java中的System.in、System.out、System.err
java中的标准输入输出以及错误有时候会让人迷惑,这里通过查看源码来对他们深入了解一下。
定义
- 标准输入 System.in
- 标准输出 System.out
- 标准错误 System.err
初始化分析
查看 java API或者源码可以看到定义(java.lang.System类):
public final static InputStream in = null;
public final static PrintStream out = null;
public final static PrintStream err = null;
继续查看源码我们看in、out、err是如何初始化的呢?
public final class System {
/* register the natives via the static initializer.
*
* VM will invoke the initializeSystemClass method to complete
* the initialization for this class separated from clinit.
* Note that to use properties set by the VM, see the constraints
* described in the initializeSystemClass method.
*/
private static native void registerNatives();
static {
registerNatives();
}
...
可以看到首先System这个类初始化的时候会注册native方法并执行initializeSystemClass 这个方法进行初始化,那么我们看initializeSystemClass这个方法内容:
/**
* Initialize the system class. Called after thread initialization.
*/
private static void initializeSystemClass() {
props = new Properties();
initProperties(props); // initialized by the VM
sun.misc.VM.saveAndRemoveProperties(props);
lineSeparator = props.getProperty("line.separator");
sun.misc.Version.init();
FileInputStream fdIn = new FileInputStream(FileDescriptor.in);
FileOutputStream fdOut = new FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor.out);
FileOutputStream fdErr = new FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor.err);
setIn0(new BufferedInputStream(fdIn));
setOut0(newPrintStream(fdOut, props.getProperty("sun.stdout.encoding")));
setErr0(newPrintStream(fdErr, props.getProperty("sun.stderr.encoding")));
...
这里我删掉了部分注释与后续代码,方便阅读,看最后三个方法setInt0、setOut0、setErr0。找到这三个方法:
private static native void setIn0(InputStream in);
private static native void setOut0(PrintStream out);
private static native void setErr0(PrintStream err);
发现又是native方法,这时候就不能继续查看native方法了,因为这种方法都是系统层面的C语言实现的,其实可以下载OpenJDK看一下源码,我这里下载了OpenJDK8源码
下载下来解压,然后打开System.c查看
vim OpenJDK8-master/jdk/src/share/native/java/lang/System.c
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_java_lang_System_setIn0(JNIEnv *env, jclass cla, jobject stream)
{
jfieldID fid =
(*env)->GetStaticFieldID(env,cla,"in","Ljava/io/InputStream;");
if (fid == 0)
return;
(*env)->SetStaticObjectField(env,cla,fid,stream);
}
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_java_lang_System_setOut0(JNIEnv *env, jclass cla, jobject stream)
{
jfieldID fid =
(*env)->GetStaticFieldID(env,cla,"out","Ljava/io/PrintStream;");
if (fid == 0)
return;
(*env)->SetStaticObjectField(env,cla,fid,stream);
}
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_java_lang_System_setErr0(JNIEnv *env, jclass cla, jobject stream)
{
jfieldID fid =
(*env)->GetStaticFieldID(env,cla,"err","Ljava/io/PrintStream;");
if (fid == 0)
return;
(*env)->SetStaticObjectField(env,cla,fid,stream);
}
可以看到C代码对in、out和err初始化的过程。
使用
System.in
对于System.in是很少使用的,使用最多的估计就是刚开始入门学习java的时候的经典echo程序:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNext()) {
System.out.println("echo:"+sc.nextLine());
}
}
System.out与System.err
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("out");
System.err.println("err");
}
输出结果:

这里out是黑色,二err为红色。表面上看就是这点区别。
不过继续看下面的程序:
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 0; i<100 ;i++) {
System.out.println(i);
System.err.println(i);
}
}
查看输出结果:
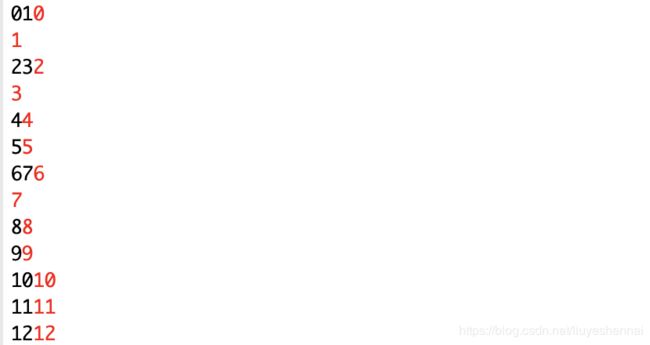
按理来说,输出的结果都应该是成对出现,可是为何最终输出是乱的呢?
这里实际上就不是java层面的问题了。因为几乎对于所有操作系统都有标准输入、标准输出、标准错误三个概念以及实现,也几乎都是C语言实现的,C语言的标准输入输出是分缓冲和无缓冲的,一般地,标准输入stdin和标准输出stdout为行缓冲,标准错误输出stderr无缓冲。
java中的标准输出以及标准错误,都是直接用native方法调用系统的标准输出以及标准错误,所以java中的System.out是行缓冲,System.err是无缓冲。正因为有缓冲区的存在,在同时使用System.out和System.err的时候,err会在out还未达到缓冲界限提前输出的情况。导致打印结果是乱的。
类似的还有异常捕获的时候,查看Throwable源码
public void printStackTrace() {
printStackTrace(System.err);
}
可以看到默认的printStackTrace()方法传入的是System.err。所以如果同时使用System.in与printStackTrace()也可能出现乱序问题,当然实际开发中只有写程序测试的时候才会出现这种情况,这种情况对开发也没用影响,只是看到现象不用奇怪即可。