从入门到放弃(2)-tomcat -spring web.xml
接着从入门到放弃(1)-tomcat -spring web.xml继续对spring启动的探索
上文讲到
ServletContextListener listener =
(ServletContextListener) instances[i];
listener.contextInitialized(event);
调用到我们项目即可找到,idea 快捷键ctrl+shift+n 打开对应的类

获取类的路径:copy referene : org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader

找到 org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader源码,找到285行打印日志处,可以看到打印了info lever 日志,并且可以找到对应的方法org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext)
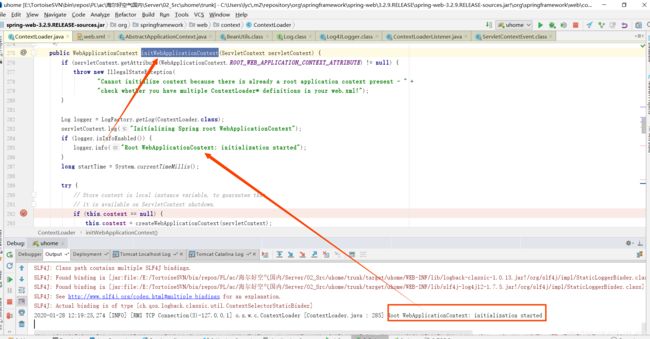
先看下org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext)是从哪里调用进来的,熟悉idea同学可以知道ctrl+鼠标左键可以看到在这个方法在哪里调用
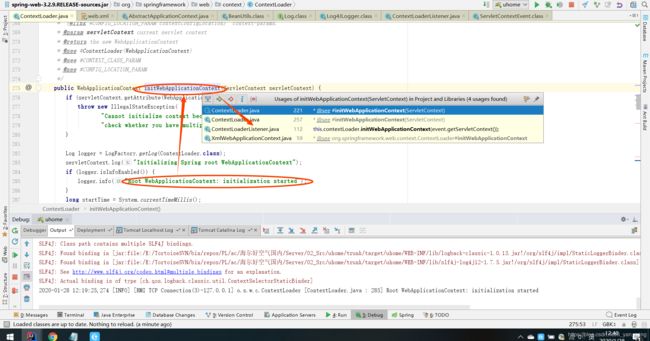
进入org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener.contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event)的112行,可以找到对应的调用位置,详细的contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event)源码
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.contextLoader = createContextLoader();
if (this.contextLoader == null) {
this.contextLoader = this;
}
this.contextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
因为我三个listen中第一个listen 继承了ContextLoaderListener 并且调用了 super.contextInitialized(event);

查看当前类的关系,public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener,继承于ContextLoader 实现于ServletContextListener,这与上篇讲的tomcat启动web.xml 正好合到一起了。并且把event 从tomcat容器成功传递到spring 中

先看下ContextLoader 加载的内容
private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
//ContextLoader.properties 内容为
// Default WebApplicationContext implementation class for ContextLoader.
// Used as fallback when no explicit context implementation has been specified as context- param.
// Not meant to be customized by application developers.
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
defaultStrategies 会在后面初始化org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext用到

继续接着org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener.contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event)的112行 this.contextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
下面看下 createWebApplicationContext(servletContext)的源码
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
再看 determineContextClass(sc)的源码
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
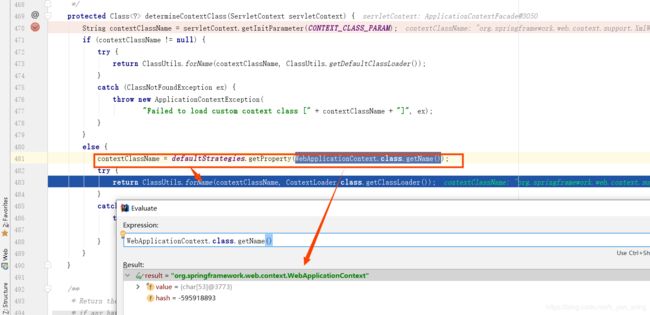

看上面两张图片最终返回的结果:org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
再回到 createWebApplicationContext(servletContext)的代码中

通过BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass)方法根据类名创建对应实例,并且进行强制转换得到ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口的实例,BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass)源码
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Class<T> clazz) throws BeanInstantiationException {
return instantiateClass(clazz.getDeclaredConstructor());
}
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);
return ctor.newInstance(args);
}
接着this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);这一行往下看
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
核心代码又跑到了configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);这个方法
wac.setServletContext(sc);
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
wac.refresh();

对应web.xml内容

继续看wac.refresh()其位置

代码如下
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
}
}
当进入第一个方法prepareRefresh(); 会打印如下日志

obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法是refresh()方法中的核心之一。
作用:初始化beanFactory,加载并解析配置
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
//1.初始化beanFactory,并执行加载和解析配置操作
refreshBeanFactory();
//返回beanFactory实例
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
obtainFreshBeanFactory()方法中做了二件事:
refreshBeanFactory():创建beanFactory、指定序列化Id、定制beanFactory、加载bean定义
getBeanFactory():返回beanFactory实例
一. refreshBeanFactory():刷新beanFactory
初始化beanFactory,并执行加载和解析配置操作
进入到refreshBeanFactory()方法,分析refreshBeanFactory()方法的具体实现:
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
...
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
//判断是否存在beanFactory
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
// 注销所有的单例
destroyBeans();
//重置beanFactory
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//创建beanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
//指定序列化id,如果需要的话,让这个BeanFactory从id反序列化到BeanFactory对象
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
//定制BeanFactory
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
...
}
refreshBeanFactory()方法中做了四件事情:
如果有bean工厂,销毁bean以及关闭bean工厂
createBeanFactory():创建beanFactory
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()):指定序列化Id
customizeBeanFactory():定制BeanFactory
loadBeanDefinitions():加载bean定义
先介绍到这里后面继续从loadBeanDefinitions()解析