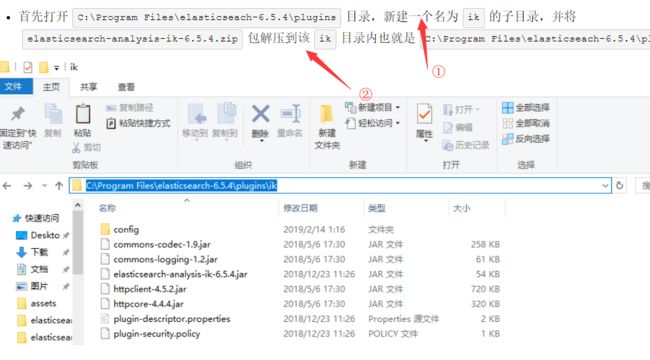
一.IK中文分词器
1.下载安装
官网地址
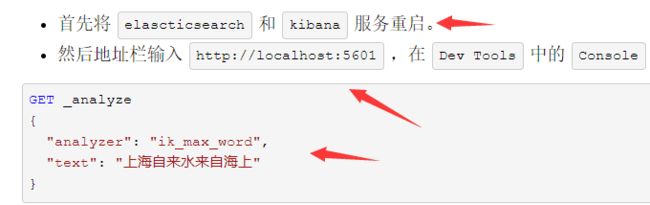
2.测试
#显示结果
{ "tokens" : [ { "token" : "上海", "start_offset" : 0, "end_offset" : 2, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 0 }, { "token" : "自来水", "start_offset" : 2, "end_offset" : 5, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 1 }, { "token" : "自来", "start_offset" : 2, "end_offset" : 4, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 2 }, { "token" : "水", "start_offset" : 4, "end_offset" : 5, "type" : "CN_CHAR", "position" : 3 }, { "token" : "来自", "start_offset" : 5, "end_offset" : 7, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 4 }, { "token" : "海上", "start_offset" : 7, "end_offset" : 9, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 5 } ] }
二. Ik 分词器的基本操作
1.ik_max_word(最细粒度的拆分)
#建立索引
PUT ik1 { "mappings": { "doc": { "dynamic": false, "properties": { "content": { "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" } } } } }
#添加数据
PUT ik1/doc/1 { "content":"今天是个好日子" } PUT ik1/doc/2 { "content":"心想的事儿都能成" } PUT ik1/doc/3 { "content":"我今天不活了" }
开始查询
GET ik1/_search { "query": { "match": { "content": "心想" } } }
显示结果
{ "took" : 1, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 5, "successful" : 5, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : 1, "max_score" : 0.2876821, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "ik1", "_type" : "doc", "_id" : "2", "_score" : 0.2876821, "_source" : { "content" : "心想的事儿都能成" } } ] } }
2.ik_smart(最粗粒度的拆分)
①以最粗粒度拆分
GET _analyze { "analyzer": "ik_smart", "text": "今天是个好日子" }
结果是:
{ "tokens" : [ { "token" : "今天是", "start_offset" : 0, "end_offset" : 3, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 0 }, { "token" : "个", "start_offset" : 3, "end_offset" : 4, "type" : "CN_CHAR", "position" : 1 }, { "token" : "好日子", "start_offset" : 4, "end_offset" : 7, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 2 } ] }
②以最细粒度拆分文档
GET _analyze { "analyzer": "ik_max_word", "text": "今天是个好日子" }
结果是:
{ "tokens" : [ { "token" : "今天是", "start_offset" : 0, "end_offset" : 3, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 0 }, { "token" : "今天", "start_offset" : 0, "end_offset" : 2, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 1 }, { "token" : "是", "start_offset" : 2, "end_offset" : 3, "type" : "CN_CHAR", "position" : 2 }, { "token" : "个", "start_offset" : 3, "end_offset" : 4, "type" : "CN_CHAR", "position" : 3 }, { "token" : "好日子", "start_offset" : 4, "end_offset" : 7, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 4 }, { "token" : "日子", "start_offset" : 5, "end_offset" : 7, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 5 } ] }
3.短语查询(即match_phrase)
GET ik1/_search { "query": { "match_phrase": { "content": "今天" } } }
4.短语前缀查询(match_phrase_prefix)
GET ik1/_search { "query": { "match_phrase_prefix": { "content": { "query": "今天好日子", "slop": 2 } } } }
三.python操作elasticsearch
1.安装elasticsearch模块
pip install elasticsearch # 豆瓣源 pip install -i https://pypi.doubanio.com/simple/ elasticsearch
2.连接
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch # es = Elasticsearch() # 默认连接本地elasticsearch # es = Elasticsearch(['127.0.0.1:9200']) # 连接本地9200端口 es = Elasticsearch( ["192.168.1.10", "192.168.1.11", "192.168.1.12"], # 连接集群,以列表的形式存放各节点的IP地址 sniff_on_start=True, # 连接前测试 sniff_on_connection_fail=True, # 节点无响应时刷新节点 sniff_timeout=60 # 设置超时时间 )
配置忽略响应状态码
es = Elasticsearch(['127.0.0.1:9200'],ignore=400) # 忽略返回的400状态码 es = Elasticsearch(['127.0.0.1:9200'],ignore=[400, 405, 502]) # 以列表的形式忽略多个状态码
3.常用的连接方式
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch es = Elasticsearch() # 默认连接本地elasticsearch
#创建 print(es.index(index='py2', doc_type='doc', id=1, body={'name': "张开", "age": 18}))
#查询指定文档 print(es.get(index='py2', doc_type='doc', id=1))
4.结果过滤
filter_path参数用于减少elasticsearch返回的响应
还支持*通配符以匹配字段名称、任何字段或者字段部分:
①
print(es.search(index='py2', filter_path=['hits.total', 'hits.hits._source']))
# 可以省略type类型
print(es.search(index='w2', doc_type='doc')) # 可以指定type类型
print(es.search(index='w2', doc_type='doc', filter_path=['hits.total']))
②
print(es.search(index='py2', filter_path=['hits.*']))
print(es.search(index='py2', filter_path=['hits.hits._*']))
print(es.search(index='py2', filter_path=['hits.to*'])) # 仅返回响应数据的total
print(es.search(index='w2', doc_type='doc', filter_path=['hits.hits._*']))
# 可以加上可选的type类型
5.基本操作
①es.index,向指定索引添加或更新文档,如果索引不存在,首先会创建该索引,然后再执行添加或者更新操作。
# print(es.index(index='w2', doc_type='doc', id='4', body={"name":"可可", "age": 18})) # 正常
# print(es.index(index='w2', doc_type='doc', id=5, body={"name":"卡卡西", "age":22})) # 正常
# print(es.index(index='w2', id=6, body={"name": "鸣人", "age": 22})) # 会报错,TypeError: index() missing 1 required positional argument: 'doc_type'
print(es.index(index='w2', doc_type='doc', body={"name": "鸣人", "age": 22})) # 可以不指定id,默认生成一个id
② es.get,查询索引中指定文档。
print(es.get(index='w2', doc_type='doc', id=5)) # 正常 print(es.get(index='w2', doc_type='doc')) # TypeError: get() missing 1 required positional argument: 'id' print(es.get(index='w2', id=5)) # TypeError: get() missing 1 required positional argument: 'doc_type'
③es.search,执行搜索查询并获取与查询匹配的搜索匹配。这个用的最多,可以跟复杂的查询条件。
index要搜索的以逗号分隔的索引名称列表; 使用_all 或空字符串对所有索引执行操作。
doc_type 要搜索的以逗号分隔的文档类型列表; 留空以对所有类型执行操作。
body 使用Query DSL(QueryDomain Specific Language查询表达式)的搜索定义。
_source 返回_source字段的true或false,或返回的字段列表,返回指定字段。
_source_exclude要从返回的_source字段中排除的字段列表,返回的所有字段中,排除哪些字段。
_source_include从_source字段中提取和返回的字段列表,跟_source差不多。
print(es.search(index='py3', doc_type='doc', body={"query": {"match":{"age": 20}}})) # 一般查询 print(es.search(index='py3', doc_type='doc', body={"query": {"match":{"age": 19}}},_source=['name', 'age'])) # 结果字段过滤 print(es.search(index='py3', doc_type='doc', body={"query": {"match":{"age": 19}}},_source_exclude =[ 'age'])) print(es.search(index='py3', doc_type='doc', body={"query": {"match":{"age": 19}}},_source_include =[ 'age']))
④ es.get_source,通过索引、类型和ID获取文档的来源,其实,直接返回想要的字典。
print(es.get_source(index='py3', doc_type='doc', id='1')) # {'name': '王五', 'age': 19}
⑤ es.count,执行查询并获取该查询的匹配数。比如查询年龄是18的文档。
body = { "query": { "match": { "age": 18 } } } print(es.count(index='py2', doc_type='doc', body=body))
# {'count': 1, '_shards': {'total': 5, 'successful': 5, 'skipped': 0, 'failed': 0}}
print(es.count(index='py2', doc_type='doc', body=body)['count'])
# 1
print(es.count(index='w2'))
# {'count': 6, '_shards': {'total': 5, 'successful': 5, 'skipped': 0, 'failed': 0}}
print(es.count(index='w2', doc_type='doc'))
# {'count': 6, '_shards': {'total': 5, 'successful': 5, 'skipped': 0, 'failed':
⑥es.delete,删除指定的文档。比如删除文章id为4的文档,但不能删除仅只删除索引,
如果想要删除索引,还需要es.indices.delete来处理
print(es.delete(index='py3', doc_type='doc', id='4'))
⑦ es.delete_by_query,删除与查询匹配的所有文档。
index要搜索的以逗号分隔的索引名称列表; 使用_all 或空字符串对所有索引执行操作。doc_type要搜索的以逗号分隔的文档类型列表; 留空以对所有类型执行操作。body使用Query DSL的搜索定义。
print(es.delete_by_query(index='py3', doc_type='doc', body={"query": {"match":{"age": 20}}}))
⑧es.exists,查询elasticsearch中是否存在指定的文档,返回一个布尔值。
print(es.exists(index='py3', doc_type='doc', id='1'))
⑨es.info,获取当前集群的基本信息。
print(es.info())
⑩ es.ping,如果群集已启动,则返回True,否则返回False。
print(es.ping())
6.Indices(es.indices )
详细查看
① es.indices.create,在Elasticsearch中创建索引,用的最多。
比如创建一个严格模式、有4个字段、并为title字段指定ik_max_word查询粒度的mappings。
并应用到py4索引中。这也是常用的创建自定义索引的方式。
body = { "mappings": { "doc": { "dynamic": "strict", "properties": { "title": { "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" }, "url": { "type": "text" }, "action_type": { "type": "text" }, "content": { "type": "text" } } } } } es.indices.create('py4', body=body)
② es.indices.delete,在Elasticsearch中删除索引
print(es.indices.delete(index='py4')) print(es.indices.delete(index='w3')) # {'acknowledged': True}
③ es.indices.put_alias,为一个或多个索引创建别名,查询多个索引的时候,可以使用这个别名。
index别名应指向的逗号分隔的索引名称列表(支持通配符),使用_all对所有索引执行操作。name要创建或更新的别名的名称。body别名的设置,例如路由或过滤器。
print(es.indices.put_alias(index='py4', name='py4_alias')) # 为单个索引创建别名 print(es.indices.put_alias(index=['py3', 'py2'], name='py23_alias')) # 为多个索引创建同一个别名,联查用
④es.indices.delete_alias,删除一个或多个别名。
print(es.indices.delete_alias(index='alias1')) print(es.indices.delete_alias(index=['alias1, alias2']))
以下查看详细Node(节点相关)
Cluster(集群相关)
Cat(一种查询方式)
Snapshot(快照相关)
Task(任务相关)