Java笔试面试题整理第二波
(本系列同步更新于 个人博客小站)
本系列整理Java相关的笔试面试知识点,其他几篇文章如下:
Java笔试面试题整理第八波
Java笔试面试题整理第七波
Java笔试面试题整理第六波
Java笔试面试题整理第五波
Java笔试面试题整理第四波
Java笔试面试题整理第三波
Java笔试面试题整理第二波
Java笔试面试题整理第一波
1、List遍历时删除的几种方式比较
1.1、会报错的删除方式:
(1)在Iterator遍历时使用list删除
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String item = it.next();
list.remove(item); //报错!!!
}
(2)foreach遍历方式中删除
for(String s : list){
list.remove(s); //报错!!!
}
而对于foreach实际上使用的是iterator进行处理的,而iterator是不允许集合在iterator使用期间通过list删除的,也就是第一种方式,也就是说上面两种方式相当于是同一种。
1.2、不会报错,但是有可能漏删或不能完全的删除方式:
(1)漏删的情况(通过索引下标的方式)
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
System.out.println("----------list大小1:--"+list.size());
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if (2 == list.get(i)) {
list.remove(i);
}
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
System.out.println("最后输出=" + list.toString());
输出的结果如下:
----------list大小1:--5
1
2
3
4
最后输出=[1, 2, 3, 4]
可以看到,只删除了一个2,还有一个没有完全删除,原因是:删除了第一个2后,集合里的元素个数减1,后面的元素往前移了1位,此时,第二个2已经移到了索引index=1的位置,而此时i马上i++了,list.get(i)获得的是数据3。
(2)不能完全删除的情况
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
System.out.println("----------list大小1:--"+list.size());
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
list.remove(i);
}
System.out.println("最后输出=" + list.toString()); 输出的结果如下:
----------list大小1:--5
最后输出=[2, 3]
可以看到,结果并没有按照我们的想法,把所有数据都删除干净。原因是:在list.remove之后,list的大小发生了变化,也就是list.size()一直在变小,而 i 却一直在加大,当 i =3时,list.size()=2,此时循环的判断条件不满足,退出了程序。
以上两种情况通过for循环遍历删除,都没有正确达到目的,都是因为在remove后list.size()发生了变化(一直在减少),同时后面的元素会往前移动,导致list中的索引index指向的数据有变化。同时我们的for中的i是一直在加大的!
1.3 List遍历过程中删除元素的推荐做法
还是使用Iterator遍历,但是不用list来remove。如下代码:
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
System.out.println("----------list大小1:--"+list.size());
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Integer item = it.next();
if (2 == item) {
it.remove();
}
System.out.println(item);
}
System.out.println("最后输出=" + list.toString());
输出结果:
----------list大小1:--5
1
2
2
3
4
最后输出=[1, 3, 4]
此时,两个2被全部删除了。
对于iterator的remove()方法,也有需要我们注意的地方:
1、每调用一次iterator.next()方法,只能调用一次remove()方法。
2、调用remove()方法前,必须调用过一次next()方法。
2、Java基本数据类型及包装类
byte(字节) 8 位 Byte
shot(短整型) 16位 Short
int(整型) 32 位 Integer
long(长整型) 64 位 Long
float(浮点型) 32 位 Float
double(双精度) 64 位 Double
char(字符型) 16 位 Character
shot(短整型) 16位 Short
int(整型) 32 位 Integer
long(长整型) 64 位 Long
float(浮点型) 32 位 Float
double(双精度) 64 位 Double
char(字符型) 16 位 Character
boolean(布尔型) 1 位 Boolean
各数据类型按容量大小(表数范围大小)由小到大排列为:
byte <—— short, char <——int <——long <——float <——double
基本类型之间的转换原则:
1)运算时,容量小的类型自动转换为容量大的类型;
2)容量大的类型转换为容量小的类型时,要加强制转换符,且精度可能丢失;
如:float f = 1.2f;
int ff = (int) f;
System.out.println(ff);//输出为1,丢掉了小数部分
3)short,char之间不会互相转换(需要强制转换),byte、short、char并且三者在计算时首先转换为int类型;
4)实数常量默认为double类型, 整数常量默认为int类型;
3、switch中的参数类型
在jdk1.7 之前switch 只能支持 byte、short、char、int或者其对应的封装类以及 Enum 类型。关于枚举的使用请看我这一篇博客(http://blog.csdn.net/shakespeare001/article/details/51151650)。
如:
enum EnumTest {
LEFT,
RIGHT
}
EnumTest e = EnumTest.LEFT;
switch (e) {
case LEFT:
System.out.println("----left-----");
break;
default:
break;
}
在jdk1.7 及1.7以后,switch也支持了String类型,如下:
String str = "abc";
switch (str) {
case "abc":
System.out.println("-----abc-----");
break;
case "aaa":
System.out.println("-----aaa-----");
break;
}4、equals与==的区别
(1)==是一个运算符,它比较的是值
对于基本数据类型,直接比较其数据值是否相等。如果是不同的基本数据类型之间进行比较,则遵循基本数据类型间运算的转换原则(见上面总结的第二条)。如下:
if(12 == 12.0){
System.out.println("-----12 == 12.0-------");
}
此时打印了-----12 == 12.0-------,因为低一级的int类型的12自动转换为高一级的float类型
对于引用类型,==比较的还是值,只不过此时比较的是两个对象变量的内存地址。所以,用==来比较对象,实际上是判断这两个对象是否是同一个new出来的对象,或者是否是一个对象赋值给另一个对象的情况。如:String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = s1;//将s1对的内存地址赋给了s2,此时s1==s2返回true;
(2)equals
equals方法是属于Object类的一个方法,其实现源码如下:
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
可以看到,其实equals方法里面用的还是==运算符,所以对于那些没有重写过Object类的equals方法来说,==和equals方法是等价的!
然而,很多类都自己去重写了equals方法,比如String类、所有基本数据类型的包装类等
String类的equals源码如下:
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String) anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
首先判断是否是同一个new出来的对象,即判断内存地址是否相同;如果不同则判断对象中的内容是否相同。
Integer类的equals方法如下:
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Integer) {
return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue();
}
return false;
}
直接转成判断值是否相等了。
因此,对于String类和所有基本数据类型的包装类来说,equals方法就是判断其内容是否相等。对于其他类来说,要具体看其是否重写了equals方法及具体业务实现。
另:对于基本数据类型来说,使用equals方法,需要用该基本类型对应的包装类,因为equals是针对对象来使用的!
5、Object有哪些公用方法
Object类中的
所有
方法如下:
public boolean equals(Object obj) {//判断是否同一个对象,具体见上一点总结
return (this == obj);
}
public String toString(){
return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
//返回该对象的哈希码值,重写了equals方法一般都要重写hashCode方法
public native int hashCode();
/**
*wait方法就是使当前线程等待该对象的锁,当前线程必须是该对象的拥有者,也就是具有该对象的锁。wait()方法一直等待,直到获得锁或者被中断。wait(long timeout)设定一个超时间隔,如果在规定时间内没有获得锁就返回。
*调用该方法后当前线程进入睡眠状态,直到以下事件发生。
*(1)其他线程调用了该对象的notify方法。
*(2)其他线程调用了该对象的notifyAll方法。
*(3)其他线程调用了interrupt中断该线程。
*(4)时间间隔到了。
*此时该线程就可以被调度了,如果是被中断的话就抛出一个InterruptedException异常。
*如:Person p = new Person();
*p.wait()//使用Person p对象作为对象锁。
*/
public final void wait() throws InterruptedException {...}
public final native void wait(long timeout) throws InterruptedException;
public final void wait(long timeout, int nanos) throws InterruptedException {...}
//该方法唤醒在该对象上等待的某个线程。如p.notify();
public final native void notify();
//该方法唤醒在该对象上等待的所有线程。
public final native void notifyAll();
public final native Class getClass();//获得运行时类型
//创建并返回此对象的一个副本。只有实现了Cloneable接口才可以调用该方法,否则抛出CloneNotSupportedException异常。
protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
//用于释放资源。当垃圾回收器确定不存在对该对象的更多引用时,由对象的垃圾回收器调用此方法。也可手动调用,自己实现一些资源的释放。
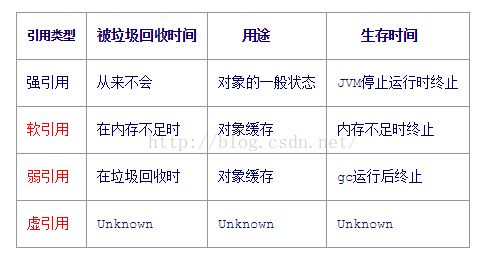
protected void finalize() throws Throwable { }6、Java中的四种引用:强引用、软引用、弱引用、虚引用
四种级别由高到低依次为:强引用 > 软引用 > 弱引用 > 虚引用
【 参考文章:
http://blog.csdn.net/ocean181/article/details/7232759
http://my.oschina.net/ydsakyclguozi/blog/404389
http://blog.csdn.net/hubenshan/article/details/7735858/#comments
】
6.1 强引用(StrongReference)
强引用是使用最普遍的引用。如果一个对象具有强引用,那垃圾回收器绝不会回收它。当内存空间不足,Java虚拟机宁愿抛出OutOfMemoryError错误,使程序异常终止,也不会靠随意回收具有强引用的对象来解决内存不足的问题。如下的定义方式:
String str = new String("abc"); //强引用,在堆中创建了String这个对象,通过栈中的变量str引用这个对象
String str2 = str; //强引用,str2也指向了堆中创建的String对象
这两个引用都是强引用.只要存在对堆中String对象的引用,gc就不会回收该对象,如果通过下面代码:str = null; str2 = null;显示的设置引用str和str2为null,则gc就会认为堆中的String对象已经不存在其他引用了,此时该对象处于可回收的状态,但是到底什么时候回收该对象,取决于gc的算法。
6.2 软引用(SoftReference)
String str= new String("abc"); //强引用
Refenrence sr = new SoftReference(str); //软引用
//引用时
if(sr!=null){
str= sr.get();
}else{
str= new String("abc");
sr = new SoftReference(str);
}
可以看到不论是强引用、软引用、弱引用或者虚引用都是针对某个对象来说的,当我们某个对象需要设置为软引用时,只需要给该对象套入到软引用对象中即可,如上面的代码SoftReference sr = new SoftReference(str);
由于软引用在内存不足时可以被回收,在内存充足时不会被回收,所以软引用经常被用来作为缓存使用。比如在Android中经常把Bitmap作为软引用来缓存图片,如HashMap> imageCache;的方式。
6.3 弱引用(WeakReference)
弱引用与软引用的区别在于:只具有弱引用的对象拥有更短暂的生命周期。在垃圾回收器线程扫描它所管辖的内存区域的过程中,一旦发现了只具有弱引用的对象,不管当前内存空间足够与否,都会回收它的内存。不过,由于垃圾回收器是一个优先级很低的线程,因此不一定会很快发现那些只具有弱引用的对象。
弱引用可以和一个引用队列(ReferenceQueue)联合使用,如果弱引用所引用的对象被垃圾回收,Java虚拟机就会把这个弱引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中。
对于软引用或者弱引用来说,gc回收软引用或弱引用对象的过程是一样的,其执行过程如下:
String str= new String("abc"); //强引用
Refenrence sr = new SoftReference(str); //软引用
1 首先将软引用或弱引用的referent设置为null(即置str = null;),不再引用堆中的对象;
2 将堆中的对象new String("abc");设置为可结束的(finalizable)。
3 当heap中的new String("abc")对象的finalize()方法被运行而且该对象占用的内存被释放, sr被添加到它的ReferenceQueue中。
可以用如下代码来说明过程:
String str = new String("abc");
SoftReference soft = new SoftReference(str); //软引用
str = null;
System.out.println("before gc:" + soft.get());
System.gc();
System.out.println("after gc:" + soft.get());
输出结果:before gc: abc
after gc: abc
对于弱引用:
String str = new String("abc");
WeakReference soft = new WeakReference(str); //弱引用
str = null;
System.out.println("before gc:" + soft.get());
System.gc();
System.out.println("after gc:" + soft.get());
输出结果:before gc :abc
after gc: null
因此可以看出,软引用和弱引用被gc回收的过程是一致的,但是最后到底会不会回收掉该对象,要分情况。对于软引用来说,如果内存不足的情况下才会回收掉;对于弱引用来说,只要gc准备回收该弱引用对象,就会被立即释放掉。
"虚引用"顾名思义,就是形同虚设,与其他几种引用都不同,虚引用并不会决定对象的生命周期。如果一个对象仅持有虚引用,那么它就和没有任何引用一样,在任何时候都可能被垃圾回收。虚引用主要用来跟踪对象被垃圾回收的活动。
虚引用与软引用和弱引用的一个区别在于:虚引用必须和引用队列(ReferenceQueue)联合使用。当垃 圾回收器准备回收一个对象时,如果发现它还有虚引用,就会在回收对象的内存之前,把这个虚引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中。程序可以通过判断引用队列中是 否已经加入了虚引用,来了解被引用的对象是否将要被垃圾回收。程序如果发现某个虚引用已经被加入到引用队列,那么就可以在所引用的对象的内存被回收之前采取必要的行动。 建立虚引用之后通过get方法返回结果始终为null。
四种引用类型的声明周期如下: