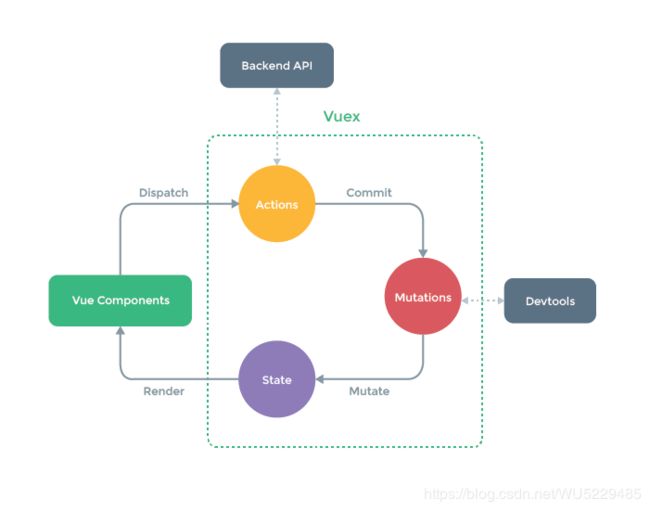
Vuex源码阅读理解
1. 提出问题:Vuex是如把store注入到Vue实例中去的呢?this.$store
目标文件:mixin.js
每个vue实例里面访问this.$store都是访问的mixin混入在beforeCreate生命周期里面的this.$store
根据这个mixin.js中的代码逻辑可以知道,在vue2.x的条件下:
if (version >= 2) {
/*通过mixin将vuexInit混淆到Vue实例的beforeCreate钩子中*/
Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate: vuexInit })
} 且vuexInit初始化vue的方法逻辑如下,保证使用的this.$store指向同一个store对象:
/*Vuex的init钩子,会存入每一个Vue实例等钩子列表*/
function vuexInit () {
const options = this.$options
// store injection
if (options.store) {
/*存在store其实代表的就是Root节点,直接执行store(function时)或者使用store(非function)*/
this.$store = typeof options.store === 'function'
? options.store()
: options.store
} else if (options.parent && options.parent.$store) {
/*子组件直接从父组件中获取$store,这样就保证了所有组件都公用了全局的同一份store*/
this.$store = options.parent.$store
}
}
}2. 解析Store的构造函数constructor内部初始化流程
(1)初始化一些state、dispatch、commit、getters等属性方法
(2)初始化module
(3)devTool插件调用注册
//构造函数,主要做了一些模块初始化的事情
constructor (rawModule, runtime) {
//缓存运行时的标志
this.runtime = runtime
//创建一个空对象来保存子模块
this._children = Object.create(null)
//缓存传入的模块
this._rawModule = rawModule
//缓存传入模块的state,如果state是一个函数,则执行这个函数
const rawState = rawModule.state
this.state = (typeof rawState === 'function' ? rawState() : rawState) || {}
}
(4)installModule方法解析
2-4-1. 为module加上namespace名字空间
/* 获取module的namespace */
const namespace = store._modules.getNamespace(path)
// register in namespace map
/* 如果有namespace则在_modulesNamespaceMap中注册 */
if (module.namespaced) {
store._modulesNamespaceMap[namespace] = module
}2-4-2. 注册mutation、action以及getter
/* 遍历注册mutation */
module.forEachMutation((mutation, key) => {
const namespacedType = namespace + key
registerMutation(store, namespacedType, mutation, local)
})
/* 遍历注册action */
module.forEachAction((action, key) => {
const namespacedType = namespace + key
registerAction(store, namespacedType, action, local)
})
/* 遍历注册getter */
module.forEachGetter((getter, key) => {
const namespacedType = namespace + key
registerGetter(store, namespacedType, getter, local)
})
/* 递归安装mudule */
module.forEachChild((child, key) => {
installModule(store, rootState, path.concat(key), child, hot)
})
(5)resetStoreVM方法解析
2-5-1 . 首先在代码逻辑中段new一个Vue实例store._vm / this._vm:
store._vm = new Vue({
data: {
$$state: state
},
computed
})2-5-2. 遍历wrappedGetters
forEachValue(wrappedGetters, (fn, key) => {
// use computed to leverage its lazy-caching mechanism
computed[key] = () => fn(store)
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key, {
get: () => store._vm[key],
enumerable: true // for local getters
})
})这段方法实现了:调用this.$store.getters.text 等价于 调用store._vm.text
下面我们来解读Vuex提供的一些API
1. 最常用的commit ( mutation )
代码占用符;
(1)commit方法会根据type找到并调用_mutations中的所有type对应的mutation方法:
/* 取出type对应的mutation的方法 */
const entry = this._mutations[type](2)所以当没有namespace的时候,commit方法会触发所有module中的mutation方法,再执行完所有的mutation之后会执行_subscribers中的所有订阅者
/* 执行mutation中的所有方法 */
this._withCommit(() => {
entry.forEach(function commitIterator (handler) {
handler(payload)
})
})
/* 通知所有订阅者 */
this._subscribers.forEach(sub => sub(mutation, this.state))2. 订阅函数subscrible
/* 注册一个订阅函数,返回取消订阅的函数 */
subscribe (fn) {
const subs = this._subscribers
if (subs.indexOf(fn) < 0) {
subs.push(fn)
}
return () => {
const i = subs.indexOf(fn)
if (i > -1) {
subs.splice(i, 1)
}
}
}3. dispath ( action ) 的实现
类似于commit的实现,也是寻找type,执行type对应的方法;只是dispatch的返回值存在差异
/* 调用action的dispatch方法 */
dispatch (_type, _payload) {
//...
/* 是数组则包装Promise形成一个新的Promise,只有一个则直接返回第0个 */
return entry.length > 1
? Promise.all(entry.map(handler =>; handler(payload)))
: entry[0](payload)
}4.registerAction注册的实现
/* 遍历注册action */
function registerAction (store, type, handler, local) {
/* 取出type对应的action */
const entry = store._actions[type] || (store._actions[type] = [])
entry.push(function wrappedActionHandler (payload, cb) {
let res = handler.call(store, {
dispatch: local.dispatch,
commit: local.commit,
getters: local.getters,
state: local.state,
rootGetters: store.getters,
rootState: store.state
}, payload, cb)
// ...
})
}5. 观察一个getter方法
watch (getter, cb, options) {
return this._watcherVM.$watch(() => getter(this.state, this.getters), cb, options)
}6. registerModule 注册一个动态module
/* 注册一个动态module,当业务进行异步加载的时候,可以通过该接口进行注册动态module */
registerModule (path, rawModule) {
/* 转化称Array */
if (typeof path === 'string') path = [path]
/*注册*/
this._modules.register(path, rawModule)
/*初始化module*/
installModule(this, this.state, path, this._modules.get(path))
// 通过vm重设store,新建Vue对象使用Vue内部的响应式实现注册state以及computed
resetStoreVM(this, this.state)
}7. unregisterModule注销一个动态module
unregisterModule (path) {
/* 转化称Array */
if (typeof path === 'string') path = [path]
/*注销*/
this._modules.unregister(path)
this._withCommit(() => {
/* 获取父级的state */
const parentState = getNestedState(this.state, path.slice(0, -1))
/* 从父级中删除 */
Vue.delete(parentState, path[path.length - 1])
})
/* 重制store */
resetStore(this)
}8. resetStore 重制store
function resetStore (store, hot) {
store._actions = Object.create(null)
store._mutations = Object.create(null)
store._wrappedGetters = Object.create(null)
store._modulesNamespaceMap = Object.create(null)
const state = store.state
// init all modules
installModule(store, state, [], store._modules.root, true)
// reset vm
resetStoreVM(store, state, hot)
}