1.基本概念
-
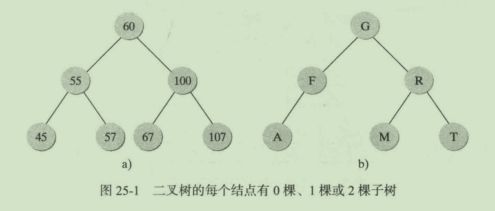
二叉树:是一种层次结构,要么是空集,要么由root元素和两棵不同的二叉树组成,左子树,右子树。允许左右子树一棵或两棵为空。
路径长度:指在该条路径上边的个数
结点60到45的路径长度为2结点深度:从该结点到根结点的路径长度
结点60:深度为0
结点55:深度为1
结点45:深度为2树的高度:从根节点到最远的叶结点路径长度,只有一个结点的树高度为0,空树高度为-1
a)b)图树的高度为2二叉查找树(BST):是特殊类型的二叉树,具有如下特点:
1) 没有重复元素
2)对于树中每一个结点,它的左子树中结点的值都小于该结点的值,它的右子树中结点的值都大于该结点的值。
2.表示二叉查找树
public class TreeNode {
protected E element;
protected TreeNode left;
protected TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(E element){
this.element=element;
}
}
3.查找一个元素
/**
* 查找一个元素
* @param element
* @param root
*/
protected boolean search(E element) {
if(root==null)
return false;
TreeNode current=root;
while (current!=null)
{
//如果元素值小于当前结点的元素值,说明在左子树
if(element.compareTo(current.element)<0){
current=current.left;
}
//如果元素大于当前结点的元素值,说明在右子树
else if(element.compareTo(current.element)>0){
current=current.right;
}
//表示元素值和当前节点元素值相等
else
return true;
}
//直到current为null,也没找到
return false;
}
4.在BST二叉查找树中插入一个元素
主要是找到插入元素的父元素parent的位置
/**
* 在BST插入一个元素
*
*/
public boolean insert(E element){
if(root==null)
root=createNewNode(element);
//定义一个parent结点,一个current结点,用于遍历寻找位置
TreeNode parent,current;
//最开始都等于根元素
parent=current=root;
while (current!=null){
//元素值比当前元素小
if(element.compareTo(current.element)<0){
parent=current;
current=current.left;
}
else if(element.compareTo(current.element)>0){
parent=current;
current=current.right;
}
//已经有这个元素,冲突
else
return false;
}
if(element.compareTo(parent.element)<0)
parent.left=createNewNode(element);
else
parent.right=createNewNode(element);
size++;
return true;
}
private TreeNode createNewNode(E element) {
return new TreeNode(element);
}
5.树的遍历
访问树中每个结点一次且只有一次的过程。
遍历方法:
1)深度优先遍历遍历:(前序、中序、后序)
- 递归:
- 前序遍历:首先访问当前结点,然后递归的访问该结点的左子树,最后递归的访问该结点的右子数。
- 中序遍历:首先递归的访问该结点的左子树,然后访问当前结点,最后递归的访问该结点的右子数。
- 后序遍历:首先递归的访问该结点的左子树,然后递归的访问该结点的右子数,最后访问当前结点。
-
非递归:使用栈stack(后进先出)实现
- 前序遍历
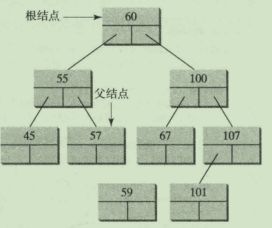
1)60放进栈。【60】
2)弹出60,将右孩子100进栈,左孩子55进栈【100,55】
3)弹出55,将右孩子57进栈,左孩子45进栈【100,57,45】
4)弹出45,45左右孩子为null。【100,57】
5)弹出57,57的左右孩子为null。【100】
6)弹出100,将右孩子107进栈,左孩子67进栈。【107,67】
7)弹出67,67的左右孩子为null。【107】
8)弹出107,右孩子为null,左孩子101进栈。【101】
9)弹出101.
弹出的元素就是前序遍历结果。
- 前序遍历
- 中序遍历
1)将根节点及其所有左侧节点压入栈【60,55,45】
2)弹出45,左右结点为null,不用处理【60,55】
3)弹出55,将右孩子57及其所有左侧结点压入栈,这里只有57.【60,57】
4)弹出57,左右结点为null,不用处理。【60】
5)弹出60,将60的右孩子100及其所有左侧结点压入栈。【100,67】
6)弹出67,左右结点为null,不用处理。【100】
7)弹出100,右孩子107及其左右左侧结点压入栈。【107,101】
8)弹出101【107】
9)弹出107 - 后序遍历
思想:将根节点及其左侧结点全部入栈,
访问一个结点前,判断其右结点是否被访问过,需要一个preNode存储前一个访问的结点。
若没访问过,按如上规则去处理右子树所有结点。
2)广度优先遍历
逐层访问树中结点。
首先访问根结点,然后从左往右访问根节点所有子结点,再从左往右访问根节点的所有孙子结点。
思想:使用队列Queue(先进先出)来实现。
1)将根节点60放入队列。(60)
2)弹出60,将60的左孩子和右孩子放入队列。(55,100)
3)弹出55,将55的左右孩子放入队列(100,45,57)
4)弹出100,将100的左孩子右孩子放入队列(45,57,67,107)
5)弹出45,没有左右孩子。(57,67,107)
6)弹出57,将左右孩子放入队列(67,107,59)
7)弹出67,没有左右孩子。(107,59)
8)弹出107,将左右孩子放入队列(59,101)
9)弹出59
10)弹出101
3) 例子
上述图片遍历情况如下。
前序:60 55 45 57 59 100 67 107 101
中序:45 55 57 59 60 67 100 101 107
后序:45 59 57 55 67 101 107 100 60
广度优先:60 55 100 45 57 67 107 59 101
4)代码实现
/**
* 二叉查找树遍历
*/
//1.前序遍历
public void preorder(){
preorder(root);
}
protected void preorder(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return;
System.out.print(root.element+" ");
preorder(root.left);
preorder(root.right);
}
//前序遍历非递归实现
public void iterativepreorder(){
iterativepreorder(root);
}
private void iterativepreorder(TreeNode root) {
Stack stack=new Stack<>();
if(root!=null){
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode current=stack.pop();
System.out.print(current.element+" ");
if(current.right!=null)
stack.add(current.right);
if(current.left!=null)
stack.add(current.left);
}
}
}
//2.中序遍历
public void inorder(){
inorder(root);
}
private void inorder(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return;
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.element+" ");
inorder(root.right);
}
//中序遍历非递归实现
public void iterativeinorder(){
iterativeinorder(root);
}
private void iterativeinorder(TreeNode root) {
Stack stack=new Stack<>();
if(root!=null){
TreeNode node=root;
while(node!=null||stack.size()>0){
//将所有的左侧结点入栈
while (node!=null){
stack.add(node);
node=node.left;
}
if(stack.size()>0){
TreeNode current=stack.pop();
System.out.print(current.element+" ");
if(current.right!=null)
node=current.right;
}
}
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postorder(){
postorder(root);
}
private void postorder(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return;
postorder(root.left);
postorder(root.right);
System.out.print(root.element+" ");
}
//非递归后序遍历
public void iterativepostorder(){
iterativepostorder(root);
}
private void iterativepostorder(TreeNode root) {
Stack stack=new Stack<>();
if(root!=null){
TreeNode node=root;
TreeNode preNode=null;
while (node!=null||stack.size()>0){
//将左侧结点全部压入栈
while (node!=null){
stack.add(node);
node=node.left;
}
if(stack.size()>0){
//如果该节点的右结点为null,或者已经被访问
if(stack.peek().right==null||stack.peek().right==preNode){
TreeNode current=stack.pop();
System.out.print(current.element+" ");
//记录前一个被访问的结点
preNode=current;
}else {
node=stack.peek().right;
}
}
}
}
}
//广度优先遍历(层次遍历)
public void layerTraversal(){
layerTraversal(root);
}
private void layerTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Queue queue=new LinkedList<>();
if(root!=null) {
queue.add(root);
//当队列不是空的
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//弹出第一个结点
TreeNode current = queue.poll();
System.out.print(current.element+" ");
//如果该结点的左孩子不是null,加入到队列中
if (current.left != null)
queue.offer(current.left);
//如果该结点的右孩子不是null,加入到队列中
if (current.right != null)
queue.offer(current.right);
}
}
}
6.删除一个元素
有两种情况:
-
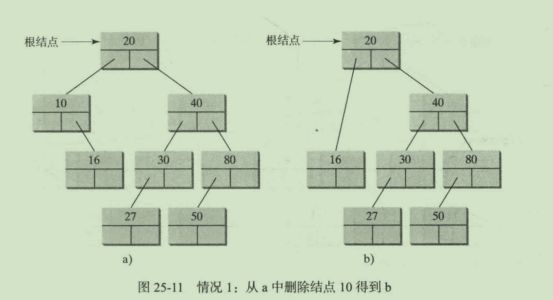
情况1:要删除的元素,没有左子结点
如图所示,要删除10,只需要将该节点的父结点与该结点的右子结点相连。
-
情况2:要删除的元素有左子结点
public boolean delete(E element){
TreeNode parent=null;
TreeNode current=root;
//1.先找到要删除的元素的位置,current表示,父元素的parent
while (current!=null){
if(element.compareTo(current.element)<0){
parent=current;
current=current.left;
}else if(element.compareTo(current.element)>0){
parent=current;
current=current.right;
}else
break;
}
//2.没找到这个元素
if(current==null)
return false;
//3.case1:要删除的元素没有左子结点
if(current.left==null){
//如果没有父节点,相当于要删除的是根节点,
if(parent==null)
root=current.right;
//判断要删除的元素是在父元素的左子树上
else if(element.compareTo(parent.element)<0)
parent.left=current.right;
else
parent.right=current.right;
}
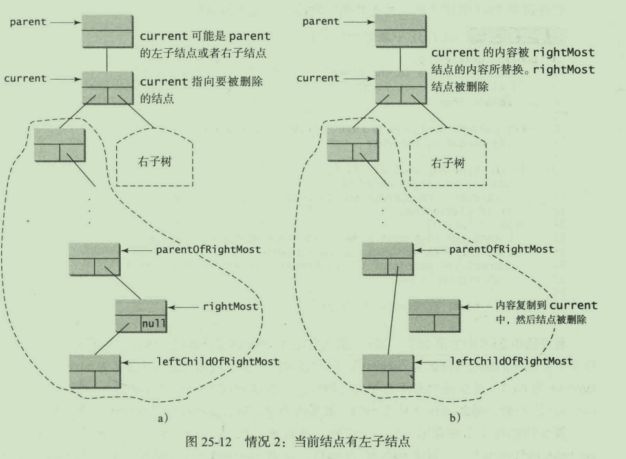
//4.case2:要删除的结点有左子结点
else{
TreeNode parentOfRightMost=current;
TreeNode rightMost=current.left;
//通过此方法得到要删除结点左子树最大的元素(也就是最靠右的元素)
while (rightMost.right!=null)
{
parentOfRightMost=rightMost;
rightMost=rightMost.right;
}
//将左子树最大值复制给删除节点值
current.element=rightMost.element;
//如果rightMost是父节点的右边结点,此时不可能有更右边的结点了,
// 删除之后,就让父节点连接rightMost的左结点
if(parentOfRightMost.right==rightMost)
parentOfRightMost.right=rightMost.left;
else
parentOfRightMost.left=rightMost.left;
}
size--;
return true;
}
7.所有方法总结:
1)TreeNode类
package java_04_java语言程序设计.第25章_二叉查找树;
/*
一个结点包括元素本身,指向左结点的变量left,指向右结点的变量right
*/
public class TreeNode {
protected E element;
protected TreeNode left;
protected TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(E element){
this.element=element;
}
}
2)实现增删改查的类BST
package java_04_java语言程序设计.第25章_二叉查找树;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* 实现二叉查找树的增删改查
*/
public class BST>{
private TreeNode root;
private int size=0;
public BST(){
}
public BST(E[] objects){
for(int i=0;i current=root;
while (current!=null)
{
//如果元素值小于当前结点的元素值,说明在左子树
if(element.compareTo(current.element)<0){
current=current.left;
}
//如果元素大于当前结点的元素值,说明在右子树
else if(element.compareTo(current.element)>0){
current=current.right;
}
//表示元素值和当前节点元素值相等
else
return true;
}
//直到current为null,也没找到
return false;
}
/**
* 在BST插入一个元素
*
*/
public boolean insert(E element){
if(root==null)
root=createNewNode(element);
//定义一个parent结点,一个current结点,用于遍历寻找位置
TreeNode parent,current;
//最开始都等于根元素
parent=current=root;
while (current!=null){
//元素值比当前元素小
if(element.compareTo(current.element)<0){
parent=current;
current=current.left;
}
else if(element.compareTo(current.element)>0){
parent=current;
current=current.right;
}
//已经有这个元素,冲突
else
return false;
}
if(element.compareTo(parent.element)<0)
parent.left=createNewNode(element);
else
parent.right=createNewNode(element);
size++;
return true;
}
private TreeNode createNewNode(E element) {
return new TreeNode(element);
}
/**
* 二叉查找树遍历
*/
//1.前序遍历
public void preorder(){
preorder(root);
}
protected void preorder(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return;
System.out.print(root.element+" ");
preorder(root.left);
preorder(root.right);
}
//前序遍历非递归实现
public void iterativepreorder(){
iterativepreorder(root);
}
private void iterativepreorder(TreeNode root) {
Stack stack=new Stack<>();
if(root!=null){
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode current=stack.pop();
System.out.print(current.element+" ");
if(current.right!=null)
stack.add(current.right);
if(current.left!=null)
stack.add(current.left);
}
}
}
//2.中序遍历
public void inorder(){
inorder(root);
}
private void inorder(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return;
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.element+" ");
inorder(root.right);
}
//中序遍历非递归实现
public void iterativeinorder(){
iterativeinorder(root);
}
private void iterativeinorder(TreeNode root) {
Stack stack=new Stack<>();
if(root!=null){
TreeNode node=root;
while(node!=null||stack.size()>0){
//将所有的左侧结点入栈
while (node!=null){
stack.add(node);
node=node.left;
}
if(stack.size()>0){
TreeNode current=stack.pop();
System.out.print(current.element+" ");
if(current.right!=null)
node=current.right;
}
}
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postorder(){
postorder(root);
}
private void postorder(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return;
postorder(root.left);
postorder(root.right);
System.out.print(root.element+" ");
}
//非递归后序遍历
public void iterativepostorder(){
iterativepostorder(root);
}
private void iterativepostorder(TreeNode root) {
Stack stack=new Stack<>();
if(root!=null){
TreeNode node=root;
TreeNode preNode=null;
while (node!=null||stack.size()>0){
//将左侧结点全部压入栈
while (node!=null){
stack.add(node);
node=node.left;
}
if(stack.size()>0){
//如果该节点的右结点为null,或者已经被访问
if(stack.peek().right==null||stack.peek().right==preNode){
TreeNode current=stack.pop();
System.out.print(current.element+" ");
//记录前一个被访问的结点
preNode=current;
}else {
node=stack.peek().right;
}
}
}
}
}
//广度优先遍历(层次遍历)
public void layerTraversal(){
layerTraversal(root);
}
private void layerTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Queue queue=new LinkedList<>();
if(root!=null) {
queue.add(root);
//当队列不是空的
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//弹出第一个结点
TreeNode current = queue.poll();
System.out.print(current.element+" ");
//如果该结点的左孩子不是null,加入到队列中
if (current.left != null)
queue.offer(current.left);
//如果该结点的右孩子不是null,加入到队列中
if (current.right != null)
queue.offer(current.right);
}
}
}
//删除元素
public boolean delete(E element){
TreeNode parent=null;
TreeNode current=root;
//1.先找到要删除的元素的位置,current表示,父元素的parent
while (current!=null){
if(element.compareTo(current.element)<0){
parent=current;
current=current.left;
}else if(element.compareTo(current.element)>0){
parent=current;
current=current.right;
}else
break;
}
//2.没找到这个元素
if(current==null)
return false;
//3.case1:要删除的元素没有左子结点
if(current.left==null){
//如果没有父节点,相当于要删除的是根节点,
if(parent==null)
root=current.right;
//判断要删除的元素是在父元素的左子树上
else if(element.compareTo(parent.element)<0)
parent.left=current.right;
else
parent.right=current.right;
}
//4.case2:要删除的结点有左子结点
else{
TreeNode parentOfRightMost=current;
TreeNode rightMost=current.left;
//通过此方法得到要删除结点左子树最大的元素(也就是最靠右的元素)
while (rightMost.right!=null)
{
parentOfRightMost=rightMost;
rightMost=rightMost.right;
}
//将左子树最大值复制给删除节点值
current.element=rightMost.element;
//如果rightMost是父节点的右边结点,此时不可能有更右边的结点了,
// 删除之后,就让父节点连接rightMost的左结点
if(parentOfRightMost.right==rightMost)
parentOfRightMost.right=rightMost.left;
else
parentOfRightMost.left=rightMost.left;
}
size--;
return true;
}
}
3)测试类
package java_04_java语言程序设计.第25章_二叉查找树;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2017/12/7 0007.
*/
public class testTreeNode {
public static void main(String[] args){
//创建三个节点
Integer []node={60,55,100,45,57,67,107,59,101};
BST BST =new BST(node);
//前序遍历
System.out.println("前序遍历:");
BST.preorder();
System.out.println();
//非递归前序遍历
System.out.println("非递归前序遍历:");
BST.iterativepreorder();
System.out.println();
//中序遍历
System.out.println("中序遍历:");
BST.inorder();
System.out.println();
//非递归中序遍历
System.out.println("非递归中序遍历:");
BST.iterativeinorder();
System.out.println();
//后序遍历
System.out.println("后序遍历:");
BST.postorder();
System.out.println();
//非递归h后序遍历
System.out.println("非递归后序遍历:");
BST.iterativepostorder();
System.out.println();
//广度优先遍历
System.out.println("广度优先遍历:");
BST.layerTraversal();
System.out.println();
BST.delete(55);
System.out.println("删除后前序遍历:");
BST.preorder();
System.out.println();
}
}
8.示例学习:哈夫曼编码
思想:
1).字符串中每个字符出现的次数为权重
可以利用map来实现字符串中每个字符出现次数的统计。
2).创建节点类Node,包括字符、权重、左孩子、右孩子四个属性;每个字符都是一个叶子节点,将所有的叶子节点放在一个Linkedlist中。
3).创建哈夫曼树:
按从小到大的顺序对Linkedlist进行排序。
找到最小的两个节点,为他们创建父节点,父节点的权重为两个节点的权重之和。
linkedlist删除两个节点,将父节点加入。
循环上述操作,直到linkedlist只有一个节点,该节点就是root节点。
4).遍历哈夫曼树,找到叶子节点,将字符和编码存储到map中。
5).输出字符串的编码。
/*
实现哈夫曼编码
提示用户输入一个字符串,显示每个字符的哈夫曼编码
*/
public class HuffmanCode {
/*
定义节点类,包括字符,权重,左孩子,右孩子
*/
public static class Node{
//定义节点的字符
private Character elem;
//定义该字符的权值就是字符出现的次数
private double weight;
//定义左孩子
private Node leftChild;
//定义右孩子
private Node rightChild;
//为中间的节点准备的构造函数
public Node(double weight, Node leftChild, Node rightChild) {
this.weight = weight;
this.leftChild = leftChild;
this.rightChild = rightChild;
}
//为叶子节点准备的构造函数
public Node(Character elem, double weight) {
this.elem = elem;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"elem=" + elem +
", weight=" + weight +
", leftChild=" + leftChild +
", rightChild=" + rightChild +
'}';
}
}
//实现Node的比较器,根据权重来比较Node节点,排序时需要使用
static class NodeComparator implements Comparator {
@Override
public int compare(Node o1, Node o2) {
if(o1.weighto2.weight)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入字符串");
//text存储输入的字符串
String text = input.nextLine();
//统计字符串中各个字符出现的次数
Map map = getCharacterFrequency(text);
//创建叶子节点,放在list中
LinkedList nodelist= CreateNodes(map);
//构造哈夫曼树
Node root=CreateTree(nodelist);
//将哈夫曼编码结果存储在map中
Map letterCodeMap=getLetterCode(root);
for(int i=0;i getCharacterFrequency(String text) {
Map map = new HashMap();
for (int i = 0; i < text.length(); i++) {
//字符值为键值
Character c = text.charAt(i);
//出现的次数为value值
Integer count = map.get(text.charAt(i));
//如果count是null,就把1放进去,不然就给count+1
map.put(c, count == null ? 1 : count + 1);
}
return map;
}
//创建叶子节点,放在list中
private static LinkedList CreateNodes(Map map) {
LinkedList nodeList=new LinkedList<>();
for(Map.Entry entry:map.entrySet()){
Character elem=entry.getKey();
Integer value=entry.getValue();
Node node=new Node(elem,value);
nodeList.add(node);
}
return nodeList;
}
//构造哈夫曼树
private static Node CreateTree(LinkedList nodelist) {
NodeComparator nodeComparator=new NodeComparator();
//有大于一个的元素就需要进行合并
while(nodelist.size()>1){
//将节点按从小到大的顺序排序。
nodelist.sort(nodeComparator);
//找到最小的两个节点
Node left=nodelist.get(0);
Node right=nodelist.get(1);
//创建parent节点,权值为最小的两个节点权值之和,左孩子是left节点,右孩子是right节点
Node parent=new Node(left.weight+right.weight,left,right);
//删掉集合中的最小的两个元素
nodelist.remove(0);
nodelist.remove(0);
//将parent元素加入
nodelist.add(parent);
}
//直到只剩下一个元素,就是根元素
return nodelist.get(0);
}
//将得到的哈夫曼树,转成哈夫曼编码,存储到map中(字符,编码)
private static Map getLetterCode(Node root) {
Map letterCodeMap=new HashMap<>();
//只有一个节点
if(root.leftChild==null&&root.rightChild==null){
letterCodeMap.put(root.elem,"1");
return letterCodeMap;
}
getLetterCode(root," ",letterCodeMap);
return letterCodeMap;
}
private static void getLetterCode(Node root, String suffix, Map letterCodeMap) {
if(root!=null){
//递归出口,是叶子节点
if(root.leftChild==null&&root.rightChild==null){
letterCodeMap.put(root.elem,suffix);
}
getLetterCode(root.leftChild,suffix+"0",letterCodeMap);
getLetterCode(root.rightChild,suffix+"1",letterCodeMap);
}
}
}