单向链表的逆序输出(java)
将单向链表逆序输出,方法有三种:
a.遍历链表,将每个节点的内容存入一个数组中,然后逆序输出数组(最简单的做法)
b.使用栈来逆序输出
c.直接将链表逆序然后输出
先介绍c方法:
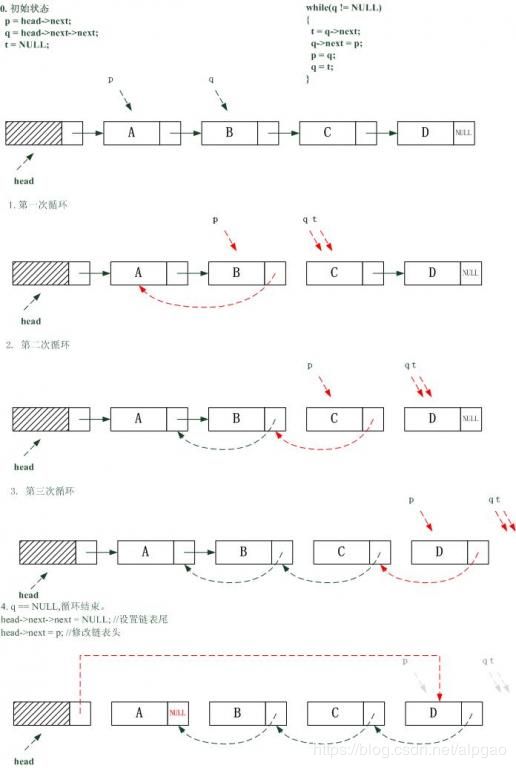
1). 若链表为空或只有一个元素,则直接返回;
2). 设置两个前后相邻的指针p,q. 将p所指向的节点作为q指向节点的后继;
3). 重复2),直到q为空
4). 调整链表头和链表尾
public class Node {
private int data;
private Node next;
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
实现
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LinkList {
public Node head;
public void createLinkList(int []x) { //创建一个链表
Node pnew; //定义一个新的结点
Node ptail = new Node();
head = ptail;
for(int i = 0; i < x.length; i ++) {
pnew = new Node();
pnew.setData(x[i]);
ptail.setNext(pnew);
ptail = pnew;
}
}
public void displayLinkList() { //正序输出链表的所有内容
Node node = head.getNext();
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.getData() + "--->");
node = node.getNext();
}
System.out.println("null");
}
public void reverseLinkList() { //逆序输出链表的所有内容
if (head == null || head.getNext() == null) { //当链表只有一个头节点或者只有一个结点,逆序还是原来的链表,所以直接返回
return;
} else {
Node p = head.getNext();
Node q = head.getNext().getNext();
p.setNext(null);//将第一个结点的next置为空,否则会出现一个环
Node temp = null;
while (q != null) {
temp = q.getNext();
q.setNext(p);
p = q;
q = temp;
}
if (q == null) {
head.setNext(p);
q = null;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkList linkList = new LinkList();
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = input.nextInt();
int [] x = new int [n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
x[i] = i;
}
linkList.createLinkList(x);
linkList.displayLinkList();
linkList.reverseLinkList();
linkList.displayLinkList();
}
}
输出结果:
10
0--->1--->2--->3--->4--->5--->6--->7--->8--->9--->null
9--->8--->7--->6--->5--->4--->3--->2--->1--->0--->null
再介绍比较简单的b方法:
借助栈先进后出的特性,将链表存入栈中,然后出栈,刚好就实现了链表的逆序输出(此方法只实现了逆序输出,但并没有将链表逆序)
public void reverseLinkList_Stack() { //借助栈来实现逆序输出
Stack stack = new Stack();
Node node = head.getNext();
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.getNext();
}
while (stack.size() > 0) {
node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.getData() + "--->");
}
System.out.println("null"); // 在最后添加上null作为结束标志
}
代码
package list;
public class ReverseList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
int[] value = {2,3,4,5};
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 0 ; i< value.length;i++) {
Node node = new Node(value[i]);
temp.next = node;
temp = temp.next;
}
printList(head);
// 反序输出一个单链表
head = reverse(head);
printList(head);
// 再次反向
head = reverseSingleList(head);
printList(head);
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
while(head!=null) {
System.out.print("\t"+head.value);
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static Node reverse(Node head) {
Node pre = null;
Node post = null;
while(head!=null) {
post = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = post;
}
return pre;
}
public static Node reverseSingleList(Node head) {
Node pre = null;
Node next = null;
while(head!=null) {
next = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
class Node {
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
经测试,代码输出正确。
1 2 3 4 5
5 4 3 2 1
1 2 3 4 5
帮助理解,下面是另一个实例:
/**
* java 实现单链表的逆序
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class SingleLinkedReverse {
class Node{
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data){
this.data = data;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleLinkedReverse slr = new SingleLinkedReverse();
Node head, tail;
head = tail = slr.new Node(0);
for (int i=1; i<10; i++){
Node p = slr.new Node(i);
tail.next = p;
tail = p;
}
tail = head;
while(tail != null){
System.out.print(tail.data+" ");
tail = tail.next;
}
head = reverse(head);
System.out.println(" ");
while(head != null){
System.out.print(head.data+" ");
head = head.next;
}
}
private static Node reverse(Node head) {
Node p1,p2 = null;
p1 = head;
while(head.next != null){
p2 = head.next;
head.next = p2.next;
p2.next = p1;
p1 = p2;
}
return p2;
}
}
测试结果:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
事实上,就是这样。
Node pre = null;
Node post = null;
while(head!=null){
post = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = post;
}
这便是逆序的核心了。
首次逆序:一开始的话,pre,post都设置为null。这是必须的,因为在head.next=pre这行代码执行完成后,我们原始的那个head节点的next将变成null,也就是我们整个链表的null了。
想象一下,原来的那个链表的最后面的next不也是一个null吗?这里道理是一致的。
此时,更新pre为原来的head节点,也是为了下一步的逆序做准备,而head也自然的变成了原来的head.next了。
不断逆序。就是一次次的将head向后移,同时更新pre节点,来达到逆序的效果。