Java之IO流 序列流,内存输出流,对象操作流,打印流,标准输入输出流,随机访问流,数据输入输出流,Properties简单介绍
序列流 整合多个输入流
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.SequenceInputStream;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Vector;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Vector<InputStream> v = new Vector<>();
v.add(new FileInputStream("xxxcopy3.txt"));
v.add(new FileInputStream("xxxcopy2.txt"));
v.add(new FileInputStream("xxxcopy.txt"));
Enumeration<InputStream> en = v.elements();
SequenceInputStream sis = new SequenceInputStream(en);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d.txt");
int b;
while((b = sis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(b);
}
sis.close();
fos.close();
}
}
内存输出流
ByteArrayOutputStream
如果使用FileOutputStream来弄中文的话可能会出错 而内存输出流不会因为他是一次性读入到内存 一次性从内存输出
然后内存输出流并不是算是真正意义上的流 反而像数组 集合 其底层是有数组实现的
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d.txt");
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] b = new byte[5];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(b)) != -1) {
baos.write(b, 0, len);
//System.out.println(new String(b,0,len));//这样操作会乱码
}
//第一种打印
// byte[] bb = baos.toByteArray();
// System.out.println(new String(bb));
//第二种打印a
System.out.println(baos); //System.out.println(baos.toString()); 两种等价
fis.close();
}
}
对象操作流
对象输出流 序列化 (相当于玩游戏存档 ) 按照一定的序列
ObjectOutputStream
对象输入流反序列化 (相当于玩游戏读档) 按照一定的序列
ObjectinputStream
1.序列化代码 写出
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
Person p1 = new Person(13,"wangwu");
Person p2 = new Person(19,"lisi");
Person p3 = new Person(15,"zhaoliu");
ArrayList<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(p1);
list.add(p2);
list.add(p3);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("存档.txt"));
//一次性 用集合写出
oos.writeObject(list);
oos.close();
}
}
- 自定义类要可序列化 所以Person类需要实现序列化接口
注意添加id号 主要目的就是来方便确认版本 !!
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Person implements Serializable{
private int age;
private String name;
public Person() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Person(int age, String name) {
super();
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "person [age=" + age + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
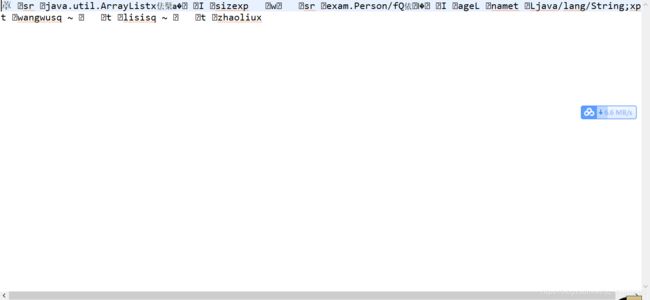
3.反序列化
读入 并且执行相应的操作
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import exam.Person;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//体现了装饰设计模式
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("存档.txt"));
//一次性读入 集合
ArrayList<Person> list = (ArrayList<Person>) ois.readObject();
//遍历打印
for (Person person : list) {
System.out.println(person);
}
ois.close();
}
}
打印流 (了解即可 用的很少)
1.PrintStream 字节打印流
println 底层是用string 来输出给控制台
write 底层是用码表来翻译 输出给控制流
2.PrintWriter 字符打印流 多了一个自动刷出功能 其实没啥用
如果流并不是关联内存和硬盘之间的话其实可以不用关闭掉
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import com.heima.bean.Person;
public class Demo05_PrintStream {
/**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
* PrintStream和PrintWriter分别是打印的字节流和字符流
* 只操作数据目的的
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//demo1();
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream("f.txt"),true);
//pw.println(97); //自动刷出功能只针对的是println方法
//pw.write(97);
pw.print(97);
pw.println(97);
pw.close();
}
public static void demo1() {
System.out.println("aaa");
PrintStream ps = System.out; //获取标注输出流
ps.println(97); //底层通过Integer.toString()将97转换成字符串并打印
ps.write(97); //查找码表,找到对应的a并打印
Person p1 = new Person("张三", 23);
ps.println(p1); //默认调用p1的toString方法
Person p2 = null; //打印引用数据类型,如果是null,就打印null,如果不是null就打印对象的toString方法
ps.println(p2);
ps.close();
}
}
标准输入流
System.in InputStream 同时注意一个程序只能用一个System.in !!
功能不够强大 通常用Scanner类的来装饰
标准输出流
System.out OutputStream
详细解释一下
System.out.println();
就是System.out 产生一个OutputStream对象 然后调用println方法
//不用关闭流的原因 :也是一个输出流,不用关,因为没有和硬盘上的文件产生关联的管道
System.setIn(new FileInputStream(“a.txt”)); //改变标准输入流
System.setOut(new PrintStream(“b.txt”)); //改变标注输出流
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class Demo06_SystemInOut {
/**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//demo1();
System.setIn(new FileInputStream("a.txt")); //改变标准输入流
System.setOut(new PrintStream("b.txt")); //改变标注输出流
InputStream is = System.in; //获取标准的键盘输入流,默认指向键盘,改变后指向文件
PrintStream ps = System.out; //获取标准输出流,默认指向的是控制台,改变后就指向文件
int b;
while((b = is.read()) != -1) {
ps.write(b);
}
//System.out.println(); //也是一个输出流,不用关,因为没有和硬盘上的文件产生关联的管道
is.close();
ps.close();
}
public static void demo1() throws IOException {
InputStream is = System.in;
int x = is.read();
System.out.println(x);
is.close();
InputStream is2 = System.in;
int y = is2.read();
System.out.println(y);
}
}
随机访问流
22.12_IO流(随机访问流概述和读写数据)(了解)
-
A:随机访问流概述
- RandomAccessFile概述
- RandomAccessFile类不属于流,是Object类的子类。但它融合了InputStream和OutputStream的功能。
- 支持对随机访问文件的读取和写入。
-
B:read(),write(),seek()
22.13_IO流(数据输入输出流)(了解)
- 1.什么是数据输入输出流
- DataInputStream, DataOutputStream可以按照基本数据类型大小读写数据
- 例如按Long大小写出一个数字, 写出时该数据占8字节. 读取的时候也可以按照Long类型读取, 一次读取8个字节.
- 2.使用方式
- DataOutputStream(OutputStream), writeInt(), writeLong()
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("b.txt"));
dos.writeInt(997);
dos.writeInt(998);
dos.writeInt(999);
dos.close();
- DataInputStream(InputStream), readInt(), readLong()
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("b.txt"));
int x = dis.readInt();
int y = dis.readInt();
int z = dis.readInt();
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
System.out.println(z);
dis.close();
Properties
是HashTable的子类 (Map集合)
主要是用来配置文件
不用关心配置文件中的内容同序列化和反序列化一样只管能读能写就行
然后一些常用的方法
22.14_IO流(Properties的概述和作为Map集合的使用)(了解)
- A:Properties的概述
- Properties 类表示了一个持久的属性集。
- Properties 可保存在流中或从流中加载。
- 属性列表中每个键及其对应值都是一个字符串。
- B:案例演示
- Properties作为Map集合的使用
###22.15_IO流(Properties的特殊功能使用)(了解)
- A:Properties的特殊功能
- public Object setProperty(String key,String value)
- public String getProperty(String key)
- public Enumeration stringPropertyNames()
- B:案例演示
- Properties的特殊功能
###22.16_IO流(Properties的load()和store()功能)(了解)
- A:Properties的load()和store()功能
- B:案例演示
- Properties的load()和store()功能
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("myconfig.properties"));
prop.store(new FileOutputStream("myconfig.properties"), "yrq");
System.out.println(prop);
}
}