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.sentRequestAtMillis(-1L)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
}
// If we don't need the network, we're done.
if (networkRequest == null) {
return cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.build();
}
Response networkResponse = null;
try {
networkResponse = chain.proceed(networkRequest);
} finally {
// If we're crashing on I/O or otherwise, don't leak the cache body.
if (networkResponse == null && cacheCandidate != null) {
closeQuietly(cacheCandidate.body());
}
}
// If we have a cache response too, then we're doing a conditional get.
//返回缓存的内容
if (cacheResponse != null) {
if (networkResponse.code() == HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED) {
Response response = cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.headers(combine(cacheResponse.headers(), networkResponse.headers()))
.sentRequestAtMillis(networkResponse.sentRequestAtMillis())
.receivedResponseAtMillis(networkResponse.receivedResponseAtMillis())
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build();
networkResponse.body().close();
// Update the cache after combining headers but before stripping the
// Content-Encoding header (as performed by initContentStream()).
//如果Header的内容更改,就更新缓存
cache.trackConditionalCacheHit();
cache.update(cacheResponse, response);
return response;
} else {
closeQuietly(cacheResponse.body());
}
}
Response response = networkResponse.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build();
if (cache != null) {
if (HttpHeaders.hasBody(response) && CacheStrategy.isCacheable(response, networkRequest)) {
// Offer this request to the cache.
CacheRequest cacheRequest = cache.put(response);
return cacheWritingResponse(cacheRequest, response);
}
if (HttpMethod.invalidatesCache(networkRequest.method())) {
try {
cache.remove(networkRequest);
} catch (IOException ignored) {
// The cache cannot be written.
}
}
}
return response;
}
(12)ConnectInterceptor配置连接RealConnection
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
RealInterceptorChain realChain = (RealInterceptorChain) chain;
Request request = realChain.request();
StreamAllocation streamAllocation = realChain.streamAllocation();
// We need the network to satisfy this request. Possibly for validating a conditional GET.
boolean doExtensiveHealthChecks = !request.method().equals("GET");
HttpCodec httpCodec = streamAllocation.newStream(client, chain, doExtensiveHealthChecks);
RealConnection connection = streamAllocation.connection(); //找到合适的连接,返回连接池负责连接
return realChain.proceed(request, streamAllocation, httpCodec, connection);
}
(13)CallServerInterceptor调用连接服务器请求
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
RealInterceptorChain realChain = (RealInterceptorChain) chain;
HttpCodec httpCodec = realChain.httpStream();
StreamAllocation streamAllocation = realChain.streamAllocation();
RealConnection connection = (RealConnection) realChain.connection();
Request request = realChain.request();
long sentRequestMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
realChain.eventListener().requestHeadersStart(realChain.call()); //响应请求头开始的回调
httpCodec.writeRequestHeaders(request); //写入请求头到请求中
realChain.eventListener().requestHeadersEnd(realChain.call(), request); //响应请求头结束的回调
Response.Builder responseBuilder = null;
if (HttpMethod.permitsRequestBody(request.method()) && request.body() != null) {
// If there's a "Expect: 100-continue" header on the request, wait for a "HTTP/1.1 100
// Continue" response before transmitting the request body. If we don't get that, return
// what we did get (such as a 4xx response) without ever transmitting the request body.
if ("100-continue".equalsIgnoreCase(request.header("Expect"))) {
httpCodec.flushRequest();
realChain.eventListener().responseHeadersStart(realChain.call());
responseBuilder = httpCodec.readResponseHeaders(true);
}
if (responseBuilder == null) {
// Write the request body if the "Expect: 100-continue" expectation was met.
realChain.eventListener().requestBodyStart(realChain.call());
long contentLength = request.body().contentLength();
CountingSink requestBodyOut =
new CountingSink(httpCodec.createRequestBody(request, contentLength));
BufferedSink bufferedRequestBody = Okio.buffer(requestBodyOut); //构建请求数据流
request.body().writeTo(bufferedRequestBody); //请求写到数据流
bufferedRequestBody.close();
realChain.eventListener()
.requestBodyEnd(realChain.call(), requestBodyOut.successfulCount); //调用请求结束
} else if (!connection.isMultiplexed()) {
// If the "Expect: 100-continue" expectation wasn't met, prevent the HTTP/1 connection
// from being reused. Otherwise we're still obligated to transmit the request body to
// leave the connection in a consistent state.
streamAllocation.noNewStreams();
}
}
httpCodec.finishRequest();
if (responseBuilder == null) {
realChain.eventListener().responseHeadersStart(realChain.call()); //读取响应头
responseBuilder = httpCodec.readResponseHeaders(false);
}
Response response = responseBuilder //读取响应消息
.request(request)
.handshake(streamAllocation.connection().handshake())
.sentRequestAtMillis(sentRequestMillis)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
realChain.eventListener()
.responseHeadersEnd(realChain.call(), response); //调用响应头回调
int code = response.code();
if (forWebSocket && code == 101) {
// Connection is upgrading, but we need to ensure interceptors see a non-null response body.
response = response.newBuilder()
.body(Util.EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.build();
} else {
response = response.newBuilder()
.body(httpCodec.openResponseBody(response))
.build();
}
if ("close".equalsIgnoreCase(response.request().header("Connection"))
|| "close".equalsIgnoreCase(response.header("Connection"))) {
streamAllocation.noNewStreams();
}
if ((code == 204 || code == 205) && response.body().contentLength() > 0) {
throw new ProtocolException(
"HTTP " + code + " had non-zero Content-Length: " + response.body().contentLength());
}
return response;
}
(14)添加拦截器。okhttp3中拦截器自定义拦截类型有两种,一种是应用拦截器,一种是网络拦截器。两种拦截器都需要继承Interceptor。
Application Interceptors应用拦截器
*不需要担心中间过程的响应,如重定向和重试.
*总是只调用一次,即使HTTP响应是从缓存中获取.
*观察应用程序的初衷. 不关心OkHttp注入的头信息如: If-None-Match.
*允许短路而不调用 Chain.proceed(),即中止调用.
*允许重试,使 Chain.proceed()调用多次
通过addInterceptor函数添加
Network Interceptors网络拦截器
*能够对中间的响应进行操作比如重定向和重试。
*当发生网络短路时,不调用缓存的响应结果。
*监控数据,就像数据再网络上传输一样。
*访问承载请求的连接Connection。
通过addNetworkInterceptor函数添加
查看一下RealCall中的拦截器排序
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors()); //自定义的应用拦截器,是一开始添加的所以可以截断请求和一些初始化拦截
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors()); //自定义网络拦截器,在真正请求前调用,可以拦截改变一切默认的参数。
}
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket)); //真正请求的拦截器
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, null, null, null, 0,
originalRequest, this, eventListener, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}
拦截器的源码就分析到这里了。