首先介绍了LINQ的用法
LINQ就是一个C#自带的数据库,实现的功能与主流的关系型数据库基本一致 ,它在对象领域和数据领域之间架起了一座桥梁,往往我们在编写日常的应用程序的时候很难绕开数据库的应用
在 Visual Studio 中,可以用 Visual Basic 或 C# 为以下数据源编写 LINQ 查询:SQL Server 数据库、XML 文档、ADO.NET 数据集,以及支持 IEnumerable 或泛型 IEnumerable
LINQ 查询既可在新项目中使用,也可在现有项目中与非 LINQ 查询一起使用。 唯一的要求是项目应面向 .NET Framework 3.5 或更高版本。
首先我们创建了一个关于Customer的集合(Customer为自己定义的一个类)
然后创建了一个IEnumberable
这里提一下关于LINQ的查询语句的写法
from 类型 in 集合
where 约束
select 要查询的键值
因为范围变量要放在最前面声明,所以from语句放在最前面
一个例子:
IEnumerableresult = from customer in customers
where customer.FirstName == "Donna"
select customer;
from 后面: range variable from the data source.
in 后面: Data source can be any collection that implements System. Collections.
Generic. IEnumerable
where后面的约束条件也可以用形如
customer.LastName.StartWith(“G”)
的更复杂的表达式
最后的select后面:
defines (or projects) the results.
the query returns the customer objects.
这样我们就完成了一个对简单的查询语句的认识
接下来看一下一个应用了LINQ的例子
// Example13-1.A simple LINQ query using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; namespace Programming_CSharp { // Simple customer class public class Customer { public string FirstName { get; set; } public string LastName { get; set; } public string EmailAddress { get; set; } // Overrides the Object.ToString() to provide a // string representation of the object properties. public override string ToString() { return string.Format("{0} {1}\nEmail: {2}", FirstName, LastName, EmailAddress); } } // Create a customer list with sample data public class Tester { private static ListCreateCustomerList() { List customers = new List { new Customer { FirstName = "Orlando",LastName = "Gee", EmailAddress = "[email protected]"}, new Customer { FirstName = "Keith", LastName = "Harris", EmailAddress = "[email protected]" }, new Customer { FirstName = "Donna", LastName = "Carreras", EmailAddress = "[email protected]" }, new Customer { FirstName = "Janet", LastName = "Gates", EmailAddress = "[email protected]" }, new Customer { FirstName = "Lucy", LastName = "Harrington", EmailAddress = "[email protected]" } }; return customers; } static void Main() // Main program { List customers = CreateCustomerList(); IEnumerable result = from customer in customers where customer.FirstName == "Donna" select customer; Console.WriteLine("FirstName == \"Donna\""); foreach (Customer customer in result) { Console.WriteLine(customer.ToString());} customers[3].FirstName = "Donna"; Console.WriteLine("FirstName == \"Donna\" (take two)"); foreach (Customer customer in result) { Console.WriteLine(customer.ToString());} Console.ReadLine(); } } }
这里是用的IEnumberable接口。
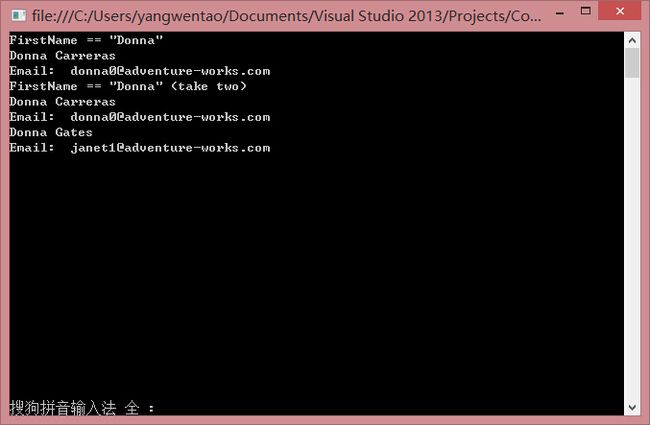
运行结果
我们可以看到首先我们第一次对集合进行firstname为donna的查询,得到了一个对象是donna carreras为关键字的
而当我们直接更改掉customers[3]的firstname的时候我们再次查询就可以得到所有Donna的对象
如上结果中
之后还有LINQ中提供累内联的函数也就是join
方式
[data source 1] join [data source 2] on [join condition]
并且注意LINQ的join子句仅在满足连接条件的对象在所有的数据源中都存在时才会返回结果。
var这个关键字是用来声明一个隐藏类型的
我们可以用var来声明一个没有类型的变量,不过并不是变量没有类型而是我们不用写C#会自动识别
如
var num = 2147483647;
这样的num就会被默认为是一个int而这样
var strstr = "2147483647";
strstr则会被认为是一个字符串
但是注意我们必须要在声明var的时候就给var赋初值(个人觉得这里类似于一个语法糖)
其实lambada表达式同样也是运用着这种感觉
lambada表达式这里介绍一下
形式:参数列表 => 语句或语句块
string[] names={"agen","balen","coure","apple"};
string[] findNameA=Array.FindAll(names,delegate(string v){return v.StartsWith("a");});
string[] findNameB=Array.FindAll(names,v=>v.StartsWith("a"));
string[]findNameA=Array.FindAll(names,delegate(stringv){returnv.StartsWith("a");}); string[]findNameB=Array.FindAll (names,delegate(stringv){returnv.StartsWith("a");});
<Customer> <FirstName>OrlandoFirstName> <LastName>GeeLastName> <EmailAddress>[email protected]EmailAddress> Customer>
这里的customer是一个类里面包含有三个数据就是firstname lastname和emailaddress
我们可以理解为一个大叔组,假如我们要将一大堆customer传进去也就是传一个customers就可以再外面再套一个
这是关于xml
在C#中如何生成xml文档呢
XmlElement firstNameElem = customerXml.CreateElement("FirstName"); firstNameElem.InnerText = customer.FirstName; //存入元素的值 //添加到customer元素 customerElem.AppendChild(firstNameElem);
这里注意要using System.xml;
这样就可以生成一个最简单的xml文件了
还是用之前的LINQ的那个集合生成一个xml代码
// Example13-1.A simple LINQ query using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Xml; namespace Programming_CSharp { // Simple customer class public class Customer { public string FirstName { get; set; } public string LastName { get; set; } public string EmailAddress { get; set; } // Overrides the Object.ToString() to provide a // string representation of the object properties. public override string ToString() { return string.Format("{0} {1}\nEmail: {2}", FirstName, LastName, EmailAddress); } } // Create a customer list with sample data public class Tester { private static ListCreateCustomerList() { List customers = new List { new Customer { FirstName = "Orlando",LastName = "Gee", EmailAddress = "[email protected]"}, new Customer { FirstName = "Keith", LastName = "Harris", EmailAddress = "[email protected]" }, new Customer { FirstName = "Donna", LastName = "Carreras", EmailAddress = "[email protected]" }, new Customer { FirstName = "Janet", LastName = "Gates", EmailAddress = "[email protected]" }, new Customer { FirstName = "Lucy", LastName = "Harrington", EmailAddress = "[email protected]" } }; return customers; } static void Main() // Main program { List customers = CreateCustomerList(); // Find customer by first name XmlDocument customerXml = new XmlDocument(); XmlElement rootElem = customerXml.CreateElement("Customers"); customerXml.AppendChild(rootElem); foreach (Customer customer in customers) { // Create new element representing the customer object. XmlElement customerElem = customerXml.CreateElement("Customer"); // Add element “FirstName” property to the customer element. XmlElement firstNameElem = customerXml.CreateElement("FirstName"); firstNameElem.InnerText = customer.FirstName; customerElem.AppendChild(firstNameElem); // Add element: LastName property to the customer element. XmlElement lastNameElem = customerXml.CreateElement("LastName"); lastNameElem.InnerText = customer.LastName; customerElem.AppendChild(lastNameElem); // Add element: EmailAddress property to the customer element. XmlElement emailAddress = customerXml.CreateElement("EmailAddress"); emailAddress.InnerText = customer.EmailAddress; customerElem.AppendChild(emailAddress); // Finally add the customer element to the XML document rootElem.AppendChild(customerElem); } Console.WriteLine(customerXml.OuterXml); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
生成的结果是
<Customers> <Customer> <FirstName>OrlandoFirstName> <LastName>GeeLastName> <EmailAddress>[email protected]EmailAddress> Customer> <Customer> <FirstName>KeithFirstName> <LastName>HarrisLastName> <EmailAddress>[email protected]EmailAddress> Customer> <> …. Customers>
这节课的知识复习到这里,因为xml还有一些细致的并没有弄懂。。。至此已经能生成建议的xml了~
因为课堂内容讲述较快,所以课下的压力略有增加,感觉有点吃不太透,要更加努力了,以上!