Qt5开发学习之网络与通信(十二)
在应用程序开发中网络编程非常重要,目前互联网通行的TCP/IP协议,自上而下分为四层:应用层、传输层、网络层和网络接口层。实际编写网络应用程序时只使用到传输层和应用层,所用到的协议主要为UDP、TCP、HTTP和FTP。
虽然目前主流的操作系统都提供了统一的套接字抽象编程接口,用于编写不同层次的网络程序,但是这种方式比较繁琐,甚至有时需要应用底层操作系统相关数据结构,Qt提供了一个网络模块QtNetwork完美解决了问题。
获取本机网络信息
在网络应用中,经常需要获得本机的主机名、IP地址和硬件地址等信息。运用QHostInfo、QNetworkInterface、QNetworkAddressEntry可获得本机信息。
实例使用网络模块获取主机名和IP地址:
#include
#include "NetworkInfo.h"
NetworkInfo::NetworkInfo(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
{
this->resize(500, 500);
hostLabel = new QLabel(tr("HostName"));
hostLineEdit = new QLineEdit;
ipLabel = new QLabel(tr("ipAdress"));
ipLineEdit = new QLineEdit;
detailBtn = new QPushButton(tr("Detail"));
mainLayout = new QGridLayout(this);
mainLayout->addWidget(hostLabel, 0, 0);
mainLayout->addWidget(hostLineEdit, 0, 1);
mainLayout->addWidget(ipLabel, 1, 0);
mainLayout->addWidget(ipLineEdit, 1, 1);
mainLayout->addWidget(detailBtn, 2, 0, 1, 2);
getHostInformation();
connect(detailBtn, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &NetworkInfo::slotDetail);
}
NetworkInfo::~NetworkInfo()
{
}
void NetworkInfo::getHostInformation()
{
// 获得主机名
QString localHostName = QHostInfo::localHostName();
hostLineEdit->setText(localHostName);
// 根据主机名获得相关主机信息
QHostInfo hostInfo = QHostInfo::fromName(localHostName);
// 获得主机IP地址列表
QList listAddress = hostInfo.addresses();
if (!listAddress.isEmpty())
{
ipLineEdit->setText(listAddress.first().toString());
}
}
void NetworkInfo::slotDetail()
{
QString detail = "";
// 主机IP地址和网络接口列表
QList list = QNetworkInterface::allInterfaces();
for (int i = 0; i < list.count(); ++i)
{
QNetworkInterface interface = list.at(i);
// 获得网络接口名称
detail = detail + tr("设备:") + interface.name() + "\n";
// 获得硬件名称
detail = detail + tr("硬件地址:") + interface.hardwareAddress() + "\n";
QList entryList = interface.addressEntries();
for (int j = 0; j < entryList.count(); ++j)
{
QNetworkAddressEntry entry = entryList.at(j);
// 没个接口包含多个IP地址
detail = detail + "\t" + tr("IP地址:") + entry.ip().toString() + "\n";
detail = detail + "\t" + tr("子网掩码:") + entry.netmask().toString() + "\n";
detail = detail + "\t" + tr("广播地址:") + entry.broadcast().toString() + "\n";
}
}
QMessageBox::information(this, tr("Detail"), detail);
} 基于UDP的网络广播程序
用户数据报协议(User Data Protocol,UDP)是一种简单轻量级、不可靠、面向数据报、无连接的传输层协议,可以应用在可靠性不是十分高的场合,如短消息和广播信息等。
- 适合应用的场景有:
-
1、网络数据大多为短消息;
2、拥有大量客户端;
3、对数据安全性无特殊要求;
4、网络负担非常重,但对相应速度要求高。
UDP协议的工作原理:UDP客户端向UDP服务器发送一定长度的请求报文,报文大小的限制与各系统的协议实现相关,但不能超过其下层IP协议规定的64K;UDP服务器同样以报文形式做出响应。如果服务器未收到此请求,客户端不会重发,因此报文的传输是不可靠的。例如-QQ就是用UDP协议发送消息的, 因此有时会出现收不到消息的情况。
UDP的客户端与服务器是不建立连接,直接调用发送和接收函数进行数据通信的,Qt通过QUdpSocket类实现UDP协议的编程。
首先模拟UDP服务器编程:
#include #include "UDPServer.h"
#include 接下来是接收服务器发送数据的客户端:
#include #include "UDPClient.h"
#include 完成之后,在服务端的输入框内输入数据点击start。客户端就会自动将接收到的数据显示出来:
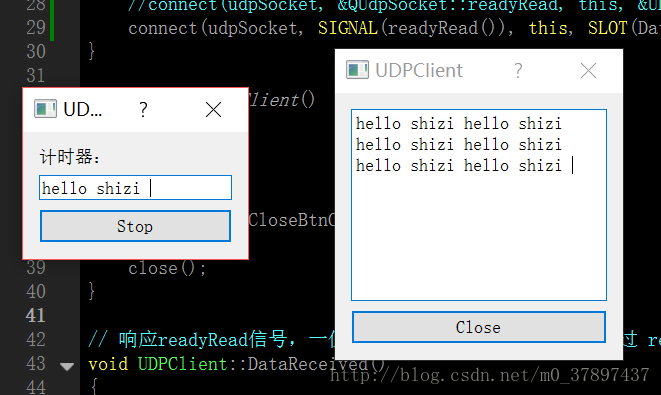
基于TCP的网络聊天室程序
传输控制协议(Transmission Control Protocol ,TCP)是一种可靠地、面向连接的、面向数据流的传输协议,许多高层应用协议(HTTP、FTP)都是以它为基础的,TCP协议非常适合数据的连续传输。
Qt中使用QTcpSocket和QTcpServer类实现TCP编程。
首先创建TCP服务端:
第一步,编写服务器的处理客户端的逻辑
#include 第二步,新建一个Server类,处理服务端逻辑
#include tcpClientList;
signals:
void updateServer(QString, int);
public slots:
void updateClients(QString, int);
void slotDisconnected(int);
protected:
void incomingConnection(int socketDescriptor);
};
#include "Server.h"
Server::Server(QObject *parent, int port) : QTcpServer(parent)
{
// QHostAddress::Any对指定端口的任意地址进行监听,Ipv4的任意地址为0.0.0.0
listen(QHostAddress::Any, port);
// QHostAddress::Null 表示一个空地址
// QHostAddress::LocalHost 表示Ipv4的本机地址为127.0.0.1
// QHostAddress::Broadcast 表示广播地址为255.255.255.255
}
// 将任意客户端发来的信息进行广播
void Server::updateClients(QString msg, int length)
{
// 通知服务器更新相应的显示状态
emit updateServer(msg, length);
// 实现信息的广播
for (int i = 0; i < tcpClientList.count(); ++i)
{
QTcpSocket *item = tcpClientList.at(i);
if (item->write(msg.toLatin1(), length) != length)
{
continue;
}
}
}
// 从tcpClientList列表中将断开连接的对象删除
void Server::slotDisconnected(int discriptor)
{
for (int i = 0; i < tcpClientList.count(); ++i)
{
QTcpSocket *item = tcpClientList.at(i);
if (item->socketDescriptor() == discriptor)
{
tcpClientList.removeAt(i);
return;
}
}
return;
}
// 当出现一个新的连接时,触发函数,socketDescriptor指定了连接的Socket描述符
void Server::incomingConnection(int socketDescriptor)
{
TcpClient *tmp_client = new TcpClient(this);
connect(tmp_client, SIGNAL(updateClients(QString,int)), this, SLOT(updateClients(QString,int)));
connect(tmp_client, SIGNAL(disconnected(int)), this, SLOT(slotDisconnected(int)));
tmp_client->setSocketDescriptor(socketDescriptor);
tcpClientList.append(tmp_client);
} 最后,制作服务端界面
#include 接下来创建TCP聊天室的客户端:
#include #include "TcpClient.h"
#include Qt网络应用初步开发
QUdpSocket、QTcpSocke、QTcpServer都是网络传输层上的类,他们封装实现的是低层次的网络进程通信的功能。而Qt网络应用开发是在此基础上进一步实现应用型的协议功能。应用协议(HTTP/FTP/SMTP)运行在TCP/UDP之上。
网络请求由QNetworkRequest类来表示,作为与请求有关的统一容器,在创建请求对象时指定的URL决定了请求使用的协议。QNetworkAccessManager类用于协调网络操作,每当一个请求创建后,该类用来调度他,并发送信号来报告进度;QNetworkReply用于网络请求的应答,他会在请求呗完成调度时由QNetworkAccessManager创建。
