ElasticSearch_入门
Docker安装ElasticSearch
- 下载ealastic search和kibana
docker pull elasticsearch:7.4.2
docker pull kibana:7.4.2
- 配置
mkdir -p /mydata/elasticsearch/config
mkdir -p /mydata/elasticsearch/data
echo "http.host: 0.0.0.0" >/mydata/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml
chmod -R 777 /mydata/elasticsearch/
- 启动Elastic search
docker run --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 \
-e "discovery.type=single-node" \
-e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms64m -Xmx512m" \
-v /mydata/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml \
-v /mydata/elasticsearch/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data \
-v /mydata/elasticsearch/plugins:/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins \
-d elasticsearch:7.4.2
- 设置开机启动elasticsearch
docker update elasticsearch --restart=always
- 启动kibana
docker run --name kibana -e ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS=http://192.168.31.2:9200 -p 5601:5601 -d kibana:7.4.2
- 设置开机启动kibana
docker update kibana --restart=always
- 查看elasticsearch版本信息:
http://192.168.31.2:9200/
{
"name" : "56414c08186c",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "VoAPfguwSwez2S5rIvJYgA",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.4.2",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "docker",
"build_hash" : "2f90bbf7b93631e52bafb59b3b049cb44ec25e96",
"build_date" : "2019-10-28T20:40:44.881551Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.2.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
初步检索
_cat
GET/_cat/nodes:查看所有节点GET/_cat/health:查看es健康状况GET/_cat/master:查看主节点GET/_cat/indicies:查看所有索引 ,等价于mysql数据库的show databases;
索引一个文档
保存一个数据,保存在哪个索引的哪个类型下,指定用那个唯一标识
PUT customer/external/1;在customer索引下的external类型下保存1号数据为
PUT customer/external/1
{
"name":"John Doe"
}
PUT和POST都可以
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "external",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1
}
“_index”: “customer” 表明该数据在哪个数据库下;
“_type”: “external” 表明该数据在哪个类型下;
“_id”: “1” 表明被保存数据的id;
“_version”: 1, 被保存数据的版本
“result”: “created” 这里是创建了一条数据,如果重新put一条数据,则该状态会变为updated,并且版本号也会发生变化。
下面选用POST方式:
添加数据的时候,不指定ID,会自动的生成id,并且类型是新增:

再次使用POST插入数据,仍然是新增的:
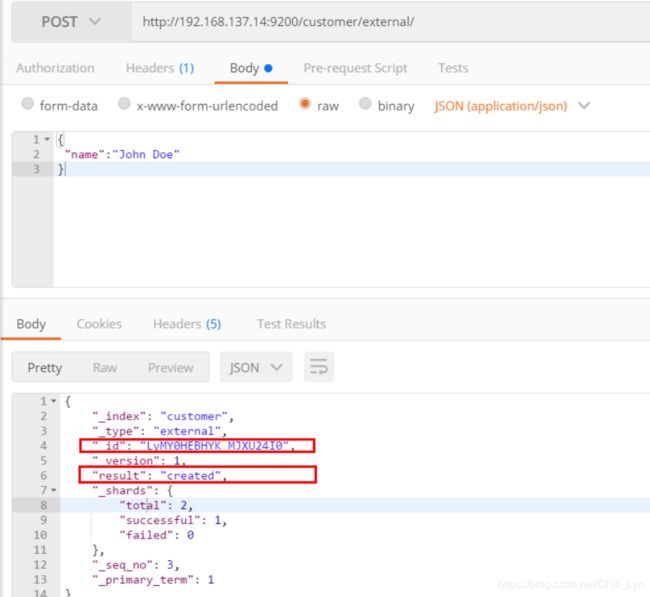
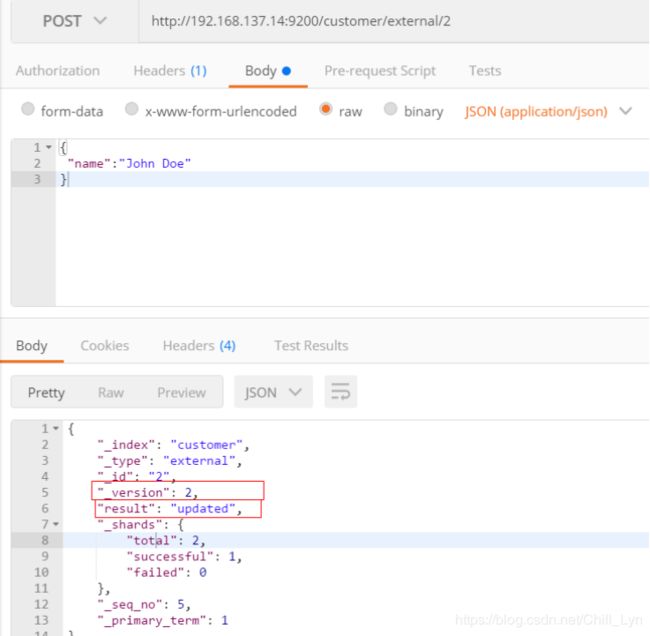
添加数据的时候,指定ID,会使用该id,并且类型是新增:

再次使用POST插入数据,类型为updated
查看文档
GET /customer/external/1
{
"_index": "customer",//在哪个索引
"_type": "external",//在哪个类型
"_id": "1",//记录id
"_version": 3,//版本号
"_seq_no": 6,//并发控制字段,每次更新都会+1,用来做乐观锁
"_primary_term": 1,//同上,主分片重新分配,如重启,就会变化
"found": true,
"_source": {
"name": "John Doe"
}
}
通过“if_seq_no=1&if_primary_term=1 ”,当序列号匹配的时候,才进行修改,否则不修改。
实例:将id=1的数据更新为name=1,然后再次更新为name=2,起始_seq_no=6,_primary_term=1
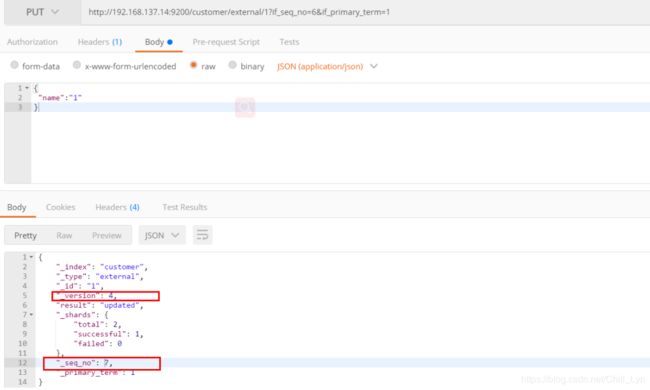
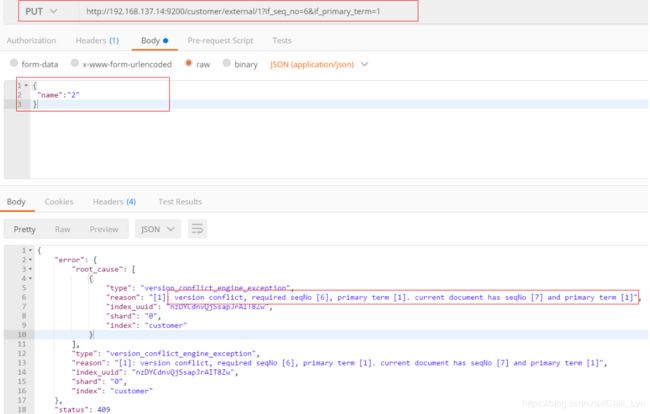
更新文档
POST customer/external/1/_update
{
"doc":{
"name":"John"
}
}
POST customer/external/1
{
"name":"John"
}
PUT customer/external/1
{
"name":"John"
}
第一种在更新的时候,会比较元数据,如果相同则不进行更新,版本号不变;后两种即使内容相同也会更新版本号。
删除索引或文档
DELETE customer/external/1
DELETE customer
批量操作-bulk
{action:{metadata}}\n
{request body }\n
{action:{metadata}}\n
{request body }\n
这里的批量操作,当发生某一条执行发生失败时,其他的数据仍然能够接着执行,也就是说彼此之间是独立的。
bulk api以此按顺序执行所有的action(动作)。如果一个单个的动作因任何原因失败,它将继续处理它后面剩余的动作。当bulk api返回时,它将提供每个动作的状态(与发送的顺序相同),所以您可以检查是否一个指定的动作是否失败了。
实例1: 执行多条数据
POST customer/external/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":"1"}}
{"name":"John Doe"}
{"index":{"_id":"2"}}
{"name":"John Doe"}
#! Deprecation: [types removal] Specifying types in bulk requests is deprecated.
{
"took" : 491,
"errors" : false,
"items" : [
{
"index" : {
"_index" : "customer",
"_type" : "external",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 201
}
},
{
"index" : {
"_index" : "customer",
"_type" : "external",
"_id" : "2",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 1,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 201
}
}
]
}
实例2:对于整个索引执行批量操作
POST /_bulk
{"delete":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog","_id":"123"}}
{"create":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog","_id":"123"}}
{"title":"my first blog post"}
{"index":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog"}}
{"title":"my second blog post"}
{"update":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog","_id":"123"}}
{"doc":{"title":"my updated blog post"}}
检索
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/getting-started-search.html
Query DSL
基本语法格式
QUERY_NAME:{
ARGUMENT:VALUE,
ARGUMENT:VALUE,...
}
{
QUERY_NAME:{
FIELD_NAME:{
ARGUMENT:VALUE,
ARGUMENT:VALUE,...
}
}
}
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 5,
"sort": [
{
"account_number": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
- match_all查询类型【代表查询所有的所有】,es中可以在query中组合非常多的查询类型完成复杂查询;
- 除了query参数之外,我们可也传递其他的参数以改变查询结果,如sort,size;
- from+size限定,完成分页功能;
- sort排序,多字段排序,会在前序字段相等时后续字段内部排序,否则以前序为准;
返回部分字段
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 5,
"sort": [
{
"account_number": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
],
// 返回部分字段
"_source": ["balance","firstname"]
}
match匹配查询
- 基本类型(非字符串),精确控制
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"account_number": "20"
}
}
}
- 字符串,全文检索,最终会按照评分进行排序,会对检索条件进行分词匹配。
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "kings"
}
}
}
match_phrase [短句匹配]
将需要匹配的值当成一整个单词(不分词)进行检索
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"address": "mill road"
}
}
}
match keyword匹配的条件就是要显示字段的全部值,要进行精确匹配
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address.keyword": "990 Mill Road"
}
}
}
multi_math多字段匹配
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "mill",
"fields": [
"state",
"address"
]
}
}
}
bool 复合查询
复合语句可以合并,任何其他查询语句,包括符合语句。这也就意味着,复合语句之间
可以互相嵌套,可以表达非常复杂的逻辑。
- must:必须达到must所列举的所有条件
GET bank/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"must":[
{"match":{"address":"mill"}},
{"match":{"gender":"M"}}
]
}
}
}
- must_not,必须不匹配must_not所列举的所有条件。
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"gender": "M"
}
},
{
"match": {
"address": "mill"
}
}
],
"must_not": [
{
"match": {
"age": "38"
}
}
]
}
}
- should,应该达到should列举的条件,如果到达会增加相关文档的评分,并不会改变查询的结果。如果query中只有should且只有一种匹配规则,那么should的条件就会被作为默认匹配条件二区改变查询结果.
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"gender": "M"
}
},
{
"match": {
"address": "mill"
}
}
],
"must_not": [
{
"match": {
"age": "18"
}
}
],
"should": [
{
"match": {
"lastname": "Wallace"
}
}
]
}
}
}
Filter 结果过滤
并不是所有的查询都需要产生分数,特别是哪些仅用于filtering过滤的文档。为了不计算分数,elasticsearch会自动检查场景并且优化查询的执行。
查询所有匹配address=mill的文档,然后再根据10000<=balance<=20000进行过滤查询结果
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"address": "mill"
}
}
],
"filter": {
"range": {
"balance": {
"gte": "10000",
"lte": "20000"
}
}
}
}
}
}
term
和match一样。匹配某个属性的值。全文检索字段用match,其他非text字段匹配用term。
Aggregation 执行聚合
聚合提供了从数据中分组和提取数据的能力。最简单的聚合方法大致等于SQL Group by和SQL聚合函数。在elasticsearch中,执行搜索返回this(命中结果),并且同时返回聚合结果,把以响应中的所有hits(命中结果)分隔开的能力。这是非常强大且有效的,你可以执行查询和多个聚合,并且在一次使用中得到各自的(任何一个的)返回结果,使用一次简洁和简化的API避免网络往返。
"aggs":{
"aggs_name这次聚合的名字,方便展示在结果集中":{
"AGG_TYPE聚合的类型(avg,term,terms)":{}
}
}
搜索address中包含mill的所有人的年龄分布以及平均年龄,但不显示这些人的详情
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "Mill"
}
},
"aggs": {
"ageAgg": {
"terms": {
"field": "age",
"size": 10
}
},
"ageAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "age"
}
},
"balanceAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
按照年龄聚合,并且求这些年龄段的这些人的平均薪资:
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"ageAgg": {
"terms": {
"field": "age",
"size": 100
},
"aggs": {
"ageBalanceAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
查出所有年龄分布,并且这些年龄段中M的平均薪资和F的平均薪资以及这个年龄段的总体平均薪资:
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"ageAgg": {
"terms": {
"field": "age",
"size": 100
},
"aggs": {
"genderAgg": {
"terms": {
"field": "gender.keyword"
},
"aggs": {
"balanceAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
},
"ageBalanceAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
Mapping
字段类型
映射
Maping是用来定义一个文档(document),以及它所包含的属性(field)是如何存储和索引的。比如:使用maping来定义:
- 哪些字符串属性应该被看做全文本属性(full text fields);
- 哪些属性包含数字,日期或地理位置;
- 文档中的所有属性是否都嫩被索引(all 配置);
- 日期的格式;
- 自定义映射规则来执行动态添加属性;
查看mapping信息
GET bank/_mapping
{
"bank" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"account_number" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"address" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"age" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"balance" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"city" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"email" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"employer" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"firstname" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"gender" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"lastname" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"state" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
新版本改变
ElasticSearch7-去掉type概念
-
关系型数据库中两个数据表示是独立的,即使他们里面有相同名称的列也不影响使用,但ES中不是这样的。elasticsearch是基于Lucene开发的搜索引擎,而ES中不同type下名称相同的filed最终在Lucene中的处理方式是一样的。
- 两个不同type下的两个user_name,在ES同一个索引下其实被认为是同一个filed,你必须在两个不同的type中定义相同的filed映射。否则,不同type中的相同字段名称就会在处理中出现冲突的情况,导致Lucene处理效率下降。
- 去掉type就是为了提高ES处理数据的效率。
-
Elasticsearch 7.x URL中的type参数为可选。比如,索引一个文档不再要求提供文档类型。
-
Elasticsearch 8.x 不再支持URL中的type参数。
-
解决:
将索引从多类型迁移到单类型,每种类型文档一个独立索引
将已存在的索引下的类型数据,全部迁移到指定位置即可。详见数据迁移
创建索引并指定映射
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"email": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
查看映射
GET /my_index
{
"my_index" : {
"aliases" : { },
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"age" : {
"type" : "integer"
},
"email" : {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"employee-id" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"index" : false
},
"name" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
},
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"creation_date" : "1588410780774",
"number_of_shards" : "1",
"number_of_replicas" : "1",
"uuid" : "ua0lXhtkQCOmn7Kh3iUu0w",
"version" : {
"created" : "7060299"
},
"provided_name" : "my_index"
}
}
}
}
添加新的字段映射
PUT /my_index/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"employee-id": {
"type": "keyword",
// 这里的 "index": false,表明新增的字段不能被检索,只是一个冗余字段。
"index": false
}
}
}
更新映射
对于已经存在的字段映射,我们不能更新。更新必须创建新的索引,进行数据迁移。
数据迁移
先创建new_twitter的正确映射。然后使用如下方式进行数据迁移。
POST reindex [固定写法]
{
"source":{
"index":"twitter"
},
"dest":{
"index":"new_twitters"
}
}
将旧索引的type下的数据进行迁移
POST reindex [固定写法]
{
"source":{
"index":"twitter",
"twitter":"twitter"
},
"dest":{
"index":"new_twitters"
}
}
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.6/docs-reindex.html
分词
一个tokenizer(分词器)接收一个字符流,将之分割为独立的tokens(词元,通常是独立的单词),然后输出tokens流。
例如:whitespace tokenizer遇到空白字符时分割文本。它会将文本“Quick brown fox!”分割为[Quick,brown,fox!]。
该tokenizer(分词器)还负责记录各个terms(词条)的顺序或position位置(用于phrase短语和word proximity词近邻查询),以及term(词条)所代表的原始word(单词)的start(起始)和end(结束)的character offsets(字符串偏移量)(用于高亮显示搜索的内容)。
elasticsearch提供了很多内置的分词器,可以用来构建custom analyzers(自定义分词器)。
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes jumped over the lazy dog's bone."
}
安装ik分词器
所有的语言分词,默认使用的都是“Standard Analyzer”,但是这些分词器针对于中文的分词,并不友好。为此需要安装中文的分词器。
注意:不能用默认elasticsearch-plugin install xxx.zip 进行自动安装
https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases/download 对应es版本安装
在前面安装的elasticsearch时,我们已经将elasticsearch容器的“/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins”目录,映射到宿主机的“ /mydata/elasticsearch/plugins”目录下,所以比较方便的做法就是下载“/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.4.2.zip”文件,然后解压到该文件夹下即可。安装完毕后,需要重启elasticsearch容器。
测试ik分词
GET my_index/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"text":"我是中国人"
}
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "我",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "是",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "中国人",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 2
}
]
}
GET my_index/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text":"我是中国人"
}
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "我",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "是",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "中国人",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "中国",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "国人",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 4
}
]
}
自定义词库
修改/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins/ik/config中的IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml
<properties>
<comment>IK Analyzer 扩展配置comment>
<entry key="ext_dict">entry>
<entry key="ext_stopwords">entry>
<entry key="remote_ext_dict">http://192.168.31.2/es/fenci.txtentry>
properties>
修改完成后,需要重启elasticsearch容器,否则修改不生效。
更新完成后,es只会对于新增的数据用更新分词。历史数据是不会重新分词的。如果想要历史数据重新分词,需要执行:
POST my_index/_update_by_query?conflicts=proceed
http://192.168.31.2/es/fenci.txt,这个是nginx上资源的访问路径
SpringBoot整合ElasticSearch
导入依赖
版本要和所按照的ELK版本匹配
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.clientgroupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-clientartifactId>
<version>7.4.2version>
dependency>
在spring-boot-dependencies中所依赖的ELK版本6.8.3,需要在项目中将它改为7.4.2
<properties>
...
<elasticsearch.version>7.4.2elasticsearch.version>
properties>
编写配置类
@Configuration
public class ElasticSearchConfig {
/**
* 单实例通用设置
*/
public static final RequestOptions COMMON_OPTIONS;
static {
RequestOptions.Builder builder = RequestOptions.DEFAULT.toBuilder();
// builder.addHeader("Authorization", "Bearer " + TOKEN);
// builder.setHttpAsyncResponseConsumerFactory(
// new HttpAsyncResponseConsumerFactory
// .HeapBufferedResponseConsumerFactory(30 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024));
COMMON_OPTIONS = builder.build();
}
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient esestClient() {
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(
RestClient.builder(
new HttpHost("192.168.31.2", 9200, "http")));
return client;
}
}
编写测试类
测试索引数据
@Test
public void indexData() throws IOException {
IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest ("users");
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("张三");
user.setAge(20);
user.setGender("男");
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user);
//设置要保存的内容
indexRequest.source(jsonString, XContentType.JSON);
//执行创建索引和保存数据
IndexResponse index = client.index(indexRequest, ElasticSearchConfig.COMMON_OPTIONS);
System.out.println(index);
}
测试检索数据
/**
* 复杂检索:在bank中搜索address中包含mill的所有人的年龄分布以及平均年龄,平均薪资
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void searchData() throws IOException {
//1. 创建检索请求
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest();
//1.1)指定索引
searchRequest.indices("bank");
//1.2)构造检索条件
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("address","Mill"));
//1.2.1)按照年龄分布进行聚合
TermsAggregationBuilder ageAgg=AggregationBuilders.terms("ageAgg").field("age").size(10);
sourceBuilder.aggregation(ageAgg);
//1.2.2)计算平均年龄
AvgAggregationBuilder ageAvg = AggregationBuilders.avg("ageAvg").field("age");
sourceBuilder.aggregation(ageAvg);
//1.2.3)计算平均薪资
AvgAggregationBuilder balanceAvg = AggregationBuilders.avg("balanceAvg").field("balance");
sourceBuilder.aggregation(balanceAvg);
System.out.println("检索条件:"+sourceBuilder);
searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);
//2. 执行检索
SearchResponse searchResponse = client.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("检索结果:"+searchResponse);
//3. 将检索结果封装为Bean
SearchHits hits = searchResponse.getHits();
SearchHit[] searchHits = hits.getHits();
for (SearchHit searchHit : searchHits) {
String sourceAsString = searchHit.getSourceAsString();
Account account = JSON.parseObject(sourceAsString, Account.class);
System.out.println(account);
}
//4. 获取聚合信息
Aggregations aggregations = searchResponse.getAggregations();
Terms ageAgg1 = aggregations.get("ageAgg");
for (Terms.Bucket bucket : ageAgg1.getBuckets()) {
String keyAsString = bucket.getKeyAsString();
System.out.println("年龄:"+keyAsString+" ==> "+bucket.getDocCount());
}
Avg ageAvg1 = aggregations.get("ageAvg");
System.out.println("平均年龄:"+ageAvg1.getValue());
Avg balanceAvg1 = aggregations.get("balanceAvg");
System.out.println("平均薪资:"+balanceAvg1.getValue());
}
@Data
@ToString
static class Accout {
private int account_number;
private int balance;
private String firstname;
private String lastname;
private int age;
private String gender;
private String address;
private String employer;
private String email;
private String city;
private String state;
}