树
文章目录
- 树
- 概念
- 度
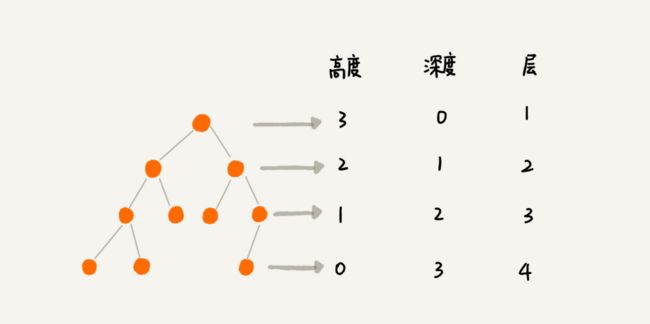
- 高度和深度
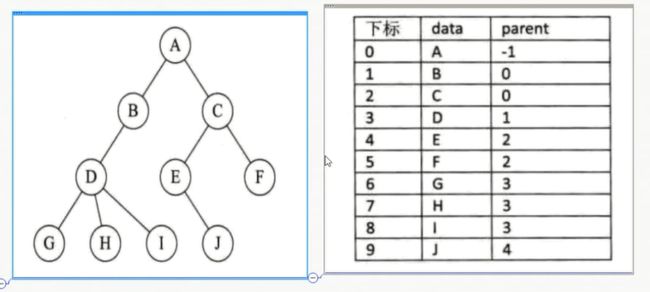
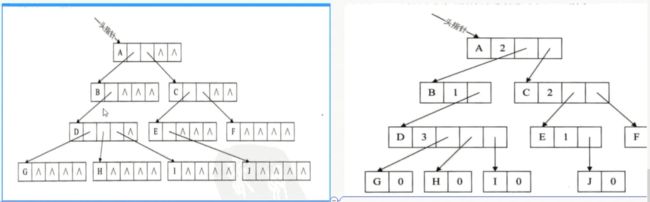
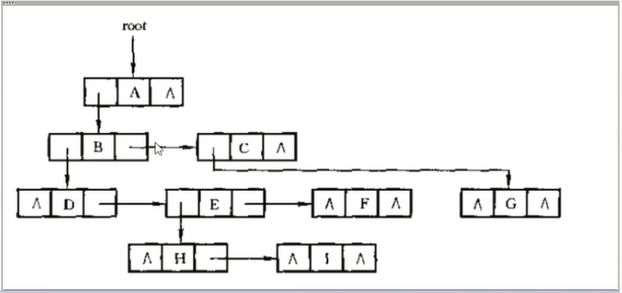
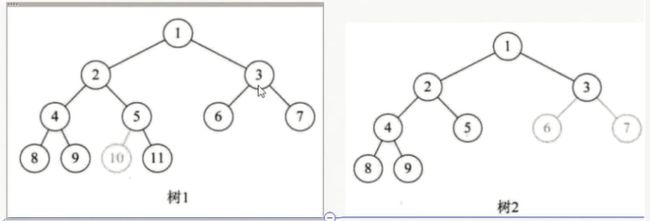
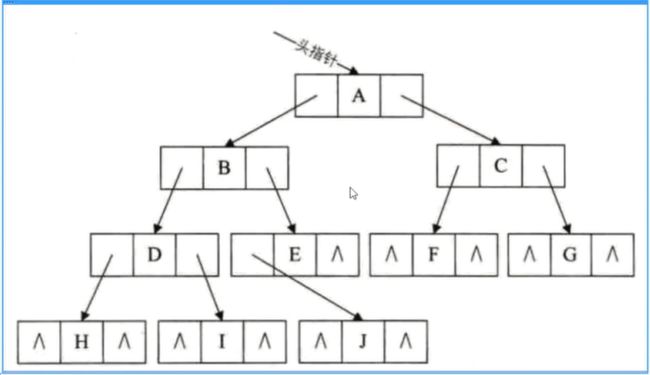
- 树的存储结构
- 斜树
- 满二叉树
- 完全二叉树
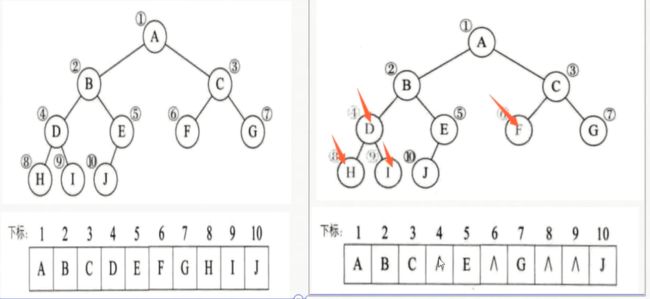
- 二叉树的存储结构
- 遍历方法
- 二叉排序树
- 概念
- 增删改查操作:
- 哈夫曼数压缩
- 基本思想
- 平衡二叉树
- 概念
- 左旋
- 左平衡树
- 右平衡树
- 红黑树
树
概念
度
高度和深度
树的存储结构
斜树
满二叉树
完全二叉树
二叉树的存储结构
遍历方法
class Node<T> {
T data;
Node<T> leftChild;
Node<T> rightChild;
public Node(T data, Node<T> leftChild, Node<T> rightChild) {
this.data = data;
this.leftChild = leftChild;
this.rightChild = rightChild;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"data=" + data +
", leftChild=" + leftChild +
", rightChild=" + rightChild +
'}';
}
}
/**
*
* 0
* 1 2
* 3 4 5 6
* 7 8 9 10
*/
public class _1Tree {
@Test
public void testTree() {
// 生成一个从左到右从上到下递增的完全二叉树
Node<String> root = new Node<>("0", null, null);
Node<String> node1 = new Node<>("1", null, null);
Node<String> node2 = new Node<>("2", null, null);
Node<String> node3 = new Node<>("3", null, null);
Node<String> node4 = new Node<>("4", null, null);
Node<String> node5 = new Node<>("5", null, null);
Node<String> node6 = new Node<>("6", null, null);
Node<String> node7 = new Node<>("7", null, null);
Node<String> node8 = new Node<>("8", null, null);
Node<String> node9 = new Node<>("9", null, null);
Node<String> node10 = new Node<>("10", null, null);
root.leftChild = node1;
root.rightChild = node2;
node1.leftChild = node3;
node1.rightChild = node4;
node2.leftChild = node5;
node2.rightChild = node6;
node3.leftChild = node7;
node3.rightChild = node8;
node4.leftChild = node9;
node4.rightChild = node10;
midOrderTraverse(root);
System.out.println();
proOrderTraverse(root);
System.out.println();
postOrderTraverse(root);
}
// 中序遍历
private void midOrderTraverse(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
midOrderTraverse(root.leftChild);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
midOrderTraverse(root.rightChild);
}
// 前序遍历
private void proOrderTraverse(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
proOrderTraverse(root.leftChild);
proOrderTraverse(root.rightChild);
}
// 后序遍历
private void postOrderTraverse(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postOrderTraverse(root.leftChild);
postOrderTraverse(root.rightChild);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
}
}
二叉排序树
概念
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-RVfcvL5K-1578637542801)(C:\Users\lizj\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1577780974665.png)]
增删改查操作:
class TreeNode {
int data;
TreeNode leftChild;
TreeNode rightChild;
TreeNode parent;
TreeNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public class _2SortBinaryTree {
private TreeNode root;
@Test
public void testSortBinaryTree() {
root = new TreeNode(5);
int[] array = new int[]{3, 2, 5, 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 1, 19, 20, 12, 15};
for (int i : array) {
putNode(i);
}
midOrderTraverse(root);
System.out.println();
TreeNode searchTreeNode = searchNode(15);
if (searchTreeNode != null) {
System.out.println(searchTreeNode.data);
} else {
System.out.println("没有查找到数据");
}
System.out.println("删除后的数据:");
delNode(searchTreeNode);
midOrderTraverse(root);
}
private TreeNode putNode(int data) {
// 生成一个新节点
TreeNode treeNode = new TreeNode(data);
if (root == null) {
root = treeNode;
return treeNode;
}
// 记录父节点,进行插入
TreeNode parent = null;
TreeNode tempRoot = root;
while (tempRoot != null) {
parent = tempRoot;
if (data < tempRoot.data) {
tempRoot = tempRoot.leftChild;
} else if (data > tempRoot.data) {
tempRoot = tempRoot.rightChild;
} else {
// 是重复值,不理会
return tempRoot;
}
}
treeNode.parent = parent;
if (data < parent.data) {
parent.leftChild = treeNode;
} else {
parent.rightChild = treeNode;
}
return treeNode;
}
private void midOrderTraverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
midOrderTraverse(root.leftChild);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
midOrderTraverse(root.rightChild);
}
private TreeNode searchNode(int data) {
TreeNode tempRoot = root;
while (tempRoot != null) {
if (data > tempRoot.data) {
tempRoot = tempRoot.rightChild;
} else if (data < tempRoot.data) {
tempRoot = tempRoot.leftChild;
} else {
return tempRoot;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 删除操作相对麻烦,考虑如下几种情况:
* 1. 叶子
* 2. 只有左孩子
* 3. 只有右孩子
* 4. 俩孩子都有
* 5. 是跟节点
* 6. 不存在
*
* @param toRemoveNode 要删除的节点
* @return 删除的节点
*/
/**
* 删除节点
* 要删除的节点在树上是一定存在的才删除
*/
public void delNode(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}else{
//先得到父亲,方便后面的操作
TreeNode parent=node.parent;
//1.叶子
if(node.leftChild==null && node.rightChild==null){
//特别的情况:1.树上只有一个节点或是空树
if(parent==null){
root=null;
}else if(parent.rightChild==node){
parent.rightChild=null;
}else if(parent.leftChild==node){
parent.leftChild=null;
}
node.parent=null;
}else if(node.leftChild!=null && node.rightChild==null){
//2.只有左孩子
if(parent==null){//如果要删除的是根
node.parent=null;
node.leftChild.parent=null;
root=node.leftChild;
}else{
if(parent.leftChild==node){//要删除的节点是父亲的左边
node.leftChild.parent=parent;
parent.leftChild=node.leftChild;
}else{//要删除的节点是父亲的右边
node.leftChild.parent=parent;
parent.rightChild=node.leftChild;
}
node.parent=null;
}
}else if(node.leftChild==null && node.rightChild!=null){
//3.只有右孩子
if(parent==null){//如果要删除的是根
node.parent=null;
node.rightChild.parent=null;
root=node.rightChild;
}else{
if(parent.leftChild==node){//要删除的节点是父亲的左边
node.rightChild.parent=parent;
parent.leftChild=node.rightChild;
}else{//要删除的节点是父亲的右边
node.rightChild.parent=parent;
parent.rightChild=node.rightChild;
}
node.parent=null;
}
}else{//4。有左右两个孩子
if(node.rightChild.leftChild==null){//1.如果被删除节点的右子树的左子树为空,就直接补上右子树
node.rightChild.leftChild=node.leftChild;
if(parent==null){
root=node.rightChild;
}else{
if(parent.leftChild==node){
parent.leftChild=node.rightChild;
//
}else{
parent.rightChild=node.rightChild;
//
}
}
node.parent=null;
}else{//2.否则就要补上右子树的左子树上最小的一个
TreeNode leftNode=getMinLeftTreeNode(node.rightChild);
//1
leftNode.leftChild=node.leftChild;
//2
TreeNode leftNodeP=leftNode.parent;
leftNodeP.leftChild=leftNode.rightChild;
//3
leftNode.rightChild=node.rightChild;
//4
if(parent==null){
root=leftNode;
}else{
if(parent.leftChild==node){
parent.leftChild=leftNode;
//
}else{
parent.rightChild=leftNode;
//
}
}
}
}
}
}
private TreeNode getMinLeftTreeNode(TreeNode node) {
TreeNode curRoot=null;
if(node==null){
return null;
}else{
curRoot=node;
while(curRoot.leftChild!=null){
curRoot=curRoot.leftChild;
}
}
return curRoot;
}
}
哈夫曼数压缩
基本思想
将ASCII码字符根据权重转为二进制编码,权重越大的字符编码后所占位数越小。
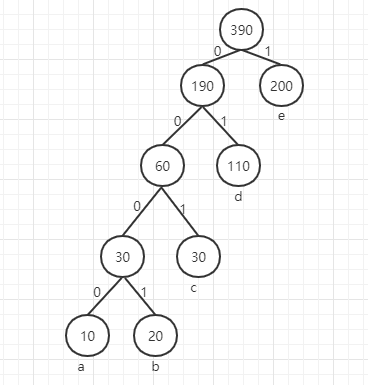
生成后的哈夫曼树:
e:1 d:01 c:001 a:0000 b:0001
节省字位数:
8 ∗ ( 200 + 110 + 30 + 10 + 20 ) − ( 200 ∗ 1 + 110 ∗ 2 + 30 ∗ 3 + 4 ∗ 10 + 4 ∗ 20 ) = 2960 − 630 = 2330 8*(200+110+30+10+20) - (200*1+110*2+30*3+4*10+4*20)=2960-630=2330 8∗(200+110+30+10+20)−(200∗1+110∗2+30∗3+4∗10+4∗20)=2960−630=2330
压缩了2960/630=4.6倍
可以看到,如果字符数越多且权重越均匀,则该算法压缩效果越差。
public class _5HuffmanTree {
TreeNode root;
public TreeNode createHuffmanTree(List<TreeNode<String>> list) {
while (list.size() > 1) {
Collections.sort(list);
TreeNode left = list.get(0);
TreeNode right = list.get(1);
TreeNode parent = new TreeNode<>("P", left.weight + right.weight);
parent.leftChild = left;
left.parent = parent;
parent.rightChild = right;
right.parent = parent;
list.remove(left);
list.remove(right);
list.add(parent);
}
root = list.get(0);
return root;
}
public static class TreeNode<T> implements Comparable<TreeNode<T>> {
T data;
int weight;
TreeNode leftChild;
TreeNode rightChild;
TreeNode parent;
public TreeNode(T data, int weight) {
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(TreeNode<T> o) {
if (this.weight > o.weight) {
return 1;
} else if (this.weight < o.weight) {
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
}
/**
* 编码
*/
public void getCode(TreeNode node) {
TreeNode tNode = node;
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
while (tNode != null && tNode.parent != null) {
if (tNode.parent.leftChild == tNode) {
stack.push("0");
} else if (tNode.parent.rightChild == tNode) {
stack.push("1");
}
tNode = tNode.parent;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(stack.pop() + " ");
}
}
private void showHuffman(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList<TreeNode> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.offer(root);
while (!list.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = list.poll();
System.out.println(node.data);
if (node.leftChild != null) {
list.offer(node.leftChild);
}
if (node.rightChild != null) {
list.offer(node.rightChild);
}
}
}
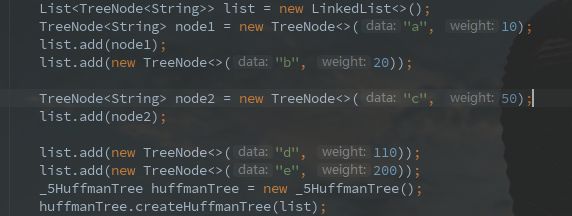
@Test
public void test() {
List<TreeNode<String>> list = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode<String> node1 = new TreeNode<>("a", 10);
list.add(node1);
list.add(new TreeNode<>("b", 20));
TreeNode<String> node2 = new TreeNode<>("c", 50);
list.add(node2);
list.add(new TreeNode<>("d", 110));
list.add(new TreeNode<>("e", 200));
_5HuffmanTree huffmanTree = new _5HuffmanTree();
huffmanTree.createHuffmanTree(list);
huffmanTree.showHuffman(huffmanTree.root);
huffmanTree.getCode(node2);
}
}
P
P
e
P
d
P
c
a
b
0 0 1
Process finished with exit code 0
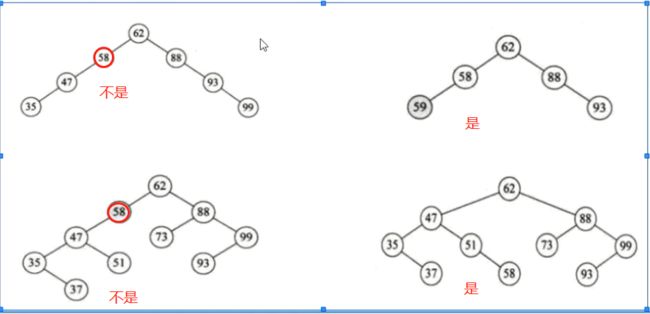
平衡二叉树
概念
平衡二叉树是一种二叉排序树,其中每一个节点的左子树和右子树高度差至多为1。
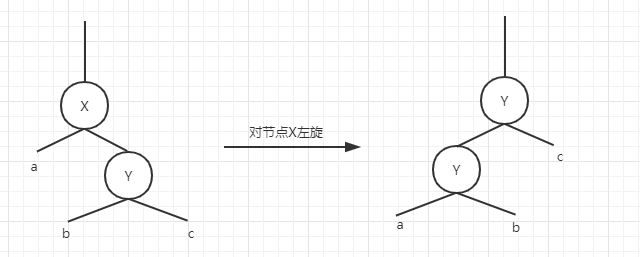
左旋
public class _6AVLBTree<E extends Comparable<E>> {
Node<E> root;
int size;
int balance;
public class Node<E extends Comparable<E>> {
E element;
// 平衡因子
int balance;
Node<E> left;
Node<E> right;
Node<E> parent;
public Node(E element, Node<E> parent) {
this.element = element;
this.parent = parent;
}
}
public void left_rotate(Node<E> x) {
if (x != null) {
// 先取到y
Node<E> y = x.right;
// 1. 把Y的左孩子作为X的右孩子
x.right = y.left;
if (y.left != null) {
y.left.parent = x;
}
// 2. 把Y移动到X原来的位置
y.parent = x.parent;
if (x.parent == null) {
root = y;
} else {
if (x.parent.left == x) {
x.parent.left = y;
} else if (x.parent.right == x) {
x.parent.right = y;
}
}
// 3. 把X移动到Y的左孩子
y.left = x;
x.parent = y;
}
}
}
左平衡树
右平衡树
public class _6AVLBTree<E extends Comparable<E>> {
Node<E> root;
int size = 0;
private static final int LH = 1;
private static final int RH = -1;
private static final int EH = 0;
public void left_rotate(Node<E> x) {
if (x != null) {
Node<E> y = x.right;//先取到Y结点
// 1。把贝塔作为X的右孩子
x.right = y.left;
if (y.left != null) {
y.left.parent = x;
}
// 2。把Y移到原来X的位置
y.parent = x.parent;
if (x.parent == null) {
root = y;
} else {
if (x.parent.left == x) {
x.parent.left = y;
} else if (x.parent.right == x) {
x.parent.right = y;
}
}
//3。X作为Y的左孩子
y.left = x;
x.parent = y;
}
}
public void right_rotate(Node<E> y) {
if (y != null) {
Node<E> yl = y.left;
//step1
y.left = yl.right;
if (yl.right != null) {
yl.right.parent = y;
}
// step2
yl.parent = y.parent;
if (y.parent == null) {
root = yl;
} else {
if (y.parent.left == y) {
y.parent.left = yl;
} else if (y.parent.right == y) {
y.parent.right = yl;
}
}
// step3
yl.right = y;
y.parent = yl;
}
}
public void rightBalance(Node<E> t) {
Node<E> tr = t.right;
switch (tr.balance) {
case RH://新的结点插入到t的右孩子的右子树中
left_rotate(t);
t.balance = EH;
tr.balance = EH;
break;
case LH://新的结点插入到t的右孩子的左子树中
Node<E> trl = tr.left;
switch (trl.balance) {
case RH:
t.balance = LH;
tr.balance = EH;
trl.balance = EH;
break;
case LH:
t.balance = EH;
tr.balance = RH;
trl.balance = EH;
break;
case EH:
tr.balance = EH;
trl.balance = EH;
t.balance = EH;
break;
}
right_rotate(t.right);
left_rotate(t);
break;
}
}
public void leftBalance(Node<E> t) {
Node<E> tl = t.left;
switch (tl.balance) {
case LH:
right_rotate(t);
tl.balance = EH;
t.balance = EH;
break;
case RH:
Node<E> tlr = tl.right;
switch (tlr.balance) {
case LH:
t.balance = RH;
tl.balance = EH;
tlr.balance = EH;
break;
case RH:
t.balance = EH;
tl.balance = LH;
tlr.balance = EH;
break;
case EH:
t.balance = EH;
tl.balance = EH;
tlr.balance = EH;
break;
default:
break;
}
left_rotate(t.left);
right_rotate(t);
break;
}
}
public boolean insertElement(E element) {
Node<E> t = root;
if (t == null) {
root = new Node<E>(element, null);
size = 1;
root.balance = 0;
return true;
} else {
//开始找到要插入的位置
int cmp = 0;
Node<E> parent;
Comparable<? super E> e = (Comparable<? super E>) element;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = e.compareTo(t.elemet);
if (cmp < 0) {
t = t.left;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
t = t.right;
} else {
return false;
}
} while (t != null);
//开始插入数据
Node<E> child = new Node<E>(element, parent);
if (cmp < 0) {
parent.left = child;
} else {
parent.right = child;
}
//节点已经放到了树上
//检查平衡,回溯查找
while (parent != null) {
cmp = e.compareTo(parent.elemet);
if (cmp < 0) {
parent.balance++;
} else {
parent.balance--;
}
if (parent.balance == 0) {//如果插入后还是平衡树,不用调整
break;
}
if (Math.abs(parent.balance) == 2) {
//出现了平衡的问题,需要修正
fixAfterInsertion(parent);
break;
} else {
parent = parent.parent;
}
}
}
size++;
return true;
}
@Test
public void test() {
Integer[] nums = {5, 8, 2, 0, 1, -2};
_6AVLBTree<Integer> tree = new _6AVLBTree<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
tree.insertElement(nums[i]);
}
showAVL((Node) tree.root);
}
public void showAVL(Node root) {
LinkedList<Node> list = new LinkedList<Node>();
list.offer(root);//队列放入
while (!list.isEmpty()) {
Node node = list.pop();//队列的取出
System.out.println(node.elemet);
if (node.left != null) {
list.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
list.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
private void fixAfterInsertion(Node<E> parent) {
if (parent.balance == 2) {
leftBalance(parent);
}
if (parent.balance == -2) {
rightBalance(parent);
}
}
public class Node<E extends Comparable<E>> {
E elemet;
int balance = 0;//平衡因子
Node<E> left;
Node<E> right;
Node<E> parent;
public Node(E elem, Node<E> pare) {
this.elemet = elem;
this.parent = pare;
}
public E getElemet() {
return elemet;
}
public void setElemet(E elemet) {
this.elemet = elemet;
}
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public Node<E> getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(Node<E> left) {
this.left = left;
}
public Node<E> getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(Node<E> right) {
this.right = right;
}
public Node<E> getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(Node<E> parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
}
}
红黑树
定义:它或者是一颗空树,或者是一颗具有如下定义的树:
- 节点非红即黑
- 根节点是黑色
- 所有null节点称为叶子节点,且颜色为黑色
- 所有红节点子节点都是黑色
- 从任一节点到其叶子节点的所有路径上都包含相同数目的黑节点
它是对平衡二叉树的改良:为了降低插入和删除操作的复杂程度,规定任意一个节点左右子树高度差不会超过一倍。