MySQL学习笔记(二)——单表查询与多表查询
一、备份数据库与恢复数据库
1.1备份数据库
备份就是将数据库导出为sql脚本。在命令行中输入:mysqldump -u用户名 -p密码 数据库名>导出文件路径
注意:1.末尾不要打分号。2.执行此语句前应该先退出mysql客户端。3.导出的内容不包括创建数据库的语句只包含数据库里面的内容。
2.2恢复数据库
恢复数据库就是将导出的sql脚本插入到数据库中。有如下两种实现方式:
第一种方式:1.登录mysql:mysql -u用户名 -p密码。2.创建数据库:create database 数据库名。3.输入命令:mysql -uroot -p密码 数据库名<备份的数据路径 并回车。
第二种方式:1.删除数据库:drop database 数据库名。2.重新创建数据库:create database 数据库名。3.切换到数据库:use 数据库名。4.输入命令:source sql脚本路径 并回车。
二、约束
约束是添加在列上用来对列进行约束的,分为主键约束、非空约束、唯一约束、默认约束、外键约束。
2.1 主键约束(primary key)
特点:1.非空。2.唯一。3.可被引用。4.表中只能有一个主键。当表的某一列被定义为主键后,该列就不能为空且不能有重复的值出现,表中只能有一个主键,这个主键可以是一个字段,或者多个字段的集合。
*创建表时指定主键的两种方式:
1.create table emp(
empno int primary key,
ename varchar(50)
);
2.create table emp(
empno int,
ename varchar(50),
primary key(empno)
);
*创建表指定多个字段为主键的方法:
create table emp(
empo int ,
ename varchar(50),
primary key(empo,ename)
);
* 修改表时指定主键的两种方式:
1.alter table emp add primary key(empo);
2.alter table emp change empo empo 类型 primary key;
* 修改表时删除主键的方式:
1.alter table emp drop primary key;2.2主键自增长(auto_increment)
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(30)
);注意:auto_increment必须添加在int类型后,指定主键自增长后,插入记录时该字段可不插入值,mysql会自动为这个字段插入一个自增长的值。
2.3非空约束(not null)
当数据库中某个字段不允许被设置为null时,对这个字段添加非空约束。
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(50) not null
);2.4唯一约束(unique)
当数据库中某个字段不允许设置重复的值时,对这个字段添加唯一约束。
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name archer(50) not null unique
);
2.5默认约束(default)
当数据库中的某个字段需要被默认赋值时,对这个字段添加默认约束。
create table student(
id int primary key aotu_increment,
name varchar(50) not null unique,
sex int(1) default 0
);2.6外键约束(foreign key)
外键用来在两个表的数据之间建立连接。特点:1.外键必须是另一个表(或自己表)的主键值,即外键要引用主键的值。2.外键可为空,若不为空值,则每一个外键必须等于另一个表中的主键值。3.外键可重复。4.一张表可以有多个外键。
create table dept(
deptno int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(50)
);
create table emp(
empno int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(50),
dno int,
constraint fk_emp_dept foreign key(dno) references dept (deptno)
);最后一行就是给emp表添加了外键,添加外键约束后,在emp表中对dno字段进行赋值时就该考虑外键的特点了。
2.7 表之间对应的关系
1对多:例如员工和部门的关系
1对1:例如老公和老婆的关系
多对1:例如老师与学生的关系
2.7.1数据库中1对1的关系:
create table husband (
hid int primary key auto_increment,
hname varchar(50)
);
insert into husband values(null,’刘备’);
insert into husband values(null,’张飞’);
insert into husband values(null,’关羽’);
create table wife(
wid int primary key auto_increment,
wname varchar(50),
constraint fk_wife_husband foreign key (wid) references husband(hid)
);特点:外键引用父表的主键。 说明: 对于两个具有关联关系的表来说,相关联字段的主键所在的那个表为父表(主表),外键所在的表为子表(从表)。
2.7.2数据库中多对多的关系:
在表中建立多对多关系需要使用中间表(关联表),即需要三张表,在中间表中使用两个外键,分别引用其它两个表的主键。
create table student(
sid int primary key auto_increment,
sname varchar(50)
);
create table teacher (
tid int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(50)
);
create table stu_tea(
sid int,
tid int,
constraint fk_student foreign key(sid) references student(sid),
constraint fk_teacher foreign key(tid) references student(tid)
);
insert into student values(null,’刘德华’);
insert into student values(null,’梁朝伟);
insert into student values(null,’黄日华’);
insert into student values(null,’苗侨伟’);
insert into student values(null,’汤镇业’);
insert into teacher values(null,’崔老师’);
insert into teacher values(null,’刘老师’);
insert into teacher values(null,’石老师’);
insert into stu_tea values(1,1);
insert into stu_tea values(2,1);
insert into stu_tea values(3,1);
insert into stu_tea values(4,1);
insert into stu_tea values(5,1);
insert into stu_tea values(1,2);
insert into stu_tea values(2,2);
insert into stu_tea values(3,2);
insert into stu_tea values(3,3);
insert into stu_tea values(4,3);
insert into stu_tea values(5,3);
select * from stu_tea;三、多表查询
多表查询分为 合并结果集、连接查询和子查询三种。
3.1合并结果集
要求两个结果集(注意这里强调的是结果集,而不是两张表)的列数、列类型完全相同。关键字union:去除重复行;关键字union all:不去除重复行。
create table student(
sid int primary key auto_increment,
sname varchar(50)
);
create table teacher (
tid int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(50)
);
create table stu_tea(
sid int,
tid int,
constraint fk_student foreign key(sid) references student(sid),
constraint fk_teacher foreign key(tid) references student(tid)
);
insert into student values(null,’刘德华’);
insert into student values(null,’梁朝伟);
insert into student values(null,’黄日华’);
insert into student values(null,’苗侨伟’);
insert into student values(null,’汤镇业’);
insert into teacher values(null,’崔老师’);
insert into teacher values(null,’刘老师’);
insert into teacher values(null,’石老师’);
insert into stu_tea values(1,1);
insert into stu_tea values(2,1);
insert into stu_tea values(3,1);
insert into stu_tea values(4,1);
insert into stu_tea values(5,1);
insert into stu_tea values(1,2);
insert into stu_tea values(2,2);
insert into stu_tea values(3,2);
insert into stu_tea values(3,3);
insert into stu_tea values(4,3);
insert into stu_tea values(5,3);
select * from stu_tea;
合并操作为:
select * from ab
union (all)
select * from cd;3.2连接查询
分为内连接和外连接,外链接又分为左外连接和右外连接。
3.2.1内连接
方言语法:select * from 表1 as 别名1,表2 as 别名2 where 别名1.xx=别名2.xx;例如:select * from emp,dept where emp.deptno=dept.deptno;去除无用行后的笛卡尔积,where后的条件是主外键。
标准语法:select * from 表1 as 别名1 inner join 表2 as 别名2,on 别名1.xx=别名2.xx;例如:select * from emp inner join dept on emp.deptno=dept.deptno; 就是把方言版的逗号改为inner join ,把where改为on了。
自然连接语法:select * from 表1 as 别名1 natural join 表2 as 别名2;自然连接特有的特点就是它能够自己找到两个表中相同的列 即自己填全where条件。
内连接的特点:内连接查询出的所有记录都是满足条件的记录,不满足条件的记录不显示出来。
3.2.2外连接
特点:外连接有一主一次。
左外连接左表为主,那么左表中所有的记录无论满足不满足条件,都打印出来。不满足条件的值用null填补。语法为:select * from emp left outer join dept on emp.deptno=dept.deptno;
右外连接右表为主,那么右表中所有的记录无论满足不满足条件,都打印出来。不满足条件的值用null填补。语法为:select * from amp right outer join dept on emp.deptno=dept.deptno;
* 无限极分类表设计问题:
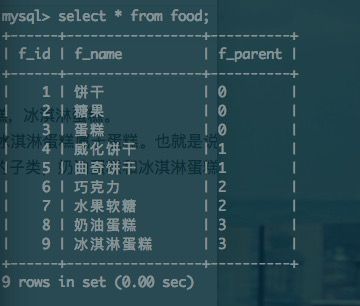
超市食品区卖各类食品 如饼干,糖果,蛋糕,威化饼干,曲奇饼干,巧克力,水果软糖,奶油蛋糕,冰淇淋蛋糕。
对这些商品进行分类,威化饼干、曲奇饼干属于饼干, 巧克力、水果软糖属于糖果,奶油蛋糕、冰淇淋蛋糕属于蛋糕。也就是说这些商品存在着父子的关系。即威化饼干和曲奇饼干是饼干的子类,巧克力和水果软糖是糖果的子类,奶油蛋糕和冰淇淋蛋糕是蛋糕的子类。
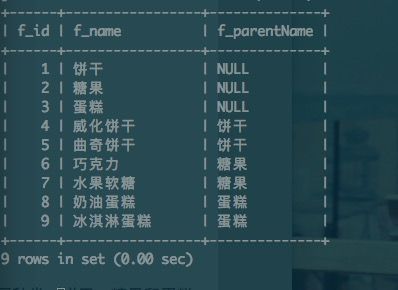
这是一个food表单。f_id表示食品的编号,f_name表示食品名称,f_parent表示食品所属种类(饼干、糖果和蛋糕没有所属种类,f_parent字段用0表示)。如果我们想更直观的去看商品所属类的名称而不是用编号表示,这时候就可以借助外连接来实现。效果如下:
原理:将1个food表单看成是2个表单,即1个看做左表(表1)1个看做右表(表2)。将表1表2左连接,查询表1的f_id和f_name字段以及表2的f_name字段(我这里在查询时将表2的f_name以f_parentName命名),条件是表2的f_name的f_id要与表1的f_parent一致。
代码如下:
foods | CREATE TABLE `foods` (
`f_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`f_name` char(30) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`f_parent` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`f_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=10 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci |
===================
插入记录 略
===================
select l.f_id,l.f_name,r.f_name as f_parentName from foods as l left join foods as r on l.f_parent=r.f_id;3.3子查询
子查询通俗来讲,就是查询中有查询。
例子:
/*查询本公司工资最高的员工的详细信息*/
select *
from amp
where sal=max(sal);
此种写法错误,因为where条件中不能有聚合函数。所以想到要用子查询。
思路:首先查出最高工资:select max(sal) from amp;然后查询该工资的员工:select * from amp where sal=刚刚的查询结果。所以合并起来为:select * from amp where sal=(select max(sal) from amp);
3.3.1子查询能出现的位置
where后作为条件(上述例子)
from后作为二次查询(下面例子)
select e.empno,e.ename from (select * from amp where deptno=30) as e where 条件;
3.3.2子查询的结果集
单行单列:select * from 表1 where 列1 [=、>、<、>=、<=、!=] (select 列 from 表2 where 条件);
多行单列:select * from 表1 where 列1 [=、>、<、>=、<=、!=] [any、all、in](select 列 from 表2 where 条件;
单行多列:select * from 表1 where (列1,列2) in (select 列1,列2 from 表2 where 条件);
多行多列:该结果集用在from后作为二次查询。select * from 表1,(select …) as 别名 where 条件;