数据库-SQL基本数据类型及常见语句
#3
| Varchar(n) | 可变长度字符串,用户指定的最大长度n。 |
| Nvarchar(n) | 与VARCHAR 类型相似。不同的是,NVARCHAR数据类型采用UNICODE 标准字符集(Character Set), n 的取值为1 到4000. |
| int | 从-2的31次方到2的31次方之间的所有正负整数。每个INT 类型的数据按4 个字节存储,其中1 位表示整数值的正负号,其它31 位表示整数值的长度和大小。 |
| smallint | -2的15次方到2的15次方-1之间的所有正负整数。每个SMALLINT 类型的数据占用2 个字节的存储空间,其中1 位表示整数值的正负号,其它15 位表示整数值的长度和大小。 |
| tinyint | 0-255正整数,每个占用1字节 |
| bigint | -2^63 到2^63-1之间的所有正负整数。每个BIGINT 类型的数据占用8个字节的存储空间。 |
| Numeric(p,d) | 定点数,用户指定精度为p位,小数点右侧为d位。 |
| Real | REAL数据类型可精确到第7 位小数,其范围为从-3.40E -38 到3.40E +38。 每个REAL类型的数据占用4 个字节的存储空间。 |
| float | FLOAT数据类型可精确到第15 位小数,其范围为从-1.79E -308 到1.79E +308。 每个FLOAT 类型的数据占用8 个字节的存储空间。 FLOAT数据类型可写为FLOAT[ n ]的形式。n 指定FLOAT 数据的精度。n 为1到15 之间的整数值。当n 取1 到7 时,实际上是定义了一个REAL 类型的数据,系统用4 个字节存储它;当n 取8 到15 时,系统认为其是FLOAT 类型,用8 个字节存储它。 |
| decimal | DECIMAL数据类型可以提供小数所需要的实际存储空间,但也有一定的限制,您可以用2 到17 个字节来存储从-10的38次方-1 到10的38次方-1 之间的数值。可将其写为DECIMAL[ p [s] ]的形式,p 和s 确定了精确的比例和数位。其中p 表示可供存储的值的总位数(不包括小数点),缺省值为18; s 表示小数点后的位数,缺省值为0。 例如:decimal (15 5),表示共有15 位数,其中整数10 位,小数5。 位表4-3 列出了各精确度所需的字节数之间的关系。 |
| datetime | 存储从公元1753 年1 月1 日零时起到公元9999 年12 月31 日23 时59 分59 秒之间的所有日期和时间,其精确度可达三百分之一秒,即3.33 毫秒。DATETIME 数据类型所占用的存储空间为8 个字节。其中前4 个字节用于存储1900 年1 月1 日以前或以后的天数,数值分正负,正数表示在此日期之后的日期,负数表示在此日期之前的日期。后4 个字节用于存储从此日零时起所指定的时间经过的毫秒数。如果在输入数据时省略了时间部分,则系统将12:00:00:000AM作为时间缺省值:如果省略了日期部分,则系统将1900 年1 月1 日作为日期缺省值。 |
| money | 有4 位小数的DECIMAL 值,其取值从-2的63次方(-922,337,203,685,477.5808到2的63次方-1(+922,337,203,685,477.5807),数据精度为万分之一货币单位。MONEY 数据类型使用8个字节存储。 |
create table branch
(branch_name char(15),
branch_city char(30),
assets integer,
primary key (branch_name))
删除数据表
1.drop table r:Deletes not only all tuples of r, but also the schema for r
2.Delete table r:Retains relation r, but deletes all tuples in r
修改数据表
1.alter table r add A D
2.alter table r drop A
基本查询语句(SQL名称不区分大小写)
1.select选择
select A1, A2, ..., An
from r1, r2, ..., rm
where P
2.distinct :强制消除重复,在select之后插入
select distinct branch_name
from loan
3.All:关键字all指定不删除重复项。(sql默认)
select all branch_name
from loan
4.全选
select
from loan
5.选择的时候可以做±*/的操作
select loan_number, branch_name, amount*100
from loan
6.Between:选择中间的值
select loan_number
from loan
where amount between 90000 and 100000
7.多个表可以一起查询
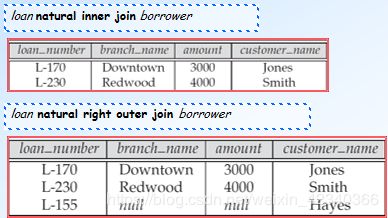
select customer_name, borrower.loan_number, amount
from borrower, loan
where borrower.loan_number = loan.loan_number
And branch_name = ‘Perryridge’
8.重命名操作 old-name as new-name
select customer_name,
borrower.loan_number as loan_id, amount
from borrower, loan
where borrower.loan_number = loan.loan_number
9.元组变量
select customer_name, T.loan_number, S.amount
from borrower as T, loan as S
where T.loan_number = S.loan_number
10.模糊查询
select customer_name
from customer
where customer_street like '% Main%'
匹配80%的时候要用 like’80%’
11.结果排序,我们可以为降序指定desc或为升序指定asc
select * from loan
order by amount desc, loan_number asc
12.union, intersect, except对应 并、交、减的集合操作,会自动消除重复

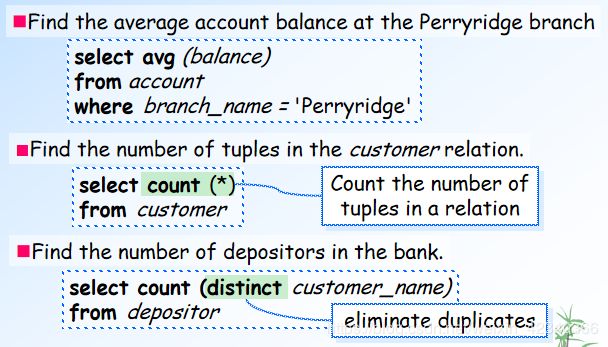
13.Aggregate Functions 聚合函数groupby
select branch_name, count (distinct customer_name)
from depositor, account
where depositor.account_number = account.account_number
group by branch_name
14.Aggregate Functions 聚合函数having
(having子句中的谓词应用于组的形成之后,而where子句中的谓词应用于组的形成之前)
select branch_name, avg (balance)
from account
group by branch_name
having avg (balance) > 1200
15.Null
任何包含null的算术表达式的结果都是null,任何与null的比较返回unknown
null is null 返回true
null = null 返回 unknown
除了count(*)以外的所有聚合操作都忽略聚合属性上具有空值的元组
where子句谓词的结果如果计算结果为unknown,则将被视为false
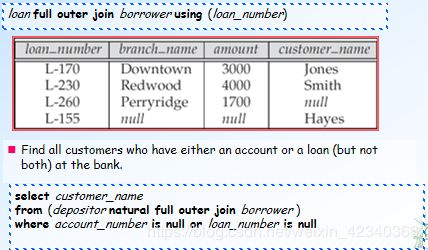
16.Nested Subqueries嵌套查询
select distinct customer_name
from borrower
where customer_name not in (select customer_name from depositor )
select branch_name, avg_balance
from (select branch_name, avg (balance)
from account
group by branch_name )
as branch_avg ( branch_name, avg_balance )
where avg_balance > 1200
17.Some语句
select branch_name
from branch
where assets > some
(select assets
from branch
where branch_city = 'Brooklyn')
select branch_name
from branch
where assets > all
(select assets from branch where branch_city = 'Brooklyn')
19.exists 语句,如果参数子查询非空,exists构造返回值true。
select distinct customer_name
from borrower
where exists (select * from depositor
where depositor.customer_name = borrower.customer_name )
20.unique 语句,惟一构造测试子查询的结果中是否有任何重复的元组。
外部变量称为相关变量(correlation variable)。
select T.customer_name
from depositor as T
where unique (
select R.customer_name
from account, depositor as R
where T.customer_name = R.customer_name and
R.account_number = account.account_number and
account.branch_name = 'Perryridge')
21.with 语句,with子句提供了一种定义临时视图的方法,该视图的定义仅对发生with子句的查询可用。
with max_balance (value) as
select max (balance)
from account
select account_number
from account, max_balance
where account.balance = max_balance.value
22.View创建视图
create view v as < query expression >
创建视图时,查询表达式存储在数据库中;使用视图将表达式替换到查询中。
一旦定义了视图,视图名称就可以用来引用视图生成的虚拟关系。
create view all_customer as
(select branch_name, customer_name
from depositor, account
where depositor.account_number =
account.account_number )
union
(select branch_name, customer_name
from borrower, loan
where borrower.loan_number = loan.loan_number)
然后使用view
select customer_name
from all_customer
where branch_name = 'Perryridge'
23.Delete语句
delete from account
where branch_name in
(select branch_name
from branch where branch_city = 'Needham')
24.Insert语句
insert into account (branch_name, balance, account_number)
values ('Perryridge', 1200, 'A-9732')
25.Update语句
update account
set balance = balance*1.06
where balance > 10000
可以加入逻辑判断
update account
set balance = case
when balance <= 10000 then balance *1.05
else balance * 1.06
end
可以更新视图view的信息
create view v as
select loan_number, branch_name, amount
from loan
where branch_name = ‘Perryridge’
insert into v values ( 'L-99','Downtown', '23')