浅谈Android注解在日常开发中的简单使用
注解一词,你第一眼看过去可能会误解为是注释,其实不然,在Java技术中它是属于一个单独的功能分类模块,它有其独特的使用功能,接下我们就来先看一下Java中的注解:
一、Java注解
我们简单来看下java的注解功能:
适用场景——通过的类的反射获取类的方法和属性
java中元注解有四个: @Retention @Target @Document @Inherited;
@Retention:注解的保留位置
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) //注解仅存在于源码中,在class字节码文件中不包含
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS) // 默认的保留策略,注解会在class字节码文件中存在,但运行时无法获得,
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 注解会在class字节码文件中存在,在运行时可以通过反射获取到
@Target:注解的作用目标
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) //接口、类、枚举、注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD) //字段、枚举的常量
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) //方法
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) //方法参数
@Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR) //构造函数
@Target(ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE)//局部变量
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)//注解
@Target(ElementType.PACKAGE) ///包
@Document:说明该注解将被包含在javadoc中
@Inherited:说明子类可以继承父类中的该注解
二、简单Demo
这个示例主要是获取一个JavaBean的类和属性的注解值。
1、我们首先编写一个类的注解类,代码如下:
package wufq.com.annotationtest;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Author:wufq on 2018/5/31 15:27
* Email:[email protected]
*
* @TODO:
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ParamType {
String value();
}结合第一小部分的知识点,ElementType.TYPE用来注解类的,另外RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME注解在class字节码文件中,并且运行时可通过反射获取到。接下来我们看来属性的注解类:
2、属性注解类
package wufq.com.annotationtest;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Author:wufq on 2018/5/31 15:29
* Email:[email protected]
*
* @TODO:
*/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ParamFiled {
String value();
}同理,我们可以知道ElementType.FIELD用来注解属性的,另外RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME注解在class字节码文件中,并且运行时可通过反射获取到。
3、JavaBean类
package wufq.com.annotationtest;
/**
* Author:wufq on 2018/5/31 15:30
* Email:[email protected]
*
* @TODO:
*/
@ParamType("tb_student")
public class Student {
@ParamFiled("tb_name")
public String name;
@ParamFiled("tb_sex")
public String sex;
@ParamFiled("tb_age")
public String age;
@ParamFiled("tb_schoolName")
public String schoolName;
public Student(String name, String sex, String age, String schoolName) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
this.schoolName = schoolName;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSchoolName() {
return schoolName;
}
public void setSchoolName(String schoolName) {
this.schoolName = schoolName;
}
}
从上面我们可以看出,代码中分别用类注解和属性注解标记了JavaBean,也即是Student类,没什么好说的,我们直接看调用的地方吧。
4、客户端
package wufq.com.annotationtest;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// Student student = new Student("张三","男","90","扬名中学");
}
public void load(View view){
Class cz = Student.class;
init(cz);
}
private void init(Class clazz){
String result;
if(clazz.getAnnotation(ParamType.class) == null){
result = clazz.getClass().getSimpleName();
} else {
result = clazz.getAnnotation(ParamType.class).value();
}
Log.i("wufq","result == "+result);
// String filed;
// if (clazz.getAnnotation(ParamFiled.class) == null){
// filed = clazz.getClass().getSimpleName();
// } else {
// filed = clazz.getAnnotation(ParamFiled.class).value();
// }
// Log.i("wufq","filed == "+filed);
// Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations();
// if (annotations != null && annotations.length > 0){
// for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
// Log.i("wufq","annotation == "+annotation.toString());
// }
// }
Field fields [] = clazz.getFields();
if (fields != null && fields.length > 0){
for (Field field : fields){
field.setAccessible(true);
}
String fieldName;
for (Field field : fields){
if (field.getAnnotation(ParamFiled.class) == null){
fieldName = field.getName();
} else {
fieldName = field.getAnnotation(ParamFiled.class).value();
}
Log.i("wufq","fieldName == "+fieldName);
}
}
}
}
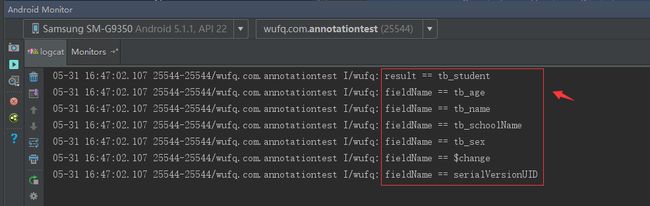
我们运行下代码,结果打印如下:
当然前提是Student的属性必须是public的。
好了,注解就简单讲了下,讲得不好的地方请多多指教。