ConcurrentHashMap 详解
以hashmap这一篇为基础,分析一下ConcurrentHashMap。
hashmap是线程不安全的,而hashtable性能低下,所以concurrentHashMap应运而生。
这个类设计的主要目标是维持并发访问时的可读性,将更新冲突减小到最少。第二个目标是保持和hashmap相同或者更低的空间消耗,多线程环境中支持在一个空表中有一个更高的插入比例。
jdk1.7的concurrentHashMap是有锁的,使用的分段锁。
Java 8的concurrenthashMap用无锁操作,基于CAS原子指令。
下面分析下Java 8的ConcurrentHashMap的源码:
首先是Node节点,和hashmap的差不多,用于储存key-value。提供了判断相等以及查找的方法。

static class Node implements Map.Entry {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V val;
volatile Node next;
Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return val; }
public final int hashCode() { return key.hashCode() ^ val.hashCode(); }
public final String toString(){ return key + "=" + val; }
public final V setValue(V value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
Object k, v, u; Map.Entry e;
return ((o instanceof Map.Entry) &&
(k = (e = (Map.Entry)o).getKey()) != null &&
(v = e.getValue()) != null &&
(k == key || k.equals(key)) &&
(v == (u = val) || v.equals(u)));
}
/**
* Virtualized support for map.get(); overridden in subclasses.
*/
Node find(int h, Object k) {
Node e = this;
if (k != null) {
do {
K ek;
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
return null;
}
}
下面这个方法是通过位运算改变哈希值,高位不变只是首位 强制转换为0。
因为浮点数的哈希值可能发生大量聚集,比如 Float a=3.4f;
Float b=3.9f;他们的哈希值对16取余数,都是10,那么这两个key就会发生碰撞,如果使用了下面的位传播算法,就能降低这个冲突。
& HASH_BITS这个运算,是为了把最高位置为0
static final int spread(int h) {
return (h ^ (h >>> 16)) & HASH_BITS;
}
ASHIFT,记录左移的位数。
参数i是元素在数组tab中的索引。这个方法是查找在数组tab中,索引i处的元素。ABASE表示基础偏移距,i << ASHIFT表示第i个元素相对于基础偏移距以外的偏移距。
get操作是无锁的。
static final Node tabAt(Node[] tab, int i) {
return (Node)U.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE);
}
查找到e这一步是原子性的,但是后续在e这个链表上查找时,不是原子的。
public V get(Object key) {
Node[] tab; Node e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node[] tab = table;;) {
Node f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
刚开始插入第一个元素时,表肯定还是空 的,所以先看看initTable方法。
sizeCtl是表的初始容量,默认是16,也可以通过构造函数指定。
这个方法也是线程安全的,它没有加锁,但是通过sizeCtl的值来控制,初始化前修改sizeCtl为-1,初始化完成后再把sizeCtl的值修改回原来值的一半。
private final Node[] initTable() {
Node[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node[] nt = (Node[])new Node[n];
table = tab = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
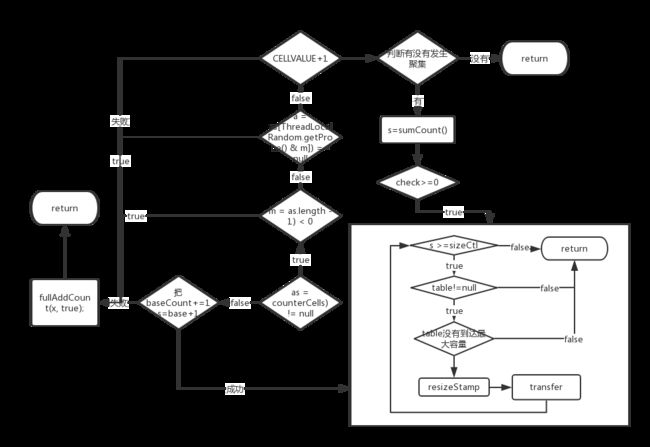
每次新增一个元素,都会调用addCount
baseCount的初始值为0
counterCells一开始也是null.counterCells的长度最大值是CPU的最大线程并行数(真并行,比如4核8线程,那么长度最大值就是8),这个用于计数,统计当前Map中共有多少个元素,如果只用Basecount计数,那要么加锁,要么cas竞争激烈,不管哪一种情况,效率都比较低,使用counterCells可以更好的利用多核计算机的性能,又不需要加锁。
有流程图可以看出,如果在单线程或者并发低的情况下,总数只由basecount计数,但是在竞争激烈的情况下,由foundcount方法增加计数。
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
CounterCell[] as; long b, s;
if ((as = counterCells) != null ||
!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
CounterCell a; long v; int m;
boolean uncontended = true;
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
if (check <= 1)
return;
s = sumCount();
}
if (check >= 0) {
Node[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
if (sc < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
s = sumCount();
}
}
}
private final void fullAddCount(long x, boolean wasUncontended) {
int h;
if ((h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe()) == 0) {
ThreadLocalRandom.localInit(); // force initialization
h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe();
wasUncontended = true;
}
boolean collide = false; // True if last slot nonempty
for (;;) {
CounterCell[] as; CounterCell a; int n; long v;
if ((as = counterCells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) {
if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) {
if (cellsBusy == 0) { // Try to attach new Cell
CounterCell r = new CounterCell(x); // Optimistic create
if (cellsBusy == 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean created = false;
try { // Recheck under lock
CounterCell[] rs; int m, j;
if ((rs = counterCells) != null &&
(m = rs.length) > 0 &&
rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) {
rs[j] = r;
created = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (created)
break;
continue; // Slot is now non-empty
}
}
collide = false;
}
else if (!wasUncontended) // CAS already known to fail
wasUncontended = true; // Continue after rehash
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))
break;
else if (counterCells != as || n >= NCPU)
collide = false; // At max size or stale
else if (!collide)
collide = true;
else if (cellsBusy == 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
try {
if (counterCells == as) {// Expand table unless stale
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[n << 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
rs[i] = as[i];
counterCells = rs;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
collide = false;
continue; // Retry with expanded table
}
h = ThreadLocalRandom.advanceProbe(h);
}
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && counterCells == as &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean init = false;
try { // Initialize table
if (counterCells == as) {
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[2];
rs[h & 1] = new CounterCell(x);
counterCells = rs;
init = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (init)
break;
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, v = baseCount, v + x))
break; // Fall back on using base
}
}
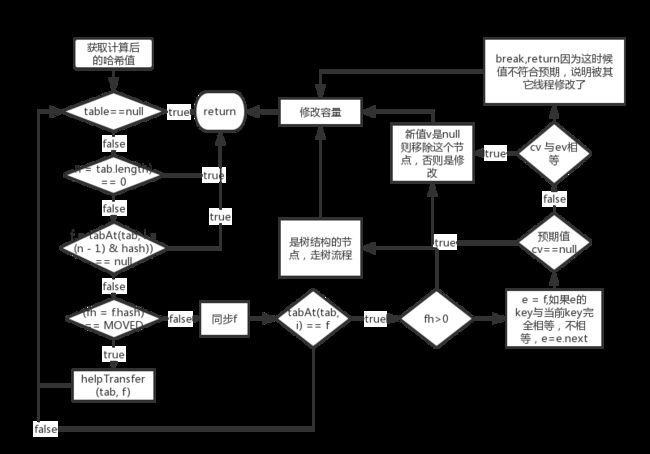
remove方法:
public V remove(Object key) {
return replaceNode(key, null, null);
}
final V replaceNode(Object key, V value, Object cv) {
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
for (Node[] tab = table;;) {
Node f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ||
(f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null)
break;
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
boolean validated = false;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
validated = true;
for (Node e = f, pred = null;;) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
V ev = e.val;
if (cv == null || cv == ev ||
(ev != null && cv.equals(ev))) {
oldVal = ev;
if (value != null)
e.val = value;
else if (pred != null)
pred.next = e.next;
else
setTabAt(tab, i, e.next);
}
break;
}
pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null)
break;
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
validated = true;
TreeBin t = (TreeBin)f;
TreeNode r, p;
if ((r = t.root) != null &&
(p = r.findTreeNode(hash, key, null)) != null) {
V pv = p.val;
if (cv == null || cv == pv ||
(pv != null && cv.equals(pv))) {
oldVal = pv;
if (value != null)
p.val = value;
else if (t.removeTreeNode(p))
setTabAt(tab, i, untreeify(t.first));
}
}
}
}
}
if (validated) {
if (oldVal != null) {
if (value == null)
addCount(-1L, -1);
return oldVal;
}
break;
}
}
}
return null;
}
get操作,没加锁,找到指定key的索引,然后遍历一遍。
public V get(Object key) {
Node[] tab; Node e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}