Leetcode 304 二维区域和检索 - 矩阵不可变 C++,Java,Python
Leetcode304 二维区域和检索 - 矩阵不可变
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/range-sum-query-2d-immutable/
博主Github:https://github.com/GDUT-Rp/LeetCode
![]()
题目:
给定一个二维矩阵,计算其子矩形范围内元素的总和,该子矩阵的左上角为 (row1, col1) ,右下角为 (row2, col2)。
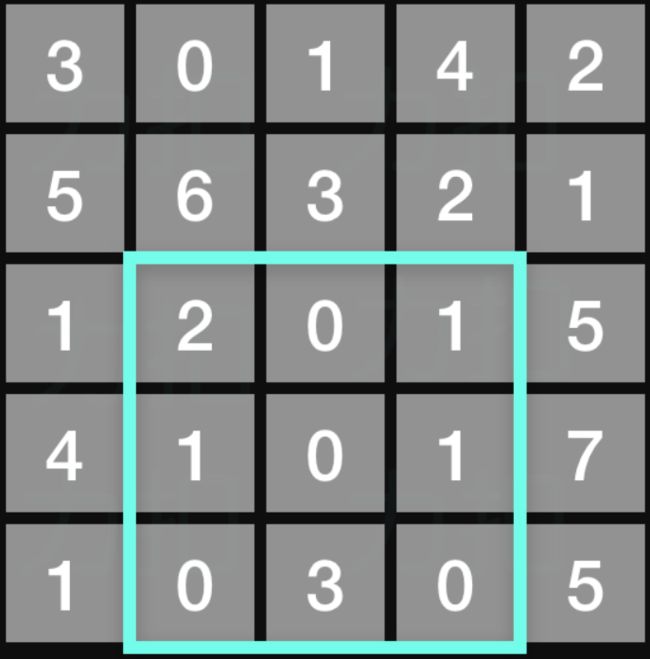
上图子矩阵左上角 (row1, col1) = (2, 1) ,右下角(row2, col2) = **(4, 3),**该子矩形内元素的总和为 8。
示例 1:
给定 matrix = [
[3, 0, 1, 4, 2],
[5, 6, 3, 2, 1],
[1, 2, 0, 1, 5],
[4, 1, 0, 1, 7],
[1, 0, 3, 0, 5]
]
sumRegion(2, 1, 4, 3) -> 8
sumRegion(1, 1, 2, 2) -> 11
sumRegion(1, 2, 2, 4) -> 12
说明:
- 你可以假设矩阵不可变。
- 会多次调用 sumRegion 方法*。*
- 你可以假设 row1 ≤ row2 且 col1 ≤ col2。
解题思路:
方法一:缓存
直观想法
尝试将二维矩阵视为一维数组的 m m m 行。为了找到区域和,我们只需要在区域中逐行累积和。
C++
class NumMatrix {
public:
vector<vector<int>> dp;
NumMatrix(vector<vector<int>> &matrix) {
if (matrix.size() == 0 || matrix[0].size() == 0)
return;
dp = vector<vector<int>>(matrix.size(), vector<int>(matrix[0].size() + 1, 0));
for (int r = 0; r < matrix.size(); ++r) {
for (int c = 0; c < matrix[0].size(); ++c) {
dp[r][c + 1] = dp[r][c] + matrix[r][c];
}
}
}
int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
int sum = 0;
for (int row = row1; row <= row2; ++row) {
sum += (dp[row][col2 + 1] - dp[row][col1]);
}
return sum;
}
};
Java
private int[][] dp;
public NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) return;
dp = new int[matrix.length][matrix[0].length + 1];
for (int r = 0; r < matrix.length; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < matrix[0].length; c++) {
dp[r][c + 1] = dp[r][c] + matrix[r][c];
}
}
}
public int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
int sum = 0;
for (int row = row1; row <= row2; row++) {
sum += dp[row][col2 + 1] - dp[row][col1];
}
return sum;
}
Python
class NumArray:
def __init__(self, nums: List[int]):
def sumRange(self, i: int, j: int) -> int:
# Your NumArray object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = NumArray(nums)
# param_1 = obj.sumRange(i,j)
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:每次查询的时间 O ( m ) O(m) O(m)。 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn) 时间预计算。构造函数中的预计算需要 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn) 时间。sumregion 查询需要 O ( m ) O(m) O(m) 时间。
空间复杂度: O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn)。该算法使用 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn) 空间存储所有行的累积和。
方法二:缓存
我们在一维版本中使用了累积和数组。我们注意到累积和是根据索引 0 处的原点计算的。将这个类比扩展到二维情况,我们可以预先计算出一个与原点相关的累积区域和,即 (0,0)。

Sum(OD)是相对于原点(0,0)的累计区域和。
如何使用预先计算的累积区域和得出 S u m ( A B C D ) Sum(ABCD) Sum(ABCD) 呢?

Sum(OB)是矩形顶部的累积区域和。

Sum(OC)是矩形左侧的累积区域和。
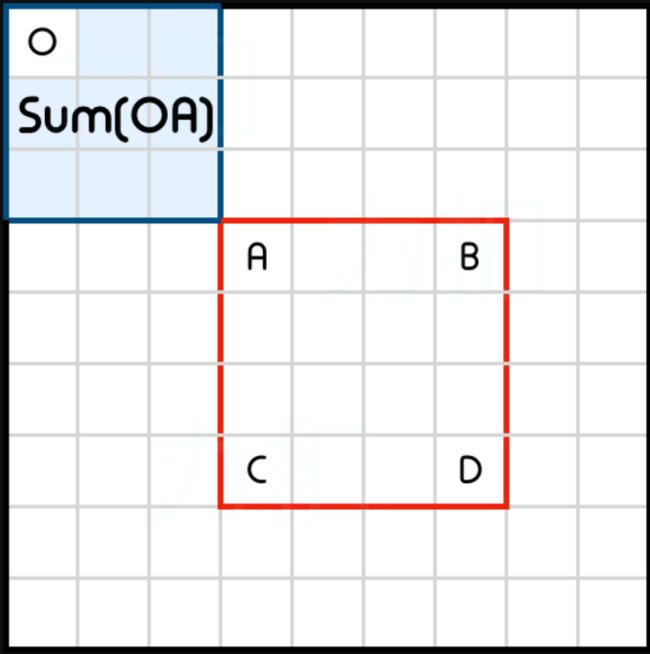
Sum(OA) 是矩形左上角的累积区域和。
区域 Sum(OA) 由 Sum(OB) 和 Sum(OC) 两次覆盖。我们可以使用包含排除原则计算 Sum(ABCD) 如下:
s u m ( a b c d ) = s u m ( o d ) − s u m ( o b ) − s u m ( o c ) + s u m ( o a ) sum(abcd)=sum(od)−sum(ob)−sum(oc)+sum(oa) sum(abcd)=sum(od)−sum(ob)−sum(oc)+sum(oa)
C++
class NumMatrix {
public:
vector<vector<int>> dp;
NumMatrix(vector<vector<int>> &matrix) {
if (matrix.size() == 0 || matrix[0].size() == 0) {
return;
}
dp = vector<vector<int>>(matrix.size() + 1, vector<int>(matrix[0].size() + 1, 0));
for (int row = 0; row < matrix.size(); ++row) {
for (int column = 0; column < matrix[0].size(); ++column) {
dp[row + 1][column + 1] =
dp[row + 1][column] + dp[row][column + 1] + matrix[row][column] - dp[row][column];
}
}
}
int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
return dp[row2 + 1][col2 + 1] - dp[row1][col2 + 1] - dp[row2 + 1][col1] + dp[row1][col1];
}
};
Java
private int[][] dp;
public NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) return;
dp = new int[matrix.length + 1][matrix[0].length + 1];
for (int r = 0; r < matrix.length; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < matrix[0].length; c++) {
dp[r + 1][c + 1] = dp[r + 1][c] + dp[r][c + 1] + matrix[r][c] - dp[r][c];
}
}
}
public int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
return dp[row2 + 1][col2 + 1] - dp[row1][col2 + 1] - dp[row2 + 1][col1] + dp[row1][col1];
}
Python
class NumMatrix:
def __init__(self, matrix: List[List[int]]):
def sumRegion(self, row1: int, col1: int, row2: int, col2: int) -> int:
# Your NumMatrix object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = NumMatrix(matrix)
# param_1 = obj.sumRegion(row1,col1,row2,col2)
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:每次查询时间 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1), O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn) 的时间预计算。构造函数中的预计算需要 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn) 时间。每个 sumregion 查询需要 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) 时间 。
- 空间复杂度: O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn),该算法使用 O ( m n ) O(mn) O(mn) 空间存储累积区域和。