#coding=utf-8
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
#使用requests抓取页面内容,并将响应赋值给page变量
html = requests.get('https://www.qiushibaike.com/text/')
#使用content属性获取页面的源页面
#使用BeautifulSoap解析,吧内容传递到BeautifulSoap类
soup = BeautifulSoup(html.content,'lxml')
links = soup.find_all('div',class_='content')
#link的内容就是div,我们取它的span内容就是我们需要段子的内容
for link in links:
print link.span.get_text()运行结果:
2. select()方法
可以按标签逐层查找到我们需要的内容,这点特别方便,就是定位,避免了单一的标签无法定位到我们所需要的内容元素。
soup.select("html head title") #标签层级查找
soup.select("td div a") #标签路径 td-->div-->a
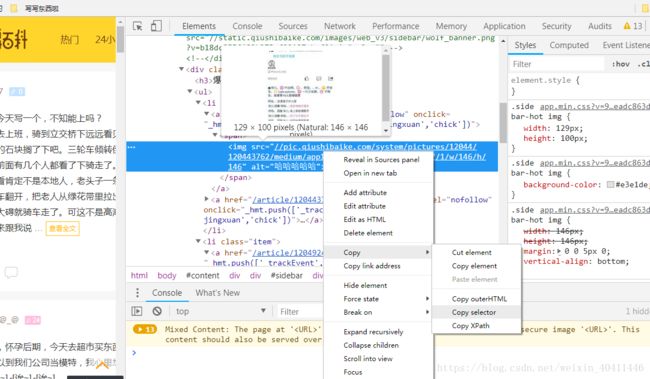
soup.select('td > div > a') #note:推荐使用这种记法选择谷歌浏览器,右键copy --copy selector
赋值得到内容:
#qiushi_tag_120529403 > a > div > span:nth-child(1)
对于这个内容要改一下~按照标签顺序去搜索
div > a > div > span (我运行的时候发现一个问题,> 前后一定要有空格,不然会报错的)
然后代码如下:(和前面的代码区别只有后三行)
#coding=utf-8
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
#使用requests抓取页面内容,并将响应赋值给page变量
html = requests.get('https://www.qiushibaike.com/text/')
#使用content属性获取页面的源页面
#使用BeautifulSoap解析,吧内容传递到BeautifulSoap类
soup = BeautifulSoup(html.content,'lxml')
#我是分隔符,下面就是select()方法咯~
links = soup.select('div > a >div >span')
for link in links:
print link.get_text()运行结果:
啊哦~是不是发现和上面运行结果不一样,这里还匹配到了评论,所以:
我们还要对定位进行修改,让它更精确,改成从标签a 开始,并且加上它的class属性。a.contentHerf 是在select方法中的写法。
具体是这样的: a.contentHerf > div > span (把它改到代码第三行再运行就好了~)
note:1)例子只介绍了抓取一页的内容
2)代码都是在python2.7中运行的
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40411446/article/details/80713339
======================================================================
【笔记】
Tips:TypeError: object of type 'Response' has no len()
源代码:
url = 'https://www.imooc.com/course/list?c=python'
wb_data = requests.get(url)
Soup = BeautifulSoup(wb_data, 'lxml', from_encoding='utf-8')出现错误的原因是因为这里的wb_data是requests对象,无法用BeautifulSoup解析,可以在wb_data后面加上content
Soup = BeautifulSoup(wb_data.content, 'lxml', from_encoding='utf-8')即可
Tips:python3中request.urlopen()和requests.get()方法的区别
urlopen打开URL网址,url参数可以是一个字符串url或者是一个Request对象,返回的是http.client.HTTPResponse对象.http.client.HTTPResponse对象大概包括read()、readinto()、getheader()、getheaders()、fileno()、msg、version、status、reason、debuglevel和closed函数,其实一般而言使用read()函数后还需要decode()函数
requests.get()方法请求了站点的网址,然后打印出了返回结果的类型,状态码,编码方式,Cookies等内容。返回一个Response对象,这个对象里面存的是服务器返回的所有信息,包括响应头,响应状态码等。其中返回的网页部分会存在.content和.text两个对象中。text返回的是Unicode型的数据 ,content返回的是是二进制的数据。 也就是说,如果你想取文本,可以通过r.text。 如果想取图片,文件,则可以通过r.content
经验:请求网页的三种方式
# 网页下载器代码示例
2 import urllib
3
4 url = "http://www.baidu.com"
5
6 print("第一种方法: 直接访问url")
7 response1 = urllib.request.urlopen(url)
8 print(response1.getcode()) # 状态码
9 print(len(response1.read())) # read读取utf-8编码的字节流数据
10
11 print("第二种方法: 设置请求头,访问Url")
12 request = urllib.request.Request(url) # 请求地址
13 request.add_header("user-agent", "mozilla/5.0") # 修改请求头
14 response2 = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
15 print(response2.getcode())
16 print(len(response2.read()))
17
18 import http.cookiejar # 不知道这是啥
19
20 print("第三种方法: 设置coockie,返回的cookie")
21 # 第三种方法的目的是为了获取浏览器的cookie内容
22 cj = http.cookiejar.CookieJar()
23 opener = urllib.request.build_opener(urllib.request.HTTPCookieProcessor(cj))
24 urllib.request.install_opener(opener)
25 response3 = urllib.request.urlopen(url)
26 print(response3.getcode())
27 print(len(response3.read()))
28 print(cj) # 查看cookie的内容Tips:Python如何提取td中的内容
import re
m = re.findall(r'(.*?) ', lines, re.I|re.M)
if m:
for x in m:
print x