ED-Join
此文需要结合ED-Join原paper一起阅读,本文提供了例子和笔记
定义
q-gram
按一个正整数q去切割字符串
q=2
s=abcd
变成q-gram
[ab,bc,cd] Set-Similarity Join
一般SSjoin
由于算edit distance需要的计算比较重
所以通常会通过以下filtering,减少需要对比的candidate pair,从而减少需要时间和计算资源
1.length filtering
如果两字符串长度差大于允许修改次数t,则t个修改内一定无法令两字符串相等
例子:
abc
abcde
则通过1个修改怎么也无法令两字符串相等
2.count filtering
通过t个修改最多可以令n个q-gram不相同
如果两个字符串之间存在大于n个q-gram不相同,则通过t个修改一定无法令两个字符串相同
n = (max(|t| ,|s|) - q + 1) - q t
(max(|t| ,|s|) - q + 1) 为最大q-gram数,qt为t个动作做多能改变的q-gram(当修改位置 iq i=1,2...的字符时候)
可以理解为在 所有q-gram里,t个操作最多修复q*t个gram
所以剩下的n个gram必须全部相同
例子:
q=2,t=1
n=(5 - 2 +1) - 2 * 1 = 2
s=abcde
[ab,bc,cd,de]
t=abbde
[ab,bb,bd,de]
至少有个n=2个gram相同,此例为ab,deq=2,t=2
n=(6 - 2 +1) - 2 * 2 = 1
s=abcdef
[ab,bc,cd,de,ef]
t=abbddf
[ab,bb,bd,dd,df]
至少有个n=1个gram相同,此例为ab3.prefix filtering
由于
A major performance bottleneck in is the generation of candidate pairs that share LBs;t matching q-grams.
所以引入prefix filtering
生成一个q·τ+1 的prefix,只对比prefix清除不匹配candidate
有引理
Lemma 1 (Prefix Filtering).
Let x and y be two qgram arrays and ed(str(x),str(y)) ≤ τ.
Then the (q·τ +1)-prefix of x and the (q · τ + 1)-prefix of y must have at least one matching q-gram.
若需要有n = (max(|t| ,|s|) - q + 1) - q t (count filtering)个gram相同
则前qt+1个 gram里一定至少要有一个gram相同
例子
q=2,t=1
s=abcde
[ab,bc,cd,de]
c=bbbde
[bb,bb,bd,de]
则prefix 2*1+1 3个gram里一定要有一个相同
而本例里前3个gram都不相同
所以可以除去t作为candidate的可能
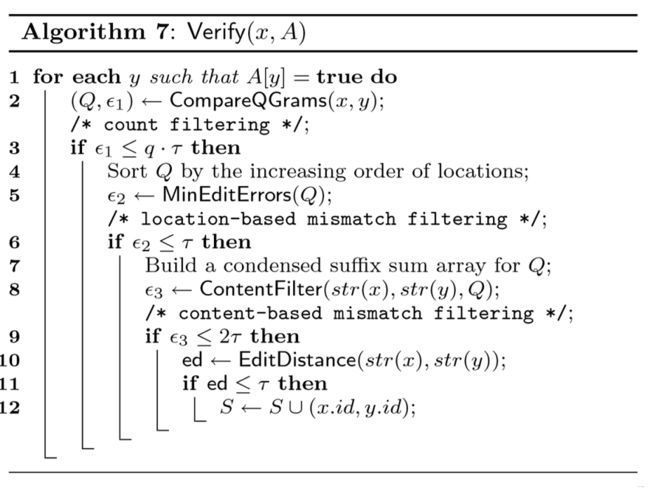
ED-Join
EDjoin提出了更好的filtering方法去达到减少candidata pair的结果
EDjoin提出了
Location-based Mismatch Filtering
这里定义一个问题
minimum edit errors problem
通过最少的操作次数e可以令一个字符串的所有q-gram都不一样
minimum edit errors problem又有两个属性
Proposition 2
(Monotonicity). min-err(Q) ≤ min-err(Q0), ∀Q ⊆ Q0
和
Proposition 3
ceil(|Q|/q) ≤ min-err(Q) ≤ |Q|
例子:
s=abcde
q=2
[ab,bc,cd,de]
#最少2个修改则可以令该字符串所有g-gram不相同
amcme
[am,mc,cm,me]
Proposition 3
ceil(4/2) = 2 ≤ 2 ≤ 4s=abcdef
q=2
[ab,bc,cd,de,ef]
#最少3个修改则可以令该字符串所有g-gram不相同
amcmem
[am,mc,cm,me,em]
ceil(5/2) = 3 ≤ 3 ≤ 5s=abcdef
q=3
[abc,bcd,cde,def]
#最少2个修改则可以令该字符串所有g-gram不相同
abmdem
[abm,bmd,mde,dem]
Proposition 3
ceil(4/3) = 2 ≤ 2 ≤ 4又有引理
Lemma 2.
Let x and y be two q-gram arrays, and let Q be the set of mismatching q-grams from x to y,
then ed(str(x),str(y)) ≥ min-err(Qp), ∀Qp ⊆ Q.
让我们回顾prefix-filtering
有可能在q*t个gram里面想令两个prefix相同需要做的e修改已经超过最大允许数 t
再根据Proposition 2
q-gram子集的min-err一定小于或等于q-gram全集的min-err,则子集不符合则全集也不符合
设字符串的某prefix长度为L的minimum edit errors为n
如果两个字符串的L长的prefix-gram全部不同则需要至少n个修改去令两字符串相同
当n>t时,则两字符串一定无法通过t次修改变相同
例子
q=3,t=1
prefix=3*1+1=4
s=abcdefgh
[abc,bcd,cde,def,efg,fgh]
prefix-s=[abc,bcd,cde,def]
t=abmmefgh
[abm,bmm,mme,mef,mfg,fgh]
prefix-t=[abm,bmm,mme,mef]则需要计算长度为4的prefix filtering
t=abcmefgh
[abm,bmm,mme,mef,mfg,fgh]
min-prefix-t=[abm,bmm,mme]
则根据min-err算出
若前3个gram没有任何一个gram相同则至少需要2个修改,大于允许的1个修改
所以这里只需要做长度为3的prefix filtering就可以排除该candidate pair
lication-based mismatch filtering更少的q-gram做prefix-filtering则可以除去不匹配的candidate pair所以
location-based mismatch filtering
可以被描述为
Lemma 3 (Location-based Mismatch Filtering).
Let the minimum prefix length for q-gram arrays x and y be lx and ly, respectively.
If ed(str(x),str(y)) ≤ τ, x’s lx-prefix and y’s ly-prefix must have at least one matching q-gram.由以上得
ED-Join的其中一个重要特点是
A shorter minimum prefix length is used instead of the standard prefix length required by prefix filtering. We note that this optimization is critical in reducing candidate size, a measure that is highly correlated to the overall join performance, in addition to other obvious benefits (e.g., smaller inverted index)
该方法比普通的prefix-filtering更优的地方是它检测的block数比其更少
Content-based Mismatch Filtering
定义
non-clustered edit errors
We define non-clustered edit errors to be a set of edit errors such that no two of them are within distance q
以上的 location-based mismatch filtering 对此类问题效果好
但相反地对于
clustered edit errors
效果则不好所以引入以下方法
content-based mismatch filtering
该方法引入定义
钻探窗口(probing windows)
A probing window w is an interval [w.s..w.e].
例子
abcdef
bcd是其中一个probing windows
定义频谱直方图Ht(frequency histogram)
Ht is a vector of size |Σ|,
where Ht[i] records the number of occurrences of a symbol σi ∈ Σ in t
例子
abbcce
[(a,1),(b,2),(c2),(e,1)]定义
The L1 distance between two n-dimensional vectors u and v is defined as Σ|u[i] − v[i]|.
例子
abbcce自己与自己对比的L1 distance为
dL1 = |1-1| + |2-2| + |2-2| + |1-1| = 0
因为字符串全等则dL1为0而且
It is obvious that each edit operation (insertion, deletion, and substitution) will contribute at most 2 to this L1 distance
例子
abbcce
[(a,1),(b,2),(c2),(e,1)]
abbcbe
[(a,1),(b,3),(c1),(e,1)]
dL1 = |1-1| + |2-3| + |2-1| + |1-1| = 2所以
Therefore, d0 ≥ dL1/2.
Finally, since the edit distance of the entire string d ≥ d0, we have d ≥ dL1/2.
当dL1为a
任何一个probing windows修改次数d0 大于等于a除以2
全字符串修改次数更加大于等于a除以2
则如果dL1已经大于最大允许修改次数t,则可以排除candidate可能
ContentFilter
选出所有mismatch的gram组成数组然后根据locaiton升序排序组成Q
然后对Q中的gram行遍历
算出两个mismatch gram 之间的L1distance
j ← 1; i ← 2;
2 while i ≤ |Q| do
3 if Q[i].loc − Q[i − 1].loc > 1 then
4 d = L1Distance(s, t, Q[j].loc, Q[i − 1].loc + q − 1) + SumRightErrs(Q[i − 1].loc + q);
5 if d > 2τ then
6 return 2τ + 1 /* early termination here */
7 j ← i;
8 i ← i + 1;
9 return L1Distance(s, t, Q[j].loc, Q[i − 1].loc + q − 1)
+ SumRightErrs(Q[i − 1].loc + q)再加上
最右边字符后面所有gram的min-err
若 L1distance/2 + min-err > t(threshold)
则除去该candidate
例子
q=2,t=2
s=abcdefg
[ab,bc,cd,de,ef,fg]
s=abmmefm
[ab,bm,mm,me,ef,fm]
mismatch grams
[bc,cd,de,fg]
[bm,mm,me,fm]
第一个probing window
2 to (3 + 2 - 1) = 2 to 4
bcd
[(b,1),(c,1),(d,1),(m,0)]
bmm
[(b,1),(c,0),(d,0),(m,2)]
dL1= |1-1| + |1-0| + |1-0| + |0-2| = 4
SumRightErrs(5) = 1 (5是e的location)
4/2 + 1 = 3 > 2
所以可以排除该candidate以上是一个probing window
综合以上得