NSGA-II算法matlab程序(翻译)
NSGA-II算法matlab程序(翻译)
- NSGA-II算法共享
- 流程图
- 1 主函数
- 2 快速非支配排序和拥挤度计算
- 3 竞标赛选择代码
- 4 交叉,变异代码
- 5 种群杂交替换
- 6 目标函数评估
- 7 测试算例
NSGA-II算法共享
最近在学习多目标优化算法,涉及到NSGA-II算法,看了网上的很多资料,挺有收获。之前一直在学网上的代码,但是发现限制函数只能用来限制决策变量的变化区间(只能在初始化中实现),对于复杂的不等式限制函数却无能为力:发现好多人同我一样,都遇到过这个问题。终于找到这个示例文件,我就对照着之前的一篇注释https://blog.csdn.net/joekepler/article/details/80820240,自学了一遍。然后又把另一个可以添加约束条件的代码贴出来,和许多初学者共享。
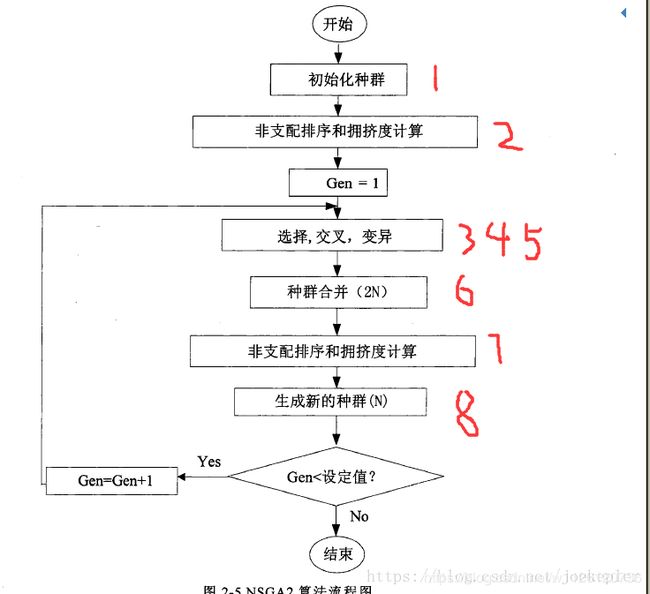
流程图
借用之前的流程图,简单介绍一下这个算法。具体的内容可以去查论文。
1 主函数
函数初始化过程包含在主函数中运行。
clear all
global V M xl xu etac etam p pop_size pm
%设定全局变量
%函数需要设置一个测试问题序号,1-14分别对应着不同的测试函数,1-9为无限制测试函数,10-14为
%不等式限制的测试函数
% pop_size定义为种群的数量,V为设计变量数目,no_runs运行次数,gen_max种群最大值,
% M目标函数个数
p=input('Test problem index : \n');
pop_size=80; % 种群数量;
no_runs=1; % 算法执行轮数;
M=2; %目标函数个数;
gen_max=500; % 最大迭代次数,500次;
fname='test_case'; % 将目标函数及限制条件copy给fname;
if p==13, % OSY
pop_size=100;
no_runs=10;
end;
if (p==2 | p==5 | p==7), gen_max=1000; end;
if p<=9 % Unconstrained test functions
tV=[2;30;3;1;30;4;30;10;10];
V=tV(p);
txl=[-5*ones(1,V);zeros(1,V);-5*ones(1,V);-1000*ones(1,V);zeros(1,V);-1/sqrt(V)*ones(1,V);zeros(1,V); 0 -5*ones(1,V-1);zeros(1,V)];
txu=[10*ones(1,V); ones(1,V);5*ones(1,V);1000*ones(1,V);ones(1,V);1/sqrt(V) *ones(1,V);ones(1,V);1 5*ones(1,V-1);ones(1,V)];
xl=(txl(p,1:V)); % lower bound vector
xu=(txu(p,1:V)); % upper bound vectorfor
etac = 20; % distribution index for crossover
etam = 20; % distribution index for mutation / mutation constant
else % Constrained test functions
p1=p-9;
tV=[2;2;2;6;2]; %p=10-14分别对应的决策变量个数,例如p=10,tV=2;
V=tV(p1);
txl=[0 0 0 0 0 0;-20 -20 0 0 0 0;0 0 0 0 0 0;0 0 1 0 1 0;0.1 0 0 0 0 0];
txu=[5 3 0 0 0 0;20 20 0 0 0 0;pi pi 0 0 0 0;10 10 5 6 5 10;1 5 0 0 0 0];
%xl和xu分别是决策变量的上下限,txl,txu分别对应着决策变量的取值范围
%如p1=1,对应p=10,0<x1<5,0<x2<3
xl=(txl(p1,1:V)); % lower bound vector
xu=(txu(p1,1:V)); % upper bound vectorfor i=1:NN
etac = 20; % 交叉分布指数
etam = 100; % 变异分布指数
end
pm=1/V; % Mutation Probability
Q=[];
for run = 1:no_runs
%% 种群初始化
xl_temp=repmat(xl, pop_size,1);
xu_temp=repmat(xu, pop_size,1);
%将种群变量初始化到search domain的区间内
x = xl_temp+((xu_temp-xl_temp).*rand(pop_size,V));
%% Evaluate objective function
for i =1:pop_size
%初始化参数时,目标函数及限制函数值计算
[ff(i,:) err(i,:)] =feval(fname, x(i,:));
end
%归一化误差初始值,将多个目标函数的误差值作和,要求最后和为0;
error_norm=normalisation(err);
population_init=[x ff error_norm];
%对初始值进行非支配排序
[population front]=NDS_CD_cons(population_init);
iii = 0;
%% 按照迭代次数循环
for gen_count=1:gen_max
%锦标赛竞选代码
parent_selected=tour_selection(population);
%模拟二进制交叉和多项式变异
child_offspring = genetic_operator(parent_selected(:,1:V));
for ii = 1:pop_size
[fff(ii,:) err(ii,:)]=feval(fname, child_offspring(ii,:)); %对子代的种群进行目标值评估;
end
error_norm=normalisation(err);
child_offspring=[child_offspring fff error_norm];
%% INtermediate population (Rt= Pt U Qt of 2N size)生成含有2N条染色体的种群;
population_inter=[population(:,1:V+M+1) ; child_offspring(:,1:V+M+1)]; %合并父代和子代种群;
[population_inter_sorted front]=NDS_CD_cons(population_inter); % 对新的种群进行快速非支配排序;
%选择合并后种群中的前N个优先个体形成新的种群N;
new_pop=replacement(population_inter_sorted, front);
population=new_pop;
if mod(gen_count,100) == 0
fprintf('The iteration times = %f \n',gen_count);
end
end
new_pop=sortrows(new_pop,V+1);
paretoset(run).trial=new_pop(:,1:V+M+1);
Q = [Q; paretoset(run).trial];
end
%% 帕累托前沿plot
if run==1
plot(new_pop(:,V+1),new_pop(:,V+2),'*')
else
[pareto_filter front]=NDS_CD_cons(Q); % Applying non domination sorting on the combined Pareto solution set
rank1_index=find(pareto_filter(:,V+M+2)==1); % Filtering the best solutions of rank 1 Pareto
pareto_rank1=pareto_filter(rank1_index,1:V+M)
plot(pareto_rank1(:,V+1),pareto_rank1(:,V+2),'*') % Final Pareto plot
end
xlabel('objective function 1')
ylabel('objective function 2')
if p==1
title(' 1 - Test case 1')
elseif p==2
title(' 2 - ZDT1')
elseif p==3
title(' 3 - KUR')
elseif p==4
title(' 4 - SCH')
elseif p==5
title(' 5 - ZDT2')
elseif p==6
title(' 6 - Test case 3')
elseif p==7
title(' 7 - ZDT3')
elseif p==8
title(' 8 - ZDT4')
elseif p==9
title(' 9 - ZDT6')
elseif p==10
title(' 10 - BNH')
elseif p==11
title(' 11 - SRN')
elseif p==12
title(' 12 - TNK')
elseif p==13
title(' 13 - OSY')
elseif p==14
title(' 14 - CONSTR')
end
2 快速非支配排序和拥挤度计算
本文的NSGA-II算法参考论文
http://www.dmi.unict.it/mpavone/nc-cs/materiale/NSGA-II.pdf
Kalyanmoy Deb, Amrit Pratap, Sameer Agarwal, and T. Meyarivan, " A Fast and Elitist Multiobjective Genetic Algorithm: NSGA-II",
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON EVOLUTIONARY COMPUTATION, VOL. 6, No. 2, APRIL 2002.
%% Description
% 1. 执行带有精英决策的快速非支配排序和拥挤度计算
% 2. 输入是种群参数,种群大小为: [size(popuation), V+M+1]
% 3. 返回种群 chromosome_NDS_CD,大小为 [size(population),V+M+3]
% 4. 'problem_type' 标志是识别种群是否为可用解,完全可行解(problem_type=0),或部分可行解(problem_type=0.5);
%% function begins
function [chromosome_NDS_CD front] = NDS_CD_cons(population)
global V M problem_type
%% Initialising structures and variables
chromosome_NDS_CD1=[];
infpop=[];
front.fr=[];
struct.sp=[];
rank=1;
% 如果种群中所有的err部分为0,则说明该种群中的决策变量首先满足限制函数,为全部可行解,
%即problem_type=0
if all(population(:,V+M+1)==0)
problem_type=0;
%满足限制函数,种群放入子代种群进行sorting寻优;
chromosome=population(:,1:V+M);
% 记录子群的个数;
pop_size1=size(chromosome,1);
elseif all(population(:,V+M+1)~=0) %全部不可行解
problem_type=1;
pop_size1=0;
infchromosome=population;
else
%部分为可行解;
problem_type=0.5;
feas_index=find(population(:,V+M+1)==0);
chromosome=population(feas_index,1:V+M);
pop_size1=size(chromosome,1);
infeas_index=find(population(:,V+M+1)~=0);
infchromosome=population(infeas_index,1:V+M+1); % infeasible chromosomes;
end
%% 处理可行解
if problem_type==0 | problem_type==0.5
pop_size1 = size(chromosome,1);
%分别提取两个目标函数值f1 f2;
f1 = chromosome(:,V+1);
f2 = chromosome(:,V+2);
%非支配排序
%struct(p).sp存储f(p)所支配的解集
%n(p)表示能够支配f(p)的解的个数,如果n(p)=0,说明f(p)不被其他解所支配;
for p=1:pop_size1
%依次比较种群中的解支配关系
struct(p).sp=find(((f1(p)-f1)<0 &(f2(p)-f2)<0) | ((f2(p)-f2)==0 &(f1(p)-f1)<0) | ((f1(p)-f1)==0 &(f2(p)-f2)<0));
n(p)=length(find(((f1(p)-f1)>0 &(f2(p)-f2)>0) | ((f2(p)-f2)==0 &(f1(p)-f1)>0) | ((f1(p)-f1)==0 &(f2(p)-f2)>0)));
end
%如果n(p)=0,说明f(p)不被可行解内的其他所有解集所支配,rank为最高=1;
front(1).fr=find(n==0);
% 创建后续各级别的rank
while (~isempty(front(rank).fr)) %循环当前支配解集中的个体;
front_indiv=front(rank).fr; %front_indiv记录该rank级的占优解位置;
n(front_indiv)=inf;
chromosome(front_indiv,V+M+1)=rank; %V+M+1这一列存储可行解的rank;
rank=rank+1;
front(rank).fr=[];
for i = 1:length(front_indiv)
temp=struct(front_indiv(i)).sp;
n(temp)=n(temp)-1; %表示个体i的被支配个数减1;
end
%循环直到某一解不被其他解所支配;
q=find(n==0); %如果q是新的非支配解,则放入改rank的集合中;
front(rank).fr=[front(rank).fr q];
end
chromosome_sorted=sortrows(chromosome,V+M+1); % 按照rank排序
%拥挤度计算
rowsindex=1;
%按rank循环
for i = 1:length(front)-1 %front-1是因为在非支配求解的时候,rank多加了一个1,front的最后一个元素为空;
l_f=length(front(i).fr);
if l_f > 2
sorted_indf1=[];
sorted_indf2=[];
sortedf1=[];
sortedf2=[];
% sorting based on f1 and f2 升序;
% sorted_indf1指示排序前的索引号;
[sortedf1 sorted_indf1]=sortrows(chromosome_sorted(rowsindex:(rowsindex+l_f-1),V+1));
[sortedf2 sorted_indf2]=sortrows(chromosome_sorted(rowsindex:(rowsindex+l_f-1),V+2));
f1min=chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf1(1)+rowsindex-1,V+1);
f1max=chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf1(end)+rowsindex-1,V+1);
%V+M+2列表示f1拥挤度,V+M+3列表示f2拥挤度;
%对排序的第一个个体和最后一个个体的距离设为无穷大
chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf1(1)+rowsindex-1,V+M+2)=inf;
chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf1(end)+rowsindex-1,V+M+2)=inf;
f2min=chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf2(1)+rowsindex-1,V+2);
f2max=chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf2(end)+rowsindex-1,V+2);
chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf2(1)+rowsindex-1,V+M+3)=inf;
chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf2(end)+rowsindex-1,V+M+3)=inf;
%循环集合中的除了第一个和最后一个个体;
for j = 2:length(front(i).fr)-1
if (f1max - f1min == 0) | (f2max - f2min == 0)
chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf1(j)+rowsindex-1,V+M+2)=inf;
chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf2(j)+rowsindex-1,V+M+3)=inf;
else %拥挤度计算,可以参考论文
chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf1(j)+rowsindex-1,V+M+2)=(chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf1(j+1)+rowsindex-1,V+1)-chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf1(j-1)+rowsindex-1,V+1))/(f1max-f1min);
chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf2(j)+rowsindex-1,V+M+3)=(chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf2(j+1)+rowsindex-1,V+2)-chromosome_sorted(sorted_indf2(j-1)+rowsindex-1,V+2))/(f2max-f2min);
end
end
else %该rank层只有一条染色体
chromosome_sorted(rowsindex:(rowsindex+l_f-1),V+M+2:V+M+3)=inf;
end
rowsindex = rowsindex + l_f; %处理下一rank的值;
end
%将按f1和f2目标值计算得到的distance相加,得到最终得拥挤度。
chromosome_sorted(:,V+M+4) = sum(chromosome_sorted(:,V+M+2:V+M+3),2);
chromosome_NDS_CD1 = [chromosome_sorted(:,1:V+M) zeros(pop_size1,1) chromosome_sorted(:,V+M+1) chromosome_sorted(:,V+M+4)];
end
%% 处理非可行解
if problem_type==1 | problem_type==0.5
%按照err误差升序
infpop=sortrows(infchromosome,V+M+1);
%对于非可行解,将它们对应的染色体按照err顺序,依次指定rank
%则infpop = [X f1 f2 err rank INF]
infpop=[infpop(:,1:V+M+1) (rank:rank-1+size(infpop,1))' inf*(ones(size(infpop,1),1))];
for kk = (size(front,2)):(size(front,2))+(length(infchromosome))-1;
front(kk).fr= pop_size1+1;
end
end
chromosome_NDS_CD = [chromosome_NDS_CD1;infpop];
3 竞标赛选择代码
二元锦标赛介绍:
https://blog.csdn.net/xuxinrk/article/details/80352815
%随机产生N*2维的数据集,参与锦标赛;N表示种群的数目;
candidate=[randperm(pop_size);randperm(pop_size)]';
%竞标赛选择法,每次随机选择两个个体,优先选择排序等级高的个体,
%如果排序等级一样,优选选择拥挤度大的个体
for i = 1: pop_size
parent=candidate(i,:);
if pool(parent(1),rank)~=pool(parent(2),rank) %rank不一致,选择rank小的个体
if pool(parent(1),rank)<pool(parent(2),rank)
mincandidate=pool(parent(1),:);
elseif pool(parent(1),rank)>pool(parent(2),rank)
mincandidate=pool(parent(2),:);
end
parent_selected(i,:)=mincandidate;
else
if pool(parent(1),distance)>pool(parent(2),distance) % 如果rank一致,选择拥挤度大的个体
maxcandidate=pool(parent(1),:);
elseif pool(parent(1),distance)< pool(parent(2),distance)
maxcandidate=pool(parent(2),:);
else %随机选择的个体是同一个,随机选择个体;
temp=randperm(2);
maxcandidate=pool(parent(temp(1)),:);
end
parent_selected(i,:)=maxcandidate; % Maximum distance individual is selected finally
end
end
4 交叉,变异代码
选择模拟二进制交叉和多项式变异;
交叉参考
https://blog.csdn.net/xuxinrk/article/details/80363733
变异参考
https://blog.csdn.net/xuxinrk/article/details/80363876
function mutated_child = poly_mutation(y)
global V xl xu etam pm
%% Description
% 1. Input is the crossovered child of size (1,V) in the vector 'y' from 'genetic_operator.m'.
% 2. Output is in the vector 'mutated_child' of size (1,V).
%% Polynomial mutation including boundary constraint
del=min((y-xl),(xu-y))./(xu-xl);
t=rand(1,V);
loc_mut=t<pm;
u=rand(1,V);
delq=(u<=0.5).*((((2*u)+((1-2*u).*((1-del).^(etam+1)))).^(1/(etam+1)))-1)+(u>0.5).*(1-((2*(1-u))+(2*(u-0.5).*((1-del).^(etam+1)))).^(1/(etam+1)));
c=y+delq.*loc_mut.*(xu-xl);
mutated_child=c;
5 种群杂交替换
function new_pop=replacement(population_inter_sorted, front)
global pop_size
%% Description
%精英策略生成新的种群from 2N个个体中。
index=0;
ii=1;
while index < pop_size
l_f=length(front(ii).fr);
if index+l_f < pop_size
new_pop(index+1:index+l_f,:)= population_inter_sorted(index+1:index+l_f,:);
index=index+l_f;
else
temp1=population_inter_sorted(index+1:index+l_f,:);
temp2=sortrows(temp1,size(temp1,2));
new_pop(index+1:pop_size,:)= temp2(l_f-(pop_size-index)+1:l_f,:);
index=index+l_f;
end
ii=ii+1;
end
6 目标函数评估
示例代码一共提供了14中测试函数,其中1-9个为无限制函数的多目标优化测试算例,
10-14为有限制函数的多目标优化算法。
% 1. 函数返回目标函数 fit = [f1 f2] 和 限制参数值 c;
% 2. V是决定变量的数目;
% 3. 所有的限制c被强制转化成 h(x)<=0 的形式;
% 4. p=1 : p=9是非限制的测试函数;
% 5. p=10 to p=14是限制的测试函数;
% 6. Refer above references for the details of each test problem: number of objectives, number of design variabes, their lower and upper limits,
% number of constraints, type of constraints etc,.
%% reference
% 1. BINH, Thanh. "A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm. The study cases".
% Technical report. Barleben, Germany. 1999.
% 2. DEB, Kalyanmoy. "Multi-Objective optimization using evolutionary
% algorithms". John Wiley & Sons, LTD. Kanpur, India. 2004.
function [fit err]=test_case(x)
global p V
%% Unconstrained Test functions (for p=1 to p=9)
if p==1 % Test case problem 1
f1=(4*x(1)^2)+(4*x(2)^2);
f2=((x(1)-5)^2)+((x(2)-5)^2);
end
if p==2 % ZDT1 from Deb paper NSGA2
cons=[0];
f1 = x(1);
g=1+(9*sum(x(2:V),2)/(V-1));
f2 = g*(1-sqrt(x(1)/g));
end
if p==3 % kUR from Deb
f1=(-10*exp(-0.2*(sqrt(x(1)^2+x(2)^2))))+(-10*exp(-0.2*(sqrt(x(2)^2+x(3)^2))));
f2=((abs(x(1))^0.8) + (5*sin(x(1))^3))+((abs(x(2))^0.8) + (5*sin(x(2))^3))+((abs(x(3))^0.8) + (5*sin(x(3))^3));
end
if p==4 % SCH frm Deb paper
f1=x.*x;
f2=(x-2).^2;
end
if p==5 % ZDT2
f1 = (x(1));
g=1+(9*sum(x(2:V),2)/(V-1));
f2 =((1-(x(1)/g)^2));
end
if p==6 % Test case problem 2
f1=1-exp(-sum((x-1/sqrt(V)).^2,2));
f2=1-exp(-sum((x+1/sqrt(V)).^2,2));
end
if p==7 % ZDT3
f1 = x(1);
g=1+(9*sum(x(2:V),2)/(V-1));
f2 = (1-(sqrt(x(1)/g)) - ((x(1)/g)*sin(10*pi*x(1))));
end
if p==8 % ZDT4
f1 = x(1); temp=0;
for ii = 2: V
temp=temp+((x(ii))^2)-(10*cos(4*pi*x(ii)));
end
g= 1 + (10*(V-1)) + temp;
f2 = (1-sqrt(x(1)/g));
end
if p==9 % ZDT6
f1 = 1-(exp(-4*x(1)))*(sin(6*pi*x(1)))^6;
g=1+(9*(sum(x(2:V),2)/(V-1))^0.25);
f2 = (1-(f1/g)^2);
end
err= zeros(1,1);
%% Constrained Test functions (for p=10 to p=14)
% c(1,1:n) = 限制条件;
% 如果c>0
if p==10 %BNH
f1=4*(x(1)^2)+4*(x(2)^2);
f2=(x(1)-5)^2+(x(2)-5)^2;
c(1,1)=(x(1)-5)^2 + x(2)^2 -25;
c(1,2)=-(x(1)-8)^2-(x(2)+3)^2+7.7;
err=(c>0).*c;
end
if p==11 %SRN
f1=(x(1)-2)^2+(x(2)-1)^2+2;
f2=9*x(1)-(x(2)-1)^2;
c(1,1)=x(1)^2+x(2)^2-225;
c(1,2)=x(1)-(3*x(2))+10;
err=(c>0).*c;
end
if p==12 %TNK
f1=x(1);
f2=x(2);
c(1,1)=-x(1)^2-x(2)^2+1+(0.1*cos(16*atan((x(1)/x(2)))));
c(1,2)=(x(1)-0.5)^2+(x(2)-0.5)^2-0.5;
err=(c>0).*c;
end
if p==13 % OSY
f1=-((25*(x(1)-2)^2)+((x(2)-2)^2)+((x(3)-1)^2)+((x(4)-4)^2)+((x(5)-1)^2));
f2=(x(1)^2)+(x(2)^2)+(x(3)^2)+(x(4)^2)+(x(5)^2)+(x(6)^2);
c(1,1)=-x(1)-x(2)+2;
c(1,2)=-6+x(1)+x(2);
c(1,3)=-2+x(2)-x(1);
c(1,4)=-2+x(1)-3*x(2);
c(1,5)=-4+((x(3)-3)^2)+x(4);
c(1,6)=-((x(5)-3)^2)-x(6)+4;
err=(c>0).*c;
end
if p==14 % CONSTR
f1=x(1);
f2=(1+x(2))/(x(1));
c(1,1)=-x(2)-(9*x(1))+6;
c(1,2)=+x(2)-9*x(1)+1;
err=(c>0).*c;
end
fit=[f1 f2];
7 测试算例
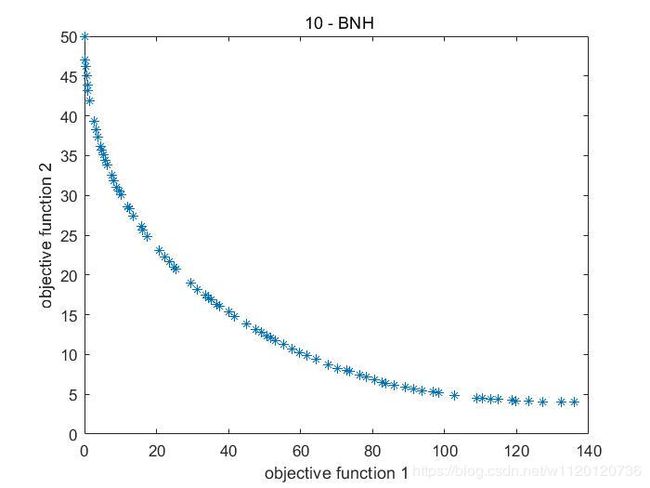
选择测试函数10(Binh and Korn function)运行测试效果。
其中测试函数10的具体形式及限制函数可以参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/miscclp/article/details/38102831
在matlab中输入目标函数Main_NSGA2及需要测试的算例序号10。
(编辑器插不进去图片,累哭 ,就贴在下面吧)
>> cd 'D:\Learning\Constrained NSGA2'
>> Main_NSGA2
Test problem index :
10
The iteration times = 100.000000
The iteration times = 200.000000
The iteration times = 300.000000
The iteration times = 400.000000
The iteration times = 500.000000
>>
帕累托前沿效果图,如下(选择种群数量为80,迭代次数100次,运行1轮)
好的,搞定bingo
所有的代码都放到下面的链接里面了。
https://download.csdn.net/download/w1120120736/11927075