B树索引学习总结。
题记:今天是2014-01-13,在春节之前打算把oracle索引技术深入研究一下,在此记录一下学习笔记。今天我学习的内容是B树索引知识。
B树索引深入总结。
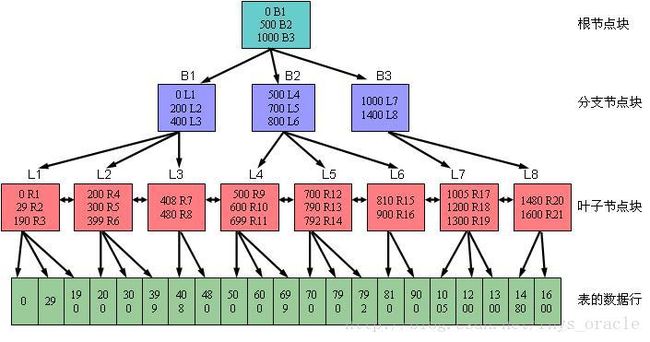
首先看一下网络上一个B树索引图,如下:
1、oracle如何使用B树索引?
B树索引有根节点块,分支节点块,叶子节点块组成。一般情况下B树索引是oracle默认创建索引使用的类型。使用B树索引可以提高数据的检索速度,可以强制执行主键和唯一键的约束性,对于减少通过主键和外键约束关联的父表和字表锁的问题。
当检索数据列位于索引指定列的时候,只需要访问索引块即可完成数据的展现,这非常提高数据的检索速率;
当检索数据列不完全位于索引指定列的时候,将会访问索引块以及数据块进而将数据进行展现;
最后一种是不适用索引,而是通过检索表块完成数据的检索;
下面分别对这三种情况进行试验说明:
NO.1:对于该情况所有字段都位于索引 段中,一般设计到index range scan表示要扫B树索引的叶子子节点一段数据;另一个是index fast full scan,表示要扫描所有索引的叶子子节点数据,一般用在count中如下:
SQL> create table emp(
2 empno number(4),
3 ename varchar2(10),
4 job varchar2(9),
5 mgr number(4),
6 hiredate date,
7 sal number(7,2),
8 comm number(7,2),
9 deptno number(2)
10 );
Table created.
SQL> create index emp_pk on emp(empno);
Index created.
SQL> insert into emp select * from scott.emp;
14 rows created.
SQL> insert into emp select * from scott.emp;
14 rows created.SQL> set autotrace trace
SQL> select empno from emp where empno=7369;
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 745440807
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 2 | 26 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 1 | INDEX RANGE SCAN| EMP_PK | 2 | 26 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - access("EMPNO"=7369)
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement (level=2)
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
22 recursive calls
0 db block gets
36 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
579 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
523 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
2 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
3 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
2 rows processed
SQL>
有个问题,在这个操作过程中,对应一下上图,该过程会扫描几个数据块?嘿嘿,可以思考一下。
以上图为例,每个大方框都代表一个数据块,那么如果要获得0号数据信息,那么就会读0B1数据块、B1数据块、L1数据块,如果为了确保L1数据都要验证是否满足需求因此需要读整个L1块的数据,这就是index range scan;
注意:
db block gets=db block gets from cache+db block gets direct
consistent gets=consistent gets from cache+consistent get direct
physical reads=physical reads cache+physical
在看一下index fast full scan:
SQL> select count(empno) from emp;
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3381701820
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 13 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | SORT AGGREGATE | | 1 | 13 | | |
| 2 | INDEX FULL SCAN| EMP_PK | 28 | 364 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement (level=2)
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
18 recursive calls
0 db block gets
34 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
530 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
523 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
2 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
3 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
1 rows processedno,貌似没有index fast full scan而是走了单块读的index full scan;
SQL> set autotrace trace
SQL> select /*+index_ffs(emp emp_pk)*/ count(empno) from emp;
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3578136827
------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | SORT AGGREGATE | | 1 | | |
| 2 | INDEX FAST FULL SCAN| EMP_PK | 14 | 2 (0)| 00:00:01 |
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement (level=2)
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
4 recursive calls
0 db block gets
23 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
530 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
523 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
2 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
1 rows processed
NO.2:部分列不存在索引列中。
SQL> select empno,ename,job from emp where empno=7369;
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 122628344
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 2 | 52 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| EMP | 2 | 52 | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
|* 2 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | EMP_PK | 2 | | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
2 - access("EMPNO"=7369)
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement (level=2)
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
7 recursive calls
0 db block gets
26 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
735 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
523 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
2 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
2 rows processed
SQL> 可以看到当查询列不存在于索引列的时候,将会通过rowid来对数据表进行访问数据,因为B数索引就是通过rowid和建立索引的列值组合的。注意当该表中存在多条记录的时候consistent gets并不能代表真正的数据块的一直性读,因为重新读取的块被收集在缓存区被钉住计数(buffer is pinned count)。
对于rowid的理解请参考我的另一篇笔记:
http://blog.csdn.net/rhys_oracle/article/details/11715735
NO。3:不适用索引的情况。
SQL> select * from emp;
28 rows selected.
Execution Plan
----------------------------------------------------------
Plan hash value: 3956160932
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 28 | 2436 | 6 (0)| 00:00:01 |
| 1 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| EMP | 28 | 2436 | 6 (0)| 00:00:01 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note
-----
- dynamic sampling used for this statement (level=2)
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
17 recursive calls
0 db block gets
54 consistent gets
0 physical reads
0 redo size
2411 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
534 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
3 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
3 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
28 rows processed这就是oracle cbo采用全表扫描方式。注意:有时候采用全表扫描可能比采用索引效率更高。
2、准备创建B树索引:
命名规则:
主键索引名应该包含表名和一个后缀,如:_PK;
唯一索引应该包含表名和一个后缀,如:_UKN,N代表一个数字;
外键索引应该包含外键表和一个后缀,如_FKN,N代表一个数字;
对于不适用约束的索引,适用表名和一个后缀,如_IDXN,N代表一个数字;
基于函数的索引的名称应该适用一个表名和一个后缀,如_FCN,N代表一个数字;
只所以采用这种命名方法是便于查看和便于问题分析。
估算索引大小;
因为当在一个大表上创建索引或是在一个业务量增长非常迅速的表上维护索引时,该索引同样需要消耗资源,当表空间资源不足的时候,就有可能导致数据库挂起。
对于估算索引一般采用如下步骤:
1、收集最新的表的统计信息
2、使用dbms_space.create_index_cost进行 索引估算。下面测试如
估算需要创建索引的大小,如下:
SQL> EXEC DBMS_STATS.gather_TABLE_STATS(OWNNAME=>'AMY',TABNAME=>'T',CASCADE=>TRUE);
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL> select index_name,table_name from user_indexes where table_name='T';
no rows selected
SQL> SET SERVEROUT ON
SQL> VAR USED_BYTES NUMBER
SQL> VAR ALLOC_BYTES NUMBER
SQL> EXEC DBMS_SPACE.CREATE_INDEX_COST('CREATE INDEX T_IDX1 ON T(A)',:USED_BYTES,:ALLOC_BYTES);
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL> PRINT USED_BYTES
USED_BYTES
----------
1135000
SQL> PRINT ALLOC_BYTES
ALLOC_BYTES
-----------
6291456
SQL> CREATE INDEX T_IDX1 ON T(A);
Index created.
SQL> SELECT SEGMENT_NAME,BYTES FROM USER_SEGMENTS WHERE SEGMENT_NAME='T_IDX1';
SEGMENT_NAME BYTES
-------------------- ----------
T_IDX1 4423680
SQL>
索引与表数据分离,单独创建表空间,这样可以单独维护索引如备份和恢复,但是减少i/0其实更应该放入不同的磁盘上面;
SQL> create tablespace reporting_index datafile '+DATAGROUP1' size 512M autoextend on next 1M maxsize 1G extent management local uniform size 128K segment space management auto nologging;
Tablespace created.
SQL> DROP INDEX T_IDX1;
Index dropped.
SQL> CREATE INDEX T_IDX1 ON T(A) TABLESPACE REPORTING_INDEX;
Index created.
SQL>
SQL> alter table emp add constraint emp_pk primary key(empno) using index tablespace reporting_index;
Table altered.
SQL> select index_name,table_name from user_indexes where table_name='EMP';
INDEX_NAME TABLE_NAME
------------------------------ ------------------------------
EMP_PK EMP
SQL> alter table emp add constraint emp_uk unique(empno,ename) using index tablespace reporting_index;
Table altered.
SQL> DROP INDEX EMP_IDX2;
Index dropped.
SQL> alter table dept add constraint dept_pk primary key(deptno) using index tablespace reporting_index;
Table altered.
SQL> CREATE INDEX EMP_IDX2 ON EMP(DEPTNO) TABLESPACE REPORTING_INDEX;
Index created.
SQL> select index_name,INDEX_TYPE,table_name,tablespace_name,status from user_indexes where table_name in('T','EMP','DEPT');
INDEX_NAME INDEX_TYPE TABLE_NAME TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ --------------------------- ------------------------------ ------------------------------ --------
T_IDX1 NORMAL T REPORTING_INDEX VALID
EMP_PK NORMAL EMP REPORTING_INDEX VALID
EMP_UK NORMAL EMP REPORTING_INDEX VALID
EMP_IDX2 NORMAL EMP REPORTING_INDEX VALID
DEPT_PK NORMAL DEPT REPORTING_INDEX VALID
SQL> col column_name for a20
SQL> col column_position for 9999
SQL> r
1* SELECT INDEX_NAME,COLUMN_NAME,COLUMN_POSITION FROM USER_ind_columns where table_name in ('T','EMP','DEPT') ORDER by index_name,column_position
INDEX_NAME COLUMN_NAME COLUMN_POSITION
------------------------------ -------------------- ---------------
DEPT_PK DEPTNO 1
EMP_IDX2 DEPTNO 1
EMP_PK EMPNO 1
EMP_UK EMPNO 1
EMP_UK ENAME 2
T_IDX1 A 1
6 rows selected.
SQL>
SQL>
修改索引状态:
SQL> alter index emp_idx2 invisible;
Index altered.
SQL> select index_name,status,visibility from user_indexes;
INDEX_NAME STATUS VISIBILIT
------------------------------ -------- ---------
EMP_UK VALID VISIBLE
EMP_PK VALID VISIBLE
EMP_IDX2 VALID INVISIBLE
DEPT_PK VALID VISIBLE
T_IDX1 VALID VISIBLE
SQL> alter index emp_idx2 visible;
Index altered.
SQL> select index_name,status,visibility from user_indexes;
INDEX_NAME STATUS VISIBILIT
------------------------------ -------- ---------
EMP_UK VALID VISIBLE
EMP_PK VALID VISIBLE
EMP_IDX2 VALID VISIBLE
DEPT_PK VALID VISIBLE
T_IDX1 VALID VISIBLE
SQL>
SQL> alter index emp_idx2 unusable;
Index altered.
SQL> select index_name,status,visibility from user_indexes;
INDEX_NAME STATUS VISIBILIT
------------------------------ -------- ---------
EMP_UK VALID VISIBLE
EMP_PK VALID VISIBLE
EMP_IDX2 UNUSABLE VISIBLE
DEPT_PK VALID VISIBLE
T_IDX1 VALID VISIBLE
SQL> alter index emp_idx2 rebuild;
Index altered.
SQL> select index_name,status,visibility from user_indexes;
INDEX_NAME STATUS VISIBILIT
------------------------------ -------- ---------
EMP_UK VALID VISIBLE
EMP_PK VALID VISIBLE
EMP_IDX2 VALID VISIBLE
DEPT_PK VALID VISIBLE
T_IDX1 VALID VISIBLE
SQL>
SQL>
SQL>
判断外键索引是否存在:
方法一:
SET VERIFY OFF;
SET LINESIZE 200;
COL IND_COLUMN FOR A25;
COL CONS_COLUMN FOR A25;
COL TAB_NAME FOR A20;
COL OWNER FOR A25;
select distinct a.owner owner,
a.constraint_name cons_name,
a.table_name tab_name,
b.column_name cons_column,
nvl(c.column_name, '***Check index****') ind_column,
c.index_name
from dba_constraints a, dba_cons_columns b, dba_ind_columns c
where constraint_type = 'R'
and a.owner = upper('&&user_name')
and a.owner = b.owner
and a.constraint_name = b.constraint_name
and b.column_name = c.column_name(+)
and b.table_name = c.table_name(+)
and b.position = c.column_position(+)
order by tab_name, ind_column;
#############################
SQL> conn amy/rhys
Connected.
SQL> drop index emp_idx2;
Index dropped.
SQL> conn sys/root as sysdba
Connected.
SQL> SET VERIFY OFF;
SET LINESIZE 200;
SQL> SQL> COL IND_COLUMN FOR A25;
SQL> COL CONS_COLUMN FOR A25;
SQL> COL TAB_NAME FOR A20;
SQL> COL OWNER FOR A25;
SQL> select distinct a.owner owner,
2 a.constraint_name cons_name,
3 a.table_name tab_name,
b.column_name cons_column,
4 5 nvl(c.column_name, '***Check index****') ind_column,
6 c.index_name
7 from dba_constraints a, dba_cons_columns b, dba_ind_columns c
8 where constraint_type = 'R'
9 and a.owner = upper('&&user_name')
10 and a.owner = b.owner
11 and a.constraint_name = b.constraint_name
12 and b.column_name = c.column_name(+)
13 and b.table_name = c.table_name(+)
14 and b.position = c.column_position(+)
15 order by tab_name, ind_column;
OWNER CONS_NAME TAB_NAME CONS_COLUMN IND_COLUMN INDEX_NAME
------------------------- ------------------------------ -------------------- ------------------------- ------------------------- ------------------------------
AMY EMP_FK EMP DEPTNO ***Check index****
SQL> SQL>
方法一只是判断用户,对于单列约束。如下判断多列约束,另外还可以检测外键上的位图索引的存在,位图索引不能防止锁的发生;
####################3
col cols for a30;
col index_type for a10;
SET VERIFY OFF;
SET LINESIZE 200;
COL IND_COLUMN FOR A25;
COL CONS_COLUMN FOR A25;
COL index_NAME FOR A20;
COL OWNER FOR A25;
select case
when ind.index_name is not null then
case
when ind.index_type in ('BITMAP') then
'**Bitmp idx**'
else
'indexed'
end
else
'**Check idx**'
end checker,
ind.index_type,
cons.owner,
cons.table_name,
ind.index_name,
cons.constraint_name,
cons.cols
from (select c.owner,
c.table_name,
c.constraint_name,
listagg(cc.column_name, ',') within group(order by cc.column_name) cols
from dba_constraints c, dba_cons_columns cc
where c.owner = cc.owner
and c.owner = upper('&&schema')
and c.constraint_name = cc.constraint_name
and c.constraint_type = 'R'
group by c.owner, c.table_name, c.constraint_name) cons
left outer join (select table_owner,
table_name,
index_name,
index_type,
cbr,
listagg(column_name, ',') within group(order by column_name) cols
from (select ic.table_owner,
ic.table_name,
ic.index_name,
ic.column_name,
ic.column_position,
i.index_type,
connect_by_root(ic.column_name) cbr
from dba_ind_columns ic, dba_indexes i
where ic.table_owner = upper('&&schema')
and ic.table_owner = i.table_owner
and ic.table_name = i.table_name
and ic.index_name = i.index_name
connect by prior ic.column_position - 1 =
ic.column_position
and prior ic.index_name = ic.index_name)
group by table_owner,
table_name,
index_name,
index_type,
cbr) ind
on cons.cols = ind.cols
and cons.table_name = ind.table_name
and cons.owner = ind.table_owner
order by checker, cons.owner, cons.table_name;
#############################
eg:
SQL> col cols for a30;
SQL> col index_type for a10;
SQL> SET VERIFY OFF;
SQL> SET LINESIZE 200;
COL IND_COLUMN FOR A25;
SQL> SQL> COL CONS_COLUMN FOR A25;
SQL> COL index_NAME FOR A20;
SQL> COL OWNER FOR A25;
SQL> select case
2 when ind.index_name is not null then
3 case
4 when ind.index_type in ('BITMAP') then
5 '**Bitmp idx**'
6 else
'indexed'
7 8 end
9 else
10 '**Check idx**'
end checker,
11 12 ind.index_type,
13 cons.owner,
14 cons.table_name,
15 ind.index_name,
16 cons.constraint_name,
17 cons.cols
18 from (select c.owner,
19 c.table_name,
20 c.constraint_name,
21 listagg(cc.column_name, ',') within group(order by cc.column_name) cols
22 from dba_constraints c, dba_cons_columns cc
where c.owner = cc.owner
23 24 and c.owner = upper('&&schema')
25 and c.constraint_name = cc.constraint_name
26 and c.constraint_type = 'R'
27 group by c.owner, c.table_name, c.constraint_name) cons
28 left outer join (select table_owner,
29 table_name,
30 index_name,
31 index_type,
32 cbr,
33 listagg(column_name, ',') within group(order by column_name) cols
34 from (select ic.table_owner,
35 ic.table_name,
36 ic.index_name,
37 ic.column_name,
38 ic.column_position,
39 i.index_type,
40 connect_by_root(ic.column_name) cbr
41 from dba_ind_columns ic, dba_indexes i
42 where ic.table_owner = upper('&&schema')
43 and ic.table_owner = i.table_owner
44 and ic.table_name = i.table_name
45 and ic.index_name = i.index_name
46 connect by prior ic.column_position - 1 =
47 ic.column_position
48 and prior ic.index_name = ic.index_name)
49 group by table_owner,
50 table_name,
51 index_name,
52 index_type,
53 cbr) ind
54 on cons.cols = ind.cols
55 and cons.table_name = ind.table_name
56 and cons.owner = ind.table_owner
57 order by checker, cons.owner, cons.table_name;
CHECKER INDEX_TYPE OWNER TABLE_NAME INDEX_NAME CONSTRAINT_NAME COLS
------------- ---------- ------------------------- ------------------------------ -------------------- ------------------------------ ------------------------------
**Check idx** AMY EMP EMP_FK DEPTNO
SQL> SQL>