Android4.4之Keyguard--KeyguardUpdateMonitor
KeyguardUpdateMonitor是典型的观察者模式的应用,涉及的类还有KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback及其多个子类。
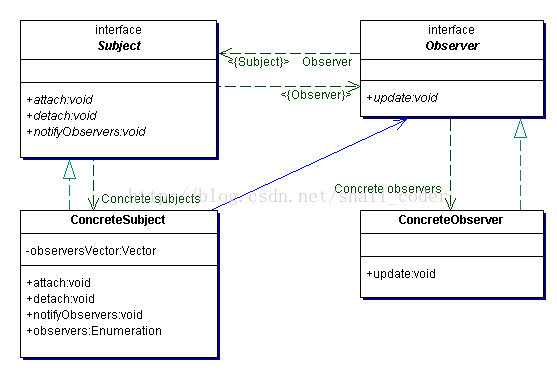
首先,来简单看看观察者模式:
下面是网上别人浅析观察者模式的截图,这里借用一下(原文地址:http://www.blogjava.net/supercrsky/articles/202544.html)。
抽象主题(Subject)角色:主题角色把所有的观察者对象的引用保存在一个列表里;每个主题都可以有任何数量的观察者。主题提供一个接口可以加上或撤销观察者对象;主题角色又叫做抽象被观察者(Observable)角色;
抽象观察者(Observer)角色:为所有的具体观察者定义一个接口,在得到通知时更新自己;
具体主题(ConcreteSubject)角色:保存对具体观察者对象有用的内部状态;在这种内部状态改变时给其观察者发出一个通知;具体主题角色又叫作具体被观察者角色;
具体观察者(ConcreteObserver)角色:保存一个指向具体主题对象的引用;和一个与主题的状态相符的状态。具体观察者角色实现抽象观察者角色所要求的更新自己的接口,以便使本身的状态与主题的状态自恰。
下面说说keyguard中的观察者模式:
没有抽象主题角色;
只有一个具体主题角色,就是KeyguardUpdateMonitor;
有抽象观察者角色,就是KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback,不过它不止有一个update方法,它有23个方法,也就是它观察很多事情,且KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback是一个类,不是接口,也不是抽象类;
有很多具体观察者角色,后面再详细介绍。
下面先说具体主题角色:KeyguardUpdateMonitor
由mCallbacks来保存所有的具体观察者角色,可以通过registerCallback和removeCallback方法来实现具体观察者角色添加和删除。
//这里的mCallbacks保存所有的观察者实例
private final ArrayList> mCallbacks = Lists.newArrayList();
public void registerCallback(KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback callback) {
// Prevent adding duplicate callbacks(这里只是为了阻止重复添加观察者实例)
for (int i = 0; i < mCallbacks.size(); i++) {
if (mCallbacks.get(i).get() == callback) {
if (DEBUG) Log.e(TAG, "Object tried to add another callback",
new Exception("Called by"));
return;
}
}
//核心在这里,就是把callback添加到mCallbacks中
mCallbacks.add(new WeakReference(callback));
removeCallback(null); // remove unused references
//对于新添加的观察者,调用sendUpdates方法去更新,这个方法的具体实现先跳过
sendUpdates(callback);
}
public void removeCallback(KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback callback) {
//把callback从mCallbacks中remove掉
for (int i = mCallbacks.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (mCallbacks.get(i).get() == callback) {
mCallbacks.remove(i);
}
}
}
再看抽象观察者角色:KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback
class KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback {
private static final long VISIBILITY_CHANGED_COLLAPSE_MS = 1000;
private long mVisibilityChangedCalled;
private boolean mShowing;
void onRefreshBatteryInfo(KeyguardUpdateMonitor.BatteryStatus status) { }
void onTimeChanged() { }
void onRefreshCarrierInfo(CharSequence plmn, CharSequence spn, int simId) { }
void onRingerModeChanged(int state) { }
void onPhoneStateChanged(int phoneState) { }
void onKeyguardVisibilityChanged(boolean showing) { }
void onKeyguardVisibilityChangedRaw(boolean showing) {
final long now = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
if (showing == mShowing
&& (now - mVisibilityChangedCalled) < VISIBILITY_CHANGED_COLLAPSE_MS) return;
onKeyguardVisibilityChanged(showing);
mVisibilityChangedCalled = now;
mShowing = showing;
}
void onClockVisibilityChanged() { }
void onDeviceProvisioned() { }
void onDevicePolicyManagerStateChanged() { }
void onUserSwitching(int userId) { }
void onUserSwitchComplete(int userId) { }
void onSimStateChanged(IccCardConstants.State simState, int simId) {}
void onUserRemoved(int userId) { }
void onUserInfoChanged(int userId) { }
void onBootCompleted() { }
void onMusicClientIdChanged(int clientGeneration, boolean clearing, PendingIntent intent) { }
public void onMusicPlaybackStateChanged(int playbackState, long eventTime) { }
void onEmergencyCallAction() { }
public void onSetBackground(Bitmap bitmap) { }
public void onScreenTurnedOn() { }
public void onScreenTurnedOff(int why) { }
void onSearchNetworkUpdate(int simId, boolean switchOn) { }
void onDockStatusUpdate(int dockState) { }
}我觉得有两个原因:其一,留意到onKeyguardVisibilityChangedRaw这个方法已经被实现,所以它不能是接口;其二,这里要观察很多的状态改变,包括电量、sim卡、音乐状态、屏幕点亮或点灭等,而具体的观察着一般并不会同时观察所有这些变化并做相应处理,如果这里是个接口,那么每一个具体观察者都需要实现一些自己并不需要观察的变化(当然一般是空的实现)。
为何也不是抽象类呢?
个人猜测这里由于前面提到的第二个原因,并不确定某个具体观察者会观察哪些改变,所以哪个方法都不好设置为abstract,既然没有一个abstract方法,那又何必设置为抽象类呢。
最后来看看具体观察者:很多,分布在各个文件中。
CameraWidgetFrame.java CarrierText.java(被MediatekCarrierText.java取代)EmergencyButton.java KeyguardDialogManager.java
KeyguardFaceUnlockView.java KeyguardHostView.java
KeyguardMessageArea.java KeyguardSelectorView.java
KeyguardSimPinPukView.java KeyguardStatusView.java
KeyguardTransportControlView.java KeyguardViewManager.java
KeyguardViewMediator.java KeyguardVoiceUnlockView.java
KeyguardWidgetFrame.java
这么列举也不能帮助我们理解的更深,不过再详细的分析也没有必要,需要的再细看到底需要监视哪些状态的改变以及如何处理吧。
最后,我们再去看看具体主题角色KeyguardUpdateMonitor的更具体的内部细节:
//从这个例子我们可以看到具体主题角色是如何通知具体观察角色更新的:遍历并调用所有callback的onScreenTurnedOn方法
protected void handleScreenTurnedOn() {
final int count = mCallbacks.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback cb = mCallbacks.get(i).get();
if (cb != null) {
cb.onScreenTurnedOn();
}
}
}
//这个例子也一样,只是需要做一些处理,比如要保存当前状态到BatteryStatus mBatteryStatus[]中
//还需要通过isBatteryUpdateInteresting方法来判断是否有通知具体观察者更新的必要,有必要的话才会更新
//无一例外地,其它的变化都是通过这种方式被通知到具体观察者的
private void handleBatteryUpdate(BatteryStatus status) {
final int idx = status.index;
final boolean batteryUpdateInteresting = isBatteryUpdateInteresting(mBatteryStatus[idx], status);
mBatteryStatus[idx] = status;
if (batteryUpdateInteresting) {
for (int i = 0; i < mCallbacks.size(); i++) {
KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback cb = mCallbacks.get(i).get();
if (cb != null) {
cb.onRefreshBatteryInfo(status);
}
}
}
}Handler mHandler负责根据Message中不同的what信息分发并调用这些handleXXX方法,所以关键是什么时候mHandler会接收到什么样的消息。
但有两个例外:onSetBackground和onSearchNetworkUpdate不是由mHandler来处理的,这里我们先说说这两个特例:
首先,onSearchNetworkUpdate
Called When network searching status changed (MTK 添加的)
private KeyguardUpdateMonitor(Context context)中会调用initMembers,然后是initPhoneStateListener,然后会调用onSearchNetworkUpdate。
它的实现(具体观察者)只有一处:MediatekCarrierText(替换了Android原生的CarrierText)。
其次,onSetBackground
Called when the transport background changes
在KeyguardHostView.java的ensureTransportPresentOrRemoved,和KeyguardTransportControlView.java的populateMetadata有调用。
具体实现类也只有一个:KeyguardViewManager.java
private KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback mBackgroundChanger = new KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback() {
@Override
public void onSetBackground(Bitmap bmp) {
mKeyguardHost.setCustomBackground(bmp != null ?
new BitmapDrawable(mContext.getResources(), bmp) : null);
updateShowWallpaper(bmp == null);
}
};说完了这两个特例,下面来看通过mHandler处理的其它观察对象吧。
在这部分中,他们的特点是:当某事件发生时(或某些方法被调用时),发送一个消息到mHandler中,mHandler根据what信息去调用handleXXX方法。
这些触发向mHandler中发送消息的事件是什么呢?有两类:一是KeyguardUpdateMonitor监听到的各种广播事件,二是其它的非广播事件。
下面先看第一类,广播事件(共11个):
Intent.ACTION_TIME_TICK Intent.ACTION_TIME_CHANGED Intent.ACTION_TIMEZONE_CHANGED
MSG_TIME_UPDATE handleTimeUpdate
TelephonyIntents.SPN_STRINGS_UPDATED_ACTION
MSG_CARRIER_INFO_UPDATE
handleCarrierInfoUpdate
Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED
MSG_BATTERY_UPDATE
handleBatteryUpdate
TelephonyIntents.ACTION_SIM_STATE_CHANGED CellConnMgr.ACTION_UNLOCK_SIM_LOCK
MSG_SIM_STATE_CHANGE
handleSimStateChange
AudioManager.RINGER_MODE_CHANGED_ACTION
MSG_RINGER_MODE_CHANGED
handleRingerModeChange
TelephonyManager.ACTION_PHONE_STATE_CHANGED
MSG_PHONE_STATE_CHANGED
handlePhoneStateChanged
DevicePolicyManager.ACTION_DEVICE_POLICY_MANAGER_STATE_CHANGED
MSG_DPM_STATE_CHANGED
handleDevicePolicyManagerStateChanged
Intent.ACTION_USER_REMOVED
MSG_USER_REMOVED
handleUserRemoved
Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED
MSG_BOOT_COMPLETED
handleBootCompleted
ACTION_SMARTBOOK_PLUG
MSG_DOCK_STATUS_UPDATE
handleDockStatusUpdate
Intent.ACTION_USER_INFO_CHANGED
MSG_USER_INFO_CHANGED
handleUserInfoChanged
第二类:非监听广播事件(共10个)
MSG_DEVICE_PROVISIONED handleDeviceProvisioned
//在KeyguardUpdateMonitor唯一的构造方法中有如下代码(KeyguardUpdateMonitor是单例模式)
if (!mDeviceProvisioned) {
watchForDeviceProvisioning();
}
private void watchForDeviceProvisioning() {
//监听器--检测到数据库中数据改变后则判断是否有必要发送消息到mHandler中
mDeviceProvisionedObserver = new ContentObserver(mHandler) {
public void onChange(boolean selfChange) {
super.onChange(selfChange);
mDeviceProvisioned = isDeviceProvisionedInSettingsDb();
if (mDeviceProvisioned) {
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MSG_DEVICE_PROVISIONED);
}
}
};
//注册监听数据库中数据的改变
mContext.getContentResolver().registerContentObserver(
Settings.Global.getUriFor(Settings.Global.DEVICE_PROVISIONED),
false, mDeviceProvisionedObserver);
......
}
protected void handleDeviceProvisioned() {
//通知具体监听器更新状态
for (int i = 0; i < mCallbacks.size(); i++) {
KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback cb = mCallbacks.get(i).get();
if (cb != null) {
cb.onDeviceProvisioned();
}
}
//??不懂这里为何要把对数据库的监听取消,难道这个数据在关机前不会再改变??
if (mDeviceProvisionedObserver != null) {
mContext.getContentResolver().unregisterContentObserver(mDeviceProvisionedObserver);
mDeviceProvisionedObserver = null;
}
}
MSG_USER_SWITCHING handleUserSwitching
MSG_USER_SWITCH_COMPLETE handleUserSwitchComplete
//在KeyguardUpdateMonitor唯一的构造方法中有如下代码(KeyguardUpdateMonitor是单例模式)
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().registerUserSwitchObserver(new IUserSwitchObserver.Stub() {
@Override
public void onUserSwitching(int newUserId, IRemoteCallback reply) {
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_USER_SWITCHING, newUserId, 0, reply));
mSwitchingUser = true;
}
@Override
public void onUserSwitchComplete(int newUserId) throws RemoteException {
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_USER_SWITCH_COMPLETE, newUserId));
mSwitchingUser = false;
}
});
MSG_SET_CURRENT_CLIENT_ID handleSetGenerationId
MSG_SET_PLAYBACK_STATE handleSetPlaybackState
private final IRemoteControlDisplay.Stub mRemoteControlDisplay = new IRemoteControlDisplay.Stub() {
public void setPlaybackState(int generationId, int state, long stateChangeTimeMs, long currentPosMs, float speed) {
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_SET_PLAYBACK_STATE, generationId, state, stateChangeTimeMs);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
......
public void setCurrentClientId(int clientGeneration, PendingIntent mediaIntent, boolean clearing) throws RemoteException {
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_SET_CURRENT_CLIENT_ID, clientGeneration, (clearing ? 1 : 0), mediaIntent);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
};
protected void handleBootCompleted() {
if (mBootCompleted) return;
mBootCompleted = true;
//在开机完成后注册RemoteControlDisplay
mAudioManager = new AudioManager(mContext);
mAudioManager.registerRemoteControlDisplay(mRemoteControlDisplay);
for (int i = 0; i < mCallbacks.size(); i++) {
KeyguardUpdateMonitorCallback cb = mCallbacks.get(i).get();
if (cb != null) {
cb.onBootCompleted();
}
}
}
MSG_SCREEN_TURNED_OFF handleScreenTurnedOff
MSG_SCREEN_TURNED_ON handleScreenTurnedOn
public void dispatchScreenTurnedOn() {
synchronized (this) {
mScreenOn = true;
}
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MSG_SCREEN_TURNED_ON);
}
public void dispatchScreenTurndOff(int why) {
synchronized(this) {
mScreenOn = false;
}
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_SCREEN_TURNED_OFF, why, 0));
}
KeyguardViewMediator.java
onScreenTurnedOn和onScreenTurnedOff方法中会调用dispatchScreenTurndOff和dispatchScreenTurnedOn
MSG_REPORT_EMERGENCY_CALL_ACTION handleReportEmergencyCallAction
/**
* Report that the emergency call button has been pressed and the emergency dialer is about to be displayed.
* @param bypassHandler runs immediately.
* NOTE: Must be called from UI thread if bypassHandler == true.
*/
public void reportEmergencyCallAction(boolean bypassHandler) {
if (!bypassHandler) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_REPORT_EMERGENCY_CALL_ACTION).sendToTarget();
} else {
handleReportEmergencyCallAction();
}
}
//EmergencyButton.java
//public class EmergencyButton extends Button
protected void onFinishInflate() {
......
setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
takeEmergencyCallAction();
}
});
......
}
MSG_KEYGUARD_VISIBILITY_CHANGED handleKeyguardVisibilityChanged
public void sendKeyguardVisibilityChanged(boolean showing) {
if (mNewClientRegUpdateMonitor || showing != mShowing) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "sendKeyguardVisibilityChanged(" + showing + ")");
Message message = mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_KEYGUARD_VISIBILITY_CHANGED);
message.arg1 = showing ? 1 : 0;
message.sendToTarget();
mNewClientRegUpdateMonitor = false;
mShowing = showing;
}
}
KeyguardViewMediator.java setHidden方法
MSG_CLOCK_VISIBILITY_CHANGED handleClockVisibilityChanged
public void reportClockVisible(boolean visible) {
mClockVisible = visible;
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_CLOCK_VISIBILITY_CHANGED).sendToTarget();
}
//??让人费解的是,没有发现代码中哪里有调用reportClockVisible这个方法??