李宏毅深度学习HW1 PM2.5预测(gradient descent)
李宏毅深度学习HW1 PM2.5预测
1.任务内容
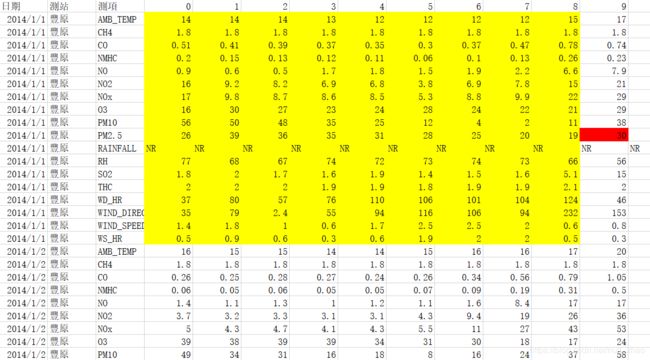
根据前9个小时的空气监测情况预测第10个小时的PM2.5含量,即根据黄色部分内容预测红色处值。
- 训练集:包含台湾丰原地区240天的气象观测资料(取每个月前20天的数据做训练集,12月X20天=240天,每月后10天数据用于测试,对学生不可见),每天的监测时间点为整时共24个时间节点。每次的检测指标包括CO、NO、PM2.5、PM10,是否降雨、刮风等气象信息,共18项;
- 任务:根据前九个小时 18*9=162 项参数,输出一个预测值。
数据集地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1o2Yx42dZBJZFZqCa5y3WzQ,提取码:qgtm。 这里WPS打开繁体字正常,但python读取会有编码错误,改变常用编码也无法解决,似乎只能加入encoding=‘ansi’方式才能正常读取,然而同样有乱码。
2.实现代码详解
示例代码通过梯度下降的方法,构建了一个线性回归模型,没有隐藏层。
1.数据读取
import sys
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import csv
raw_data = np.genfromtxt('train.csv',delimiter=',',encoding='ansi') #好在只用处理数字
data = raw_data[1:,3:] #取第一行和第三列以后的数据
where_are_NaNs = np.isnan(data) #返回一个numpy的ndarray的对象
data[where_are_NaNs] = 0 #ndarray的特殊操作
month_to_data = {} # Dictionary (key:month , value:data) 读取数据文件,去掉表头取出内容部分,genfromtxt自动将非数字转化为了NAN,直接把所有NAN赋值0。这里numpy返回的都是ndarray,相对于python的List,ndarray的操作方便了很多。
2.数据预处理
for month in range(12):
sample = np.empty(shape = (18 , 480)) #18个属性,20天*24小时,sample(x,y)代表属性x在y时的值
for day in range(20):
for hour in range(24):
sample[:,day * 24 + hour] = data[18 * (month * 20 + day): 18 * (month * 20 + day + 1),hour]
month_to_data[month] = sample #每月前20天是训练集,12*18*480
x = np.empty(shape = (12 * 471 , 18 * 9),dtype = float)
y = np.empty(shape = (12 * 471 , 1),dtype = float)#每个月480-9=471个样本(每连续九小时取样,最后9小时无法取样)
for month in range(12):
for day in range(20):
for hour in range(24):
if day == 19 and hour > 14:
continue
x[month * 471 + day * 24 + hour,:] = month_to_data[month][:,day * 24 + hour : day * 24 + hour + 9].reshape(1,-1)
#reshape将矩阵重整为新的行列数,参数-1代表自动推断,这里去掉了18*9的二维属性,转而以一维序列代替,一维序列的顺序本身可以隐含其时序信息
y[month * 471 + day * 24 + hour,0] = month_to_data[month][9 ,day * 24 + hour + 9]
mean = np.mean(x, axis = 0) #aix=0表示沿每列计算
std = np.std(x, axis = 0) #标准差
for i in range(x.shape[0]):
for j in range(x.shape[1]):
if not std[j] == 0 :
x[i][j] = (x[i][j]- mean[j]) / std[j] #所有属性归一化一个月的20天数据是连续的,可以扩展成480小时的连续数据,在其中每九个小时取一段样本,可以得到480-9=471个样本。训练集通过此方法可以扩充到12*471=5652个。
这里将输入数据的18*9的二维矩阵reshape成了1*162的一维序列,一维序列的顺序本身可以隐含其时序信息。
归一化处理,避免由于量纲的不同使数据的某些特征形成主导作用。
- 梯度下降
dim = x.shape[1] + 1
w = np.zeros(shape = (dim, 1 )) #empty创建的数组,数组中的数取决于数组在内存中的位置处的值,为0纯属巧合?
x = np.concatenate((np.ones((x.shape[0], 1 )), x) , axis = 1).astype(float) #concatenate连接两个数组,给x的162个属性补1
#初始化学习率(163个参数,163个200)和adagrad
learning_rate = np.array([[200]] * dim)
adagrad_sum = np.zeros(shape = (dim, 1 ))
#没有隐藏层的网络
for T in range(10001):
if(T % 500 == 0 ):
print("T=",T)
print("Loss:",np.sum((x.dot(w) - y)**2)/ x.shape[0] /2) #最小二乘损失
print((x.dot(w) - y)**2)
gradient = 2 * np.transpose(x).dot(x.dot(w)-y) #损失的导数x*(yh-h)
adagrad_sum += gradient ** 2
w = w - learning_rate * gradient / (np.sqrt(adagrad_sum) + 0.0005)初始化所有学习率为200,权重为0。本实验梯度下降采用的损失函数Loss和由其推导出的梯度如下(常数参数可以通过学习率调节,于是在示例代码中省略了):
这里采用了adagrad来调整学习率以获得更好的效果,初始学习率大以获得较大步长更快地接近最优解,之后随着学习进行学习率会慢慢变小以避免无法收敛的问题。
- 使用模型预测
np.save('weight.npy',w)
w = np.load('weight.npy')
test_raw_data = np.genfromtxt("test.csv", delimiter=',') ## test.csv
test_data = test_raw_data[:, 2: ]
where_are_NaNs = np.isnan(test_data)
test_data[where_are_NaNs] = 0
test_x = np.empty(shape = (240, 18 * 9),dtype = float)
for i in range(240):
test_x[i,:] = test_data[18 * i : 18 * (i+1),:].reshape(1,-1)
for i in range(test_x.shape[0]): ##Normalization
for j in range(test_x.shape[1]):
if not std[j] == 0 :
test_x[i][j] = (test_x[i][j]- mean[j]) / std[j]
test_x = np.concatenate((np.ones(shape = (test_x.shape[0],1)),test_x),axis = 1).astype(float)
answer = test_x.dot(w)
f = open("result.csv","w")
w = csv.writer(f)
title = ['id','value']
w.writerow(title)
for i in range(240):
content = ['id_'+str(i),answer[i][0]]
w.writerow(content)同样需要对测试集数据进行预处理,归一化。根据计算出的参数w,点乘即可计算预测结果,按要求格式输出。