ffmpeg http.c解析学习及以及对于ffmpeg解析http框架
本人使用的amlogic 平台android6,amlogic平台播放器amplayer中采用ffmpeg作为解析。 最近遇到 播放http ts流 ,由于buffer处于buffering导致卡住问题。 度娘资料不多:
1. ffmpeg中的http协议相关代码阅读笔记
http://blog.csdn.net/toymaker/article/details/6037926
此文解答了我的一个大疑惑 , 关于 HTTPContxt是什么?
以下是摘自上面链接。
http.c函数的URLProtocol结构体中有个PrivateData的指针,这个指针存储了http协议中的一些内部使用到的数据变量,内部处理的数据变量结构体如下:
typedef struct {
const AVClass *class;
URLContext *hd;
unsigned char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE], *buf_ptr, *buf_end;
int line_count;
int http_code;
int64_t chunksize; /**< Used if "Transfer-Encoding: chunked" otherwise -1. */
int64_t off, filesize;
char location[MAX_URL_SIZE];
HTTPAuthState auth_state;
unsigned char headers[BUFFER_SIZE];
int willclose; /**< Set if the server correctly handles Connection: close and will close the connection after feeding us the content. */
} HTTPContext;
可以看到一个比较重要的信息是:该私有的内部数据中竟然也有一个URLContext,那这个是什么呢?这个URLContext的协议又是什么呢?我通过阅读代码发现这个URLContext就是指向的tcp协议,用来通过tcp读取和返回数据。很感慨阿。这样很简单的就可以同时支持http,tcp协议,而且把tcp,udp协议封装起来以后,基本上其他的像rtsp, mms等协议也可以通过制定他们自己的内在协议来处理了。
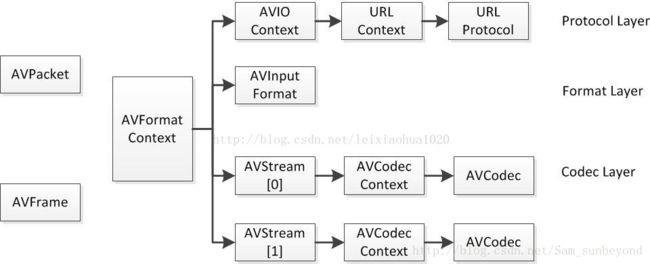
2. 接下来由点及面。 对应ffmpeg几个关键结构体帮助对于框架学习, 参照如下:
2.1 雷神的: FFMPEG中最关键的结构体之间的关系
http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020/article/details/11693997
我的使用场景 http ts流解析部分(解码部分不提), 对应的结构体主要在: libavformat/http.c libavformat/mpegts.c libavformat/avio.c avio.h, 以下为个人见解,可能出错请指出。
avio.c -> http.c -> mpegts.c
首先看了avio.c:
url_open-> ffurl_open->ffurl_alloc&ffurl_connect
ffurl_read->retry_transfer_wrapper
此处卡住了, 分析点1 :
int ffurl_connect(URLContext* uc)
{
int err = uc->prot->url_open(uc, uc->filename, uc->flags);
......
]查看URLContext:
- typedef struct URLContext {
- const AVClass *av_class; ///< information for av_log(). Set by url_open().
- struct URLProtocol *prot;
- int flags;
- int is_streamed; /**< true if streamed (no seek possible), default = false */
- int max_packet_size; /**< if non zero, the stream is packetized with this max packet size */
- void *priv_data;
- char *filename; /**< specified URL */
- int is_connected;
- AVIOInterruptCB interrupt_callback;
- } URLContext;
URLContext结构体中还有一个结构体URLProtocol。注:每种协议(rtp,rtmp,file等)对应一个URLProtocol。
uc->prot->url_open(uc, uc->filename, uc->flags);此处正是调用到http.c url_open
接着看http.c
URLProtocol ff_http_protocol = {
.name = "http",
.url_open = http_open,
.url_read = http_read_compressed,/*http_read*/
.url_write = http_write,
.url_seek = http_seek,
.url_close = http_close,
.url_getinfo = http_get_info,
.url_get_file_handle = http_get_file_handle,
.priv_data_size = sizeof(HTTPContext),
.priv_data_class = &httpcontext_class,
};
URLProtocol ff_shttp_protocol = {
.name = "shttp",
.url_open = shttp_open,
.url_read = http_read_compressed,/*http_read*/
.url_write = http_write,
.url_seek = http_seek,
.url_close = http_close,
.url_getinfo = http_get_info,
.url_get_file_handle = http_get_file_handle,
.priv_data_size = sizeof(HTTPContext),
.priv_data_class = &shttpcontext_class,
};
分析点2 retry_transfer_wrapper
ret=retry_transfer_wrapper(h, buf+readedlen, toread, toread, h->prot->url_read);
ffurl_read()调用retry_transfer_wrapper()的时候,最后一个参数是URLProtocol的url_read(),而ffurl_write()调用retry_transfer_wrapper()的时候,最后一个参数是URLProtocol的url_write(),
此处逻辑是 retry_transfer_wrapper (avio.c) -> url_read既是http_read (http.c)
至此 : Protocol layer 的应该是完成了。
url_open-> ffurl_open->ffurl_alloc&ffurl_connect (avio.c) -> http_open(http.c)
ffurl_read->retry_transfer_wrapper-> url_read既是http_read (http.c)
看了url_oepn ,
int url_open(URLContext **puc, const char *filename, int flags)
{
return ffurl_open(puc, filename, flags);
}
此处应该只是 URLContext-> URLProtocol