4、adpcm编解码
https://blog.csdn.net/wzz4420381/article/details/48812729/
https://blog.csdn.net/littlezls/article/details/83501580
https://blog.csdn.net/su_zhi_guang/article/details/3143145
http://www.mp3-tech.org/programmer/docs/adpcm.pdf
https://blog.csdn.net/forfuture3513/article/details/51764814
https://blog.csdn.net/szfhy/article/category/5773109
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43103848/article/month/2019/03
ADPCM算法浅析
- ADPCM算法简介
1.1 脉冲编码调制(PCM)的概念
(1)PCM是pulse code modulation的缩写
(2)概念上最简单、理论上最完善、最早研制成功、使用最为广泛、数据量最大的编码系统
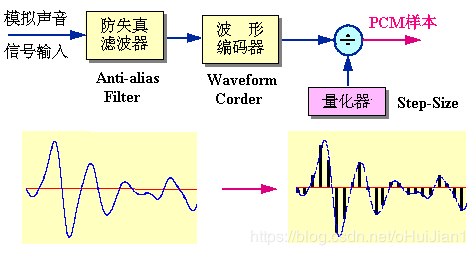
在上图中:
- 输入是模拟信号,输出是PCM样本。
- 防失真滤波器:低通滤波器,用来滤除声音频带以外的信号
- 波形编码器:可理解为采样器
- 量化器:可理解为“量化阶大小(step-size)”生成器或者称为“量化间隔”生成器
PCM实际上是模拟信号数字化:
- 第一步是采样,就是每隔一段时间间隔读一次声音的幅度
- 第二步是量化,就是把采样得到的声音信号幅度转换成数字值
1.2 量化的方法
量化的方法主要有均匀量化和非均匀量化。
均匀量化:
- 采用相等的量化间隔/等分尺度量采样得到的信号幅度,也称为线性量化。
- 量化后的样本值Y和原始值X的差E=Y-X称为量化误差或量化噪声
非均匀量化
- 大的输入信号采用大的量化间隔,小的输入信号采用小的量化间隔
- 可在满足精度要求的情况下用较少的位数来表示
- 声音数据还原时,采用相同的规则
- 采样输入信号幅度和量化输出数据之间定义了两种对应关系(μ律压扩算法,A律压扩算法)注:压扩(companding)

小结:PCM编码早期主要用于话音通信中的多路复用。一般来说,在电信网中传输媒体线路费用约占总成本的65%,设备费用约占成本的35%,因此提高线路利用率是一个重要课题。
1.3 自适应差分脉冲编码调制(ADPCM)的概念
- ADPCM的中文术语为自适应差分脉冲编码调制
- adaptive difference pulse code modulation的缩写
- 综合了APCM的自适应特性和DPCM系统的差分特性,是一种性能比较好的波形编码技术
它的核心想法是:
- 利用自适应的思想改变量化阶的大小,即使用小的量化阶(step-size)去编码小的差值,使用大的量化阶去编码大的差值。
- 使用过去的样本值估算下一个输入样本的预测值,使实际样本值和预测值之间的差值总是最小
1.4 ADPCM编码框图
接收端的译码器使用与发送端相同的算法,利用传送来的信号来确定量化器和逆量化器中的量化阶大小,并且用它来预测下一个接收信号的预测值。

2 ADPCM代码实现
2.1 ADPCM编码程序逻辑
由待编码文件的起始部分开始,依次读取长度为len的数据段,送入adpcm_encoder,得到编码后的数据,并将结果存入中间文件,直到待编码文件的所有部分都已编码完成。
adpcm_thirdparty_reset(struct adpcm_state *state);; //此函数只需在编码开始前调用一次
while(待编码文件未读完)
{
读取长度为len的数据段,存入固定的数组内;
执行adpcm_encoder,得到编码后的数据段,以及编码后的数据段长度len_2;
将编码后的数据段顺次存入中间文件内;
}
2.2 ADPCM解码程序逻辑
由中间文件的起始部分开始,依次读取长度为len_2的数据段,送入adpcm_decoder,得到编码后的数据,并将结果存入最终文件,直到中间文件的所有部分都已解码完成。
while(中间文件未读完)
{
读取长度为len_2的数据段,存入固定的数组内;
执行adpcm_decoder,得到解码后的数据段;
将解码后的数据段顺次存入最终文件内;
}
2.3 代码示例
#include
#include
struct adpcm_state
{
int valprev;
int index;
};
void adpcm_thirdparty_reset(struct adpcm_state *state);
void adpcm_encoder(short *indata, signed char *outdata, int len, struct adpcm_state *state);
void adpcm_decoder(signed char *indata, short *outdata, int len, struct adpcm_state *state);
#ifndef __STDC__
#define signed
#endif
/* Intel ADPCM step variation table */
static int indexTable[16] = {
-1, -1, -1, -1, 2, 4, 6, 8,
-1, -1, -1, -1, 2, 4, 6, 8,
};
static int stepsizeTable[89] = {
7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17,
19, 21, 23, 25, 28, 31, 34, 37, 41, 45,
50, 55, 60, 66, 73, 80, 88, 97, 107, 118,
130, 143, 157, 173, 190, 209, 230, 253, 279, 307,
337, 371, 408, 449, 494, 544, 598, 658, 724, 796,
876, 963, 1060, 1166, 1282, 1411, 1552, 1707, 1878, 2066,
2272, 2499, 2749, 3024, 3327, 3660, 4026, 4428, 4871, 5358,
5894, 6484, 7132, 7845, 8630, 9493, 10442, 11487, 12635, 13899,
15289, 16818, 18500, 20350, 22385, 24623, 27086, 29794, 32767
};
void adpcm_thirdparty_reset(struct adpcm_state *state)
{
state->valprev = 0;
state->index = 0;
}
void adpcm_encoder(short *indata, signed char *outdata, int len, struct adpcm_state *state)
{
short *inp; /* Input buffer pointer */
signed char *outp; /* output buffer pointer */
int val; /* Current input sample value */
int sign; /* Current adpcm sign bit */
int delta; /* Current adpcm output value */
int diff; /* Difference between val and valprev */
int step; /* Stepsize */
int valpred; /* Predicted output value */
int vpdiff; /* Current change to valpred */
int index; /* Current step change index */
int outputbuffer; /* place to keep previous 4-bit value */
int bufferstep; /* toggle between outputbuffer/output */
outp = (signed char *)outdata;
inp = indata;
valpred = state->valprev;
index = state->index;
step = stepsizeTable[index];
bufferstep = 1;
for ( ; len > 0 ; len-- )
{
val = *inp++; //val:当前输入的pcm数据
/* Step 1 - compute difference with previous value */
diff = val - valpred; //当前输入的pcm数据与预测的pcm数据(第一次为上一个pcm数据)的差值diff
sign = (diff < 0) ? 8 : 0;
if ( sign ) diff = (-diff);
/* Step 2 - Divide and clamp */
/* Note:
** This code *approximately* computes:
** delta = diff*4/step;
** vpdiff = (delta+0.5)*step/4;
** but in shift step bits are dropped. The net result of this is
** that even if you have fast mul/div hardware you cannot put it to
** good use since the fixup would be too expensive.
*/
delta = 0;
vpdiff = (step >> 3);
if ( diff >= step ) {
delta = 4;
diff -= step;
vpdiff += step;
}
step >>= 1;
if ( diff >= step ) {
delta |= 2;
diff -= step;
vpdiff += step;
}
step >>= 1;
if ( diff >= step ) {
delta |= 1;
vpdiff += step;
}
/* Step 3 - Update previous value */
if ( sign )
valpred -= vpdiff;
else
valpred += vpdiff;
/* Step 4 - Clamp previous value to 16 bits */
if ( valpred > 32767 )
valpred = 32767;
else if ( valpred < -32768 )
valpred = -32768;
/* Step 5 - Assemble value, update index and step values */
delta |= sign;
index += indexTable[delta];
if ( index < 0 ) index = 0;
if ( index > 88 ) index = 88;
step = stepsizeTable[index];
/* Step 6 - Output value
if ( bufferstep ) {
outputbuffer = (delta << 4) & 0xf0;
} else {
*outp++ = (delta & 0x0f) | outputbuffer;
}*/
if ( bufferstep ) {
outputbuffer = delta & 0x0f;
} else {
*outp++ = ((delta << 4) & 0xf0) | outputbuffer;
}
bufferstep = !bufferstep;
}
/* Output last step, if needed */
if ( !bufferstep )
*outp++ = outputbuffer;
state->valprev = valpred;
state->index = index;
}
void adpcm_decoder(signed char *indata, short *outdata, int len, struct adpcm_state *state)
{
signed char *inp; /* Input buffer pointer */
short *outp; /* output buffer pointer */
int sign; /* Current adpcm sign bit */
int delta; /* Current adpcm output value */
int step; /* Stepsize */
int valpred; /* Predicted value */
int vpdiff; /* Current change to valpred */
int index; /* Current step change index */
int inputbuffer; /* place to keep next 4-bit value */
int bufferstep; /* toggle between inputbuffer/input */
outp = outdata;
inp = (signed char *)indata;
valpred = state->valprev;
index = state->index;
step = stepsizeTable[index];
bufferstep = 0;
for ( ; len > 0 ; len-- ) {
/* Step 1 - get the delta value */
if ( !bufferstep ) {
inputbuffer = *inp++;
delta = inputbuffer & 0xf;
} else {
delta = (inputbuffer >> 4) & 0xf;
}
bufferstep = !bufferstep;
/* Step 2 - Find new index value (for later) */
index += indexTable[delta];
if ( index < 0 ) index = 0;
if ( index > 88 ) index = 88;
/* Step 3 - Separate sign and magnitude */
sign = delta & 8;
delta = delta & 7;
/* Step 4 - Compute difference and new predicted value */
/*
** Computes 'vpdiff = (delta+0.5)*step/4', but see comment
** in adpcm_coder.
*/
vpdiff = step >> 3;
if ( delta & 4 ) vpdiff += step;
if ( delta & 2 ) vpdiff += step>>1;
if ( delta & 1 ) vpdiff += step>>2;
if ( sign )
valpred -= vpdiff;
else
valpred += vpdiff;
/* Step 5 - clamp output value */
if ( valpred > 32767 )
valpred = 32767;
else if ( valpred < -32768 )
valpred = -32768;
/* Step 6 - Update step value */
step = stepsizeTable[index];
/* Step 7 - Output value */
*outp++ = valpred;
}
state->valprev = valpred;
state->index = index;
}
3 如何理解ADPCM
- ADPCM可以将40个量化精度为16bit的采样值压缩到20Byte,压缩比是4:1
- 假设有40个量化精度为16bit的采样值,这里表示为short
sample[40],用ADPCM算法压缩后用encoded_sample[20]表示。encoded_sample[0]和encoded_sample[1]分别存储sample[0]的高字节和低字节。从encoded_sample[2]开始,每个字节的高4位和低4位分别存储了1个sample的特征参数,且后一个sample的特征参数的值是前一个sample特征参数的函数。 - 基于上一点,如果压缩后的encoded_sample[20]在传输过程中出现丢失或误码,就会导致解码后的数据严重失真。所以在传输时建议采用可靠连接,即需要保证每次传输都被正确接收。
- 求出输入的pcm数据与预测的pcm数据(第一次为上一个pcm数据)的差值diff;
- 通过差分量化器算出delta(通过index(首次编码index为0)求出step,通过diff和step求出delta)。delta即为编码后的数据;
- 通过逆量化器求出vpdiff(通过求出的delta和step算出vpdiff);
- 求出新的预测valpred,即上次预测的valpred+vpdiff;
- 通过预测器(归一化),求出当前输入pcm input的预测pcm值,为下一次计算用;
- 量化阶调整(通过delta查表及index,计算出新的index值)。为下次计算用;
- 通过逆量化器求出vpdiff(通过存储的delta和index,求出step,算出vpdiff);
- 求出新的预测valpred,即上次预测的valpred+vpdiff;
- 通过预测器(归一化),求出当前输入pcm input的预测pcm值,为下一次计算用。预测的pcm值即为解码后的数据;
- 量化阶调整(通过delta查表及index,计算出新的index值)。为下次计算用;
注释说明
- 通过编码和解码的原理我们可以看出其实第一次编码的时候已经进行了解码,即预测的pcm。
- 因为编码再解码后输出的数据已经被量化了。根据计算公式delta = diff*4/step;vpdiff =
(delta+0.5)*step/4;考虑到都是整数运算,可以推导出:pcm数据经过编码再解码生成的预测pcm数据,如果预测pcm数据再次编码所得的数据与第一次编码所得的数据是相同的。故pcm数据经过一次编码有损后,不论后面经过几次解码再编码都是数据一样,音质不会再次损失。即相对于第一次编码后,以后数据不论多少次编解码,属于无损输出。
案例:
/* realize the adpcm code and decode, bandwidth needed is 32kbps,
is half of the ulaw coded, 64kbps
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "adpcm.h"
#define RATE 8000
#define SIZE AFMT_S16_LE
#define CHANNELS 2
#define FRAME_SIZE 1000
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd, mid;
int arg;
int status;
int i;
// for encode use
unsigned char inbuf[FRAME_SIZE*4]; // 2 channels , 16bit data , so *4
short inenc[FRAME_SIZE]; // 1 channel, 16bit data, but short type, so *1
unsigned char encbuf[FRAME_SIZE/2];
// for decode use
short decbuf[FRAME_SIZE]; // decode restore inenc
unsigned char outbuf[FRAME_SIZE*4]; // restore inbuf
// adpcm
struct adpcm_state enc_state, dec_state;
//----------------------------------------------------------------------
fd = open("/dev/dsp", O_RDWR);
arg = SIZE;
printf("SIZE:=%d\n", arg);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("Open /dev/dsp fail");
exit(1);
}
arg = SIZE;
status = ioctl(fd, SNDCTL_DSP_SETFMT, &arg);
if (status == -1)
{
perror("SNDCTL_DSP_SETFMT ioctl failed");
exit(1);
}
arg = CHANNELS;
status = ioctl(fd, SNDCTL_DSP_CHANNELS, &arg);
if (status == -1)
{
perror("SNDCTL_DSP_CHANNELS ioctl failed");
exit(1);
}
ioctl(fd, SOUND_PCM_READ_CHANNELS, &arg);
if (arg != CHANNELS)
{
perror("unable to set channels");
exit(1);
}
arg = RATE;
status = ioctl(fd, SNDCTL_DSP_SPEED, &arg);
if (status == -1)
{
perror("SNDCTL_DSP_SPEED ioctl failed");
exit(1);
}
if (arg != RATE)
{
perror("unable to set rate");
exit(1);
}
mid = open("/dev/mixer", O_RDWR);
arg = SOUND_MASK_MIC;
ioctl(mid, SOUND_MIXER_READ_VOLUME, (char *)&arg);
printf("volume is:%d\n", arg);
arg = 55000;
ioctl(mid, SOUND_MIXER_WRITE_VOLUME, (char *)&arg);
//----------------------------------------------------------------------
// encode
enc_state.valprev = 0;
enc_state.index = 0;
//----------------------------------------------------------------------
// decode
dec_state.valprev = 0;
dec_state.index = 0;
//----------------------------------------------------------------------
while(1)
{
// encode
printf("encode\n");
read(fd, inbuf, sizeof(inbuf));
for(i = 0; i < FRAME_SIZE*4; i+=4) inenc[i/4] = inbuf[i] + inbuf[i+1]*256; //获取单声道数据
adpcm_encoder(inenc, encbuf, FRAME_SIZE, &enc_state);
// decode
printf("decode\n");
adpcm_decoder(encbuf, decbuf, FRAME_SIZE/2, &dec_state);
for(i = 0; i < FRAME_SIZE; i++)
{ //由单声道得到双声道数据
outbuf[i*4] = decbuf[i] & 0xff;
outbuf[i*4+1] = decbuf[i] >> 8;
outbuf[i*4+2] = decbuf[i] & 0xff;
outbuf[i*4+3] = decbuf[i] >> 8;
}
write(fd, outbuf, sizeof(outbuf));
}
//----------------------------------------------------------------------
printf("finished\n");
return 0;
}




