一张图帮你弄懂text-cnn
1、何为textcnn
利用卷积神经网络对文本进行分类的算法,那如何用卷积神经网络对文本进行分类呢。这里就tensorflow版本的textcnn源码分析一波。要知道,对文本向量化之后一般是一个一维向量来代表这个文本,但是卷积神经网络一般是对图像进行处理的,那如何将一维转化成二维呢,textcnn在卷积层之前设置了一个embedding层,即将词向量嵌入进去。那具体如何操作的呢。
比如一句话(“白条”,“如何”,“开通”),假设给每个词一个id{“白条”:1,“如何”:2,“开通”:3},文本向量化之后则是【1,2,3】的一个一维向量,但是无法满足卷积层的输入,所以嵌入一个embedding层,此时假设每个词都有一个3维的词向量,{"白条":【2,3,4】,“如何”:【3,5,1】,“开通”:【4,5,6】},则通过embedding层的映射,原文本经过词向量嵌入之后变成【【2,3,4】,【3,5,1】,【4,5,6】】的二维向量,当然卷积神经网络对图像进行卷积时还有通道一说,这里对二维向量可以自动扩充一个维度以满足通道的这一个维度。
2、textcnn tensorflow 结构代码
'''
__author__ : 'shizhengxin'
'''
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
class TextCNN(object):
"""
A CNN for text classification.
Uses an embedding layer, followed by a convolutional, max-pooling and softmax layer.
"""
def __init__(
self, sequence_length, num_classes, vocab_size ,embedding_matrix,
embedding_size, filter_sizes, num_filters, l2_reg_lambda=0.0):
# embedding_matrix,
# Placeholders for input, output and dropout
self.input_x = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, sequence_length], name="input_x")
self.input_y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, num_classes], name="input_y")
self.dropout_keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="dropout_keep_prob")
# Keeping track of l2 regularization loss (optional)
l2_loss = tf.constant(0.0)
#Embedding layer
# with tf.device('/cpu:0'), tf.name_scope("embedding"):
# W = tf.Variable(
# tf.random_uniform([vocab_size, embedding_size], -1.0, 1.0),
# name="W")
# self.embedded_chars = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(W, self.input_x)
# self.embedded_chars_expanded = tf.expand_dims(self.embedded_chars, -1)
with tf.device('/cpu:0'), tf.name_scope("embedding"):
self.embedded_chars = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding_matrix, self.input_x)
self.embedded_chars_expanded = tf.expand_dims(self.embedded_chars, -1)
self.embedded_chars_expanded = tf.cast(self.embedded_chars_expanded,dtype=tf.float32)
print(self.embedded_chars_expanded.shape)
# Create a convo
#
# lution + maxpool layer for each filter size
pooled_outputs = []
for i, filter_size in enumerate(filter_sizes):
with tf.name_scope("conv-maxpool-%s" % filter_size):
# Convolution Layer
filter_shape = [filter_size, embedding_size, 1, num_filters]
W = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(filter_shape, stddev=0.1), name="W")
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[num_filters]), name="b")
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(
self.embedded_chars_expanded,
W,
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding="VALID",
name="conv")
# Apply nonlinearity
h = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv, b), name="relu")
# Maxpooling over the outputs
pooled = tf.nn.max_pool(
h,
ksize=[1, sequence_length - filter_size + 1, 1, 1],
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding='VALID',
name="pool")
pooled_outputs.append(pooled)
# Combine all the pooled features
num_filters_total = num_filters * len(filter_sizes)
self.h_pool = tf.concat(pooled_outputs, 3)
self.h_pool_flat = tf.reshape(self.h_pool, [-1, num_filters_total])
# Add dropout
with tf.name_scope("dropout"):
self.h_drop = tf.nn.dropout(self.h_pool_flat, self.dropout_keep_prob)
# Final (unnormalized) scores and predictions
with tf.name_scope("output"):
W = tf.get_variable(
"W",
shape=[num_filters_total, num_classes],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[num_classes]), name="b")
l2_loss += tf.nn.l2_loss(W)
l2_loss += tf.nn.l2_loss(b)
self.scores = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(self.h_drop, W, b, name="scores")
self.probability = tf.nn.sigmoid(self.scores)
self.predictions = tf.argmax(self.scores, 1, name="predictions")
# CalculateMean cross-entropy loss
with tf.name_scope("loss"):
losses = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=self.input_y, logits=self.scores)
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(losses) + l2_reg_lambda * l2_loss
# Accuracy
with tf.name_scope("accuracy"):
correct_predictions = tf.equal(self.predictions, tf.argmax(self.input_y, 1))
self.accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_predictions, "float"), name="accuracy")
可以看出textcnn的卷积方式是对输入层做三次不同卷积核的卷积,每次卷积后进行池化。
3、一张图让你搞懂textcnn
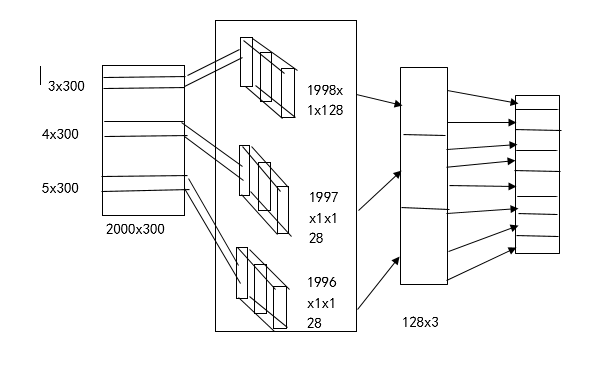
这是我画的一张textcnn结构图
1、首先输入层,将文本经过embedding之后形成了一个2000*300的维度,其中2000为文本最大长度、300为词向量的维度。
2、卷积层,卷积层设计三个不同大小的卷积核,【3*300,4*300,5*300】,每个不同大小的卷积核各128个。卷积后分别成为【1998*1*128,1997*1*128,1996*1*128】的feture-map,这里为什么会变成大小这样的,是因为tensorflow的卷积方式采用same 或者 valid的形式,这种卷积的方式采用的是valid 具体大家可以看看官方文档。
3、经过卷积之后,随后是三个池化层,池化层的目的是缩小特征图,这里同池化层的设置,将卷积层的特征池化之后的图为【1*1*128,1*1*128,1*1*28】,经过reshape维度合并成【3*128】。
4、全连接层就不必说,采用softmax就可以解决了。