仙人掌相关问题的处理方法(未完待续)
仙人掌相关问题的处理方法
目录
- 仙人掌相关问题的处理方法
- DFS 树解决仙人掌 DP 问题
- 引例
- BZOJ1023cactus仙人掌图SHOI2008
- 圆方树
- 定义
- 构造
- 性质
- BZOJ4316 小 C 的独立集
- 仙人掌最短路问题
- BZOJ2125最短路
- 仙人掌剖分
- UOJ158静态仙人掌
- 仙人掌分治问题
- UOJ23跳蚤国王下江南
- 动态仙人掌
- 介绍
- 结构
- 树上的情况
- 环上的情况
- 特殊情况
- 环上信息的处理
- 换根操作
- 实现
- UOJ65动态仙人掌 III
- 广义圆方树
- Tourists
- 参考文献
如图所示:
![]()
仙人掌图就是长得像仙人掌的图嘛(我真没看出哪里像了)
定义:对一个无向连通图,任意一条边属于至多一个简单环。
- 桥边:非环边,就是连接环的那些边;
- 环边:就是环中的边嘛。
在仙人掌上,父亲和儿子都有节点的和环的之分。
DFS 树解决仙人掌 DP 问题
仙人掌的处理是十分复杂的(本蒟蒻个人认为,神犇轻喷),这里先从简单的 DFS树开始。
- 树边:DFS 树中存在的边
- 非树边:DFS 树中不存在的边
大神们还有什么覆盖之类的定义,参考最后的参考文献。
也就是说环是由多条树边和一条非树边组成的,非树边起到了连接的作用。
我们看几道经典题目:
引例
一棵仙人掌,每条边有边权,求 1 号节点到每个节点的最短路径长度。节点个数 n≤105
我们先 dfs 一遍的到 dfs 树,这是我们之后处理的基础。
然后从一号节点开始 dp 。假设现在已经求出 1 到 u 的距离,枚举 u 的每一个儿子,如果该儿子不在环内,加上边权继续;否则,枚举换上的我们暴力求环上的每个点到 1 的距离,然后在分别从环上的每个点继续 dp 。
[BZOJ1023]cactus仙人掌图[SHOI2008]
一棵带边权仙人掌,求直径(最短路径最长的两个点的最短路径长度)。节点个数 n≤105
我们 DFS 可以得到一颗 DFS 树。这里的 DFS 与 Tarjan 比较类似(大概就是 Tarjan),对于现在访问的节点 u 我们记录下来 low[u],dfn[u],dpt[u],fa[u] (前两个含义参考 Tarjan ,dpt 是深度(deepth) , fa 是 u 在 DFS 树上的父亲),对于没访问的(即 dfn 为 0 的)节点继续递归,向上回溯时更新 low 值。
遍历每条边时如果 low[v] 大于 dfn[u] ,说明此边为树边;对于一个节点,若其某个儿子在 DFS 树上的父亲不是它(没错,它的儿子的父亲不是它,机房的小伙伴们都笑疯了),那么说明这里出现了一个环,且此节点为环的根(深度最小的节点),它的那个儿子为环的尾(环中最后被遍历到的,也就是 DFS 树的叶子节点)
我们做以上这些的目的主要就是判断环和桥,然后分别 DP 处理。
我们定义 f[i] 为以 i 为端点的最长链的长度。
对于桥来说十分简单(此时假设没有环):
这里我们在代码中的写法稍有不同:
- 先更新 ans ,后更新 f[u]。
- 遍历所有儿子,对每个儿子,f[u] 中存的可能是(我们只考虑是的情况,因为只有此时才对结果有影响,这也是为什么上一条要确保) second_max(f[v]) ,而 f[v] 可能是(依旧只考虑是的情况) max(f[v]) ,所以我们只需用 f[u]+f[v]+1 来更新 ans 即可;
现在我们考虑环的问题:
对于一个环,我们的宗旨是把它缩成一个点(即把一个环的 f 信息都存在其根上),然后就可以开心地按之前的方式 DP 啦!
由于环中更新答案的时候只转一圈不能保证答案最优(因为有可能最优的那一部分环被根分开了),又由于环中距离的定义是最短路,所以我们只要转够一圈半即可。
定义环的节点集合为 C ,记环中一点 a 在环中的遍历顺序为 aid 、环长(环中节点个数)为 L ,则在环中两个点之间的距离
我们记一个环的根为 x 、尾为 y。(我只是懒得起名)
实现的时候,我们把环中的节点的 f 依次存在一个数组(我的代码中是 a 数组懒得起名+1)里,然后将这个数组倍长(就是将其复制一遍放到尾部),遍历时动一定一(这里莫名怀念小晓笑潇),若之间相差大于 L2 就 continue,再用单调队列优化一下, ans 就能轻松更新好了。之后再按照公式更新 f[x] 即可。
整个算法过程的时间复杂度仅为 O(N) ,还是蛮快的。
/**************************************************************
Problem: 1023
User: zhangche0526
Language: C++
Result: Accepted
Time:256 ms
Memory:7076 kb
****************************************************************/
#include//遍历非树边,处理环
solve(u,v);
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int k;scanf("%d",&k);
int u,v;scanf("%d",&u);
for(j=2;j<=k;j++) scanf("%d",&v),addEdge(u,v),u=v;
}
dfs(1);printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
} 圆方树
通过前面的几道例题,我们发现:其实解决仙人掌 DP 问题不过就是参照树上的解法然后对环上的情况特殊处理一下,把环的信息记录到一个点上。
其实,神犇们很早就发现了这一点,于是他们想:既然仙人掌的许多问题在树上都有现成的解法,那么如果直接把仙人掌变成树,岂不美哉?
于是,神犇们成功的仙人掌变成树,并给这种树起了一个生动形象的名字:圆方树,它能解决大多数静态仙人掌问题
定义
仙人掌 G=(V,E) 的圆方树 T=(VT,ET) 为满足一下条件的无向图:
构造
- 从任意一个点跑 Tarjan 求点双连通分量;
- 对于每个点双,从栈中取出,这时栈中的顺序就是环上的顺序,在圆方树中建立方点,依次向栈中的圆点连边;
- 如果这条边是桥边,我们直接在圆方树中加入它。
性质
- 两个方点不会相连
圆方树是无根树
子仙人掌:以 r 为根的仙人掌上的点 p 的子仙人掌是从仙人掌中起吊 p 到 r 的简单路径上的所有边后, p 所在的连通块。
以 r 为根的仙人掌中点 p 的子仙人掌就是圆方树以 r 为根时点 p 的子树中的所有圆点。
[BZOJ4316] 小 C 的独立集
在一个无向连通图中选出若干个点,这些点互相没有边连接,并使取出的点尽量多。数据保证图的一条边属于且仅属于一个简单环,图中没有重边和自环。点数 n≤106 ,边数 m≤106
在一个无向连通图中选出若干个点,这些点互相没有边连接,并使取出的点尽量多。数据保证图的一条边属于且仅属于一个简单环,图中没有重边和自环。点数 $n\leq10^6$ ,边数 $m\leq10^6$
- 类比树上的解法:设 f[i][0/1] 表示点 i 是否选时子树内的最大独立集;
- 如果一条边连接两个圆点,用树上转移方式即可;
- 而对于连接圆点和方点的情况,把这个换中所有点拿出来,跑一个环上的 DP 。
时间复杂度: O(n)
其实我们在解这道题的时候,没有必要真正建出圆方树,我在代码里建出圆方树只是为了举例说明,是为让大家熟悉圆方树的建法。
/**************************************************************
Problem: 4316
User: zhangche0526
Language: C++
Result: Accepted
Time:204 ms
Memory:12140 kb
****************************************************************/
#include仙人掌最短路问题
[BZOJ2125]最短路
一个带权仙人掌图,求多源最短路。点数 N≤105 ,边数 M≤105 ,询问个数 Q≤105
对多源最短路问题,树上的经典做法是两点到根的距离减去两倍的 LCA 到根的距离,那么我们使用圆方树将仙人掌图转化为树后就可以按相同思路解决了。
然而我们发现原图的边权并没有很好地表现在我们建出来的圆方树上,所以我们首先解决边权问题:
- 找到换的根;
- 方点向环的根的连边的边权为 0 ;
- 环上其他点向方点连边,边权为到环的根的最短路径长度。
计算好边权后,对于两点的 LCA 是圆点的情况就可以直接按照树上的方法求距离了;而对于两点的 LCA 是方点的情况,其 LCA 是一个环,这两点一直向祖先走会到环上的两个不同位置,我们只需找到这两个位之间的到最短路。
具体方法:
Tarjan 找出所有的简单环,并记录环上信息备用,建圆方树;
这里需要注意,上一道题的图比仙人掌图还要特殊,每个节点一定属于一个环,因此我们可以对于每个节点只访问一次即可;可对于一般情况,我们在发现一个点 u 的下一个点 v 满足: low[v]=dfn[u] 时,说明我们找到了一个环,且 u 为环首,这时我们要弹出从环尾到 v 的所有点,然而我们并不能确定是否要弹出 u (因为如果 u 还属于另外一个环,那就悲剧了),所以这是我们还有走回头路更新 low 值,判断是否弹出 v 。
其实这里我们还有一种更好实现的处理方法:在 Tarjan 时维护一个边的栈,这样就可以免去许多细节处理问题。
维护圆方树的倍增数组,记录每个点到根的距离。
- 倍增法求 LCA,若果 LCA 是环,还需要把两个点倍增到这个环上,在环上查询。
第一种实现 by PoPoQQQ
/**************************************************************
Problem: 2125
User: PoPoQQQ
Language: C++
Result: Accepted
Time:684 ms
Memory:5248 kb
****************************************************************/
#include
#include for(j=15;~j;j--)
if(dpt[fa[x][j]]>=dpt[y])
x=fa[x][j];
if(x==y) return x;
for(j=15;~j;j--)
if(fa[x][j]!=fa[y][j])
x=fa[x][j],y=fa[y][j];
second_lca=make_pair(x,y);
return fa[x][0];
}
}
void Tarjan(int x)
{
static int dpt[M],low[M],T;
static int stack[M],top;
map<int,int>::iterator it;
dpt[x]=low[x]=++T;
stack[++top]=x;
for(it=f[x].begin();it!=f[x].end();it++)
{
if(dpt[it->first])
low[x]=min(low[x],dpt[it->first]);
else
{
Tarjan(it->first);
if(low[it->first]==dpt[x])
{
int t;
rings[++cnt].push_back(x);
belong[x].push_back(cnt);
Cactus_Graph::fa[cnt][0]=n+x;
do{
t=stack[top--];
rings[cnt].push_back(t);
Cactus_Graph::fa[n+t][0]=cnt;
}while(t!=it->first);
}
low[x]=min(low[x],low[it->first]);
}
}
}
void DFS(int x)
{
vector<int>::iterator it,_it;
static int stack[M];int i,j,top=0;
for(it=rings[x].begin();it!=rings[x].end();it++)
stack[++top]=*it;
stack[++top]=*rings[x].begin();
for(i=1;iint p1=stack[i],p2=stack[i+1];
size[x]+=f[p1][p2];
if(i!=top-1)
dist[x][p2]=dist[x][p1]+f[p1][p2];
}
i=2;j=top-1;
while(i<=j)
{
if(dis[stack[i-1]]+f[stack[i-1]][stack[i]]stack[j+1]]+f[stack[j+1]][stack[j]])
dis[stack[i]]=dis[stack[i-1]]+f[stack[i-1]][stack[i]],i++;
else
dis[stack[j]]=dis[stack[j+1]]+f[stack[j+1]][stack[j]],j--;
}
for(_it=rings[x].begin(),_it++;_it!=rings[x].end();_it++)
for(it=belong[*_it].begin();it!=belong[*_it].end();it++)
DFS(*it);
}
int main()
{
using namespace Cactus_Graph;
int i,x,y,z;
cin>>n>>m>>q;
for(i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z);
Add(x,y,z);Add(y,x,z);
}
Tarjan(1);
Pretreatment();
vector<int>::iterator it;
for(it=belong[1].begin();it!=belong[1].end();it++)
DFS(*it);
for(i=1;i<=q;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
int lca=LCA(n+x,n+y);
if(lca>n) printf("%d\n",dis[x]+dis[y]-2*dis[lca-n]);
else
{
int ans=dis[x]+dis[y]-dis[second_lca.first-n]-dis[second_lca.second-n];
int temp=abs(dist[lca][second_lca.first-n]-dist[lca][second_lca.second-n]);
ans+=min(temp,size[lca]-temp);
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
}
return 0;
} 第二种实现 by virgil
/**************************************************************
Problem: 2125
User: zhangche0526
Language: C++
Result: Accepted
Time:432 ms
Memory:21816 kb
****************************************************************/
#include
#includeint dpt[MAXN];
int rebuild(int u,int la)
{
dpt[u]=dpt[la]+1;
for(int i=G[u];i;i=e[i].next)
rebuild(e[i].to,u);
}
inline void initLCA()
{
for(int i=1;(1<for(int j=1;j<=N;j++)
anc[j][i]=anc[anc[j][i-1]][i-1];
}
int calDis(int x,int y)
{
int i;
if(dpt[x]std::swap(x,y);
int xDis=dis[x],yDis=dis[y];
int maxlogn=std::floor(std::log(N)/std::log(2));
for(i=maxlogn;i>=0;i--)
if(dpt[x]-(1<=dpt[y])
x=anc[x][i];
if(x==y) return xDis-dis[x];
for(i=maxlogn;i>=0;i--)
if(anc[x][i]!=anc[y][i])
x=anc[x][i],y=anc[y][i];
if(belong[x]&&belong[x]==belong[y])
{
int xyDis=abs(ringRtDis[x]-ringRtDis[y]);
int minDis=std::min(xyDis,ringLen[belong[x]]-xyDis);
return xDis+yDis-dis[x]-dis[y]+minDis;
}else return xDis+yDis-2*dis[anc[x][0]];
}
int main()
{
int i;
scanf("%d%d%d",&N,&M,&Q);
for(i=1;i<=M;i++)
{
int u,v,w;scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&w);
addEdge2(u,v,w);
}
SPFA(1);
tarjan(1,0);
initLCA();
initCFS();
for(i=2;i<=N;i++)
addEdge(anc[i][0],i,0);
rebuild(1,0);
while(Q--)
{
int x,y;scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
printf("%d\n",calDis(x,y));
}
return 0;
} 仙人掌剖分
[UOJ158]静态仙人掌
给出一棵根为 1 的仙人掌,每个点是黑色或者白色,保证所有环都是奇环,要求支持三种操作:
- 把一个点到根的最短路径上的所有点颜色取反;
- 把一个点到根的最长简单路径上的所有点颜色取反;
- 询问一个点的子仙人掌里面有多少个黑点。
树上的做法肯定是树剖,对于仙人掌,我们对圆方树进行树剖。
根据圆方树的性质,子仙人掌就是圆方树的子树,因此我们可以对树剖的方法加以扩充解决本问题。
我们回想树剖,其精髓就是支持树上重链的快速操作,而对于仙人掌来说,我们同样需要支持对重链的快速操作:就是支持对一条重链的一个前缀的最长路或最短路进行操作。
那么我们就可以把点进行分类。考虑每一条重链,将点分成 3 类:
- 割点
- 在重链上作为最短路径出现的点
- 在重链上作为最长路径出现的点。
那么显然对于第 1 类点,直接在树上修改即可。然而对于后两种点,树上路径不一定会扫过需要更改的点。
按照传统的剖分方法的话是不支持考虑方点连出的圆点的,因此我们考虑在 DFS 序中,如果一个点是方点,那么我们先访问它的所有儿子,然后再按照重边先行的顺序访问儿子的子树(不包括那些儿子了),这样的话,我们修改一段区间的时候,就会扫过这个环上所有点;而我们已经把点分类了,因此也可以选择只修改最短路径或最长路径上的点。
代码 by laofu
#include1,r,L,R,p);
c[i][0]=c[lc][0]+c[rc][0];c[i][1]=c[lc][1]+c[rc][1];c[i][2]=c[lc][2]+c[rc][2];
}
inline int query(int i,int l,int r,int L,int R) {
if (L<=l&&r<=R) return c[i][0]+c[i][1]+c[i][2];
int m;pushdown(i);m=(l+r)>>1;
if (R<=m) return query(lc,l,m,L,R);
if (mreturn query(rc,m+1,r,L,R);
return query(lc,l,m,L,R)+query(rc,m+1,r,L,R);
}
namespace tree{
int head[N],next[N<<1],to[N<<1],tot;
inline void link(int a,int b) { to[++tot]=b,next[tot]=head[a],head[a]=tot; }
inline void dfs1(int k) {
siz[k]=1;
for (int i=head[k];i;i=next[i]) {
dfs1(to[i]);siz[k]+=siz[to[i]];
if (siz[to[i]]>siz[son[k]]) son[k]=to[i];
}
}
inline void dfs2(int k) {
if (!dfn[k]) sa[dfn[k]=++tot]=k; else if (k<=n) L[k]=tot+1; if (!son[k]) { R[k]=tot; return; }int i,tp;
if (k>n) {
for (i=head[k];i;i=next[i]) dis[to[i]]=++dis[k];L[k]=tot+1;
for (i=head[k],tp=1+(dis[son[k]]>dis[k]>>1);i;i=next[i]) if (to[i]==son[k]) tp^=3; else col[to[i]]=tp,sa[dfn[to[i]]=++tot]=to[i];R[k]=tot;
sa[dfn[son[k]]=++tot]=son[k];
}
top[son[k]]=top[k];dfs2(son[k]);
for (i=head[k];i;i=next[i]) if (to[i]!=son[k]) top[to[i]]=to[i],dfs2(to[i]);
if (k<=n) R[k]=tot;
}
inline void rev(int k,int p) {
while (k)
if (top[k]==k)
if (rt[k]) {
if ((dis[k]<=dis[rt[k]]>>1)==(p==1)) {
modify(1,1,scc,L[rt[k]],dfn[k],0);
if (dis[son[rt[k]]]1,1,scc,dfn[son[rt[k]]],dfn[son[rt[k]]],0);
}
else {
modify(1,1,scc,dfn[k],R[rt[k]],0);
if (dis[son[rt[k]]]>dis[k]) modify(1,1,scc,dfn[son[rt[k]]],dfn[son[rt[k]]],0);
}
k=rt[rt[k]];
}
else modify(1,1,scc,dfn[k],dfn[k],p),k=fa[k];
else if (top[k]<=n&&rt[top[k]]) modify(1,1,scc,dfn[son[top[k]]],dfn[k],p),k=top[k];
else modify(1,1,scc,top[k]<=n?dfn[top[k]]:L[top[k]],dfn[k],p),k=fa[top[k]];
}
inline int ask(int k) { return !rt[k]||k==son[rt[k]]?query(1,1,scc,dfn[k],R[k]):query(1,1,scc,dfn[k],dfn[k])+(L[k]<=R[k]?query(1,1,scc,L[k],R[k]):0); }
}
inline void dfs(int k) {
dfn[k]=++tot;
for (int i=head[k],t,p;i;i=next[i])
if (!dfn[to[i]]) {
fa[to[i]]=k,dfs(to[i]);
if (!rt[to[i]]) tree::link(k,to[i]);
}
else if (to[i]!=fa[k]&&dfn[to[i]]for (t=k;t!=to[i];t=fa[p=t]) l[t]=fa[t],r[t]=p,tree::link(scc,t),rt[t]=scc;
l[scc]=p,r[scc]=k;
}
}
int main()
{
//freopen("cactus.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("cactus.out","w",stdout);
n=scc=gi();int m=gi(),Q=gi(),k,tot=0,a,b;
while (m--) {
a=gi(),b=gi();
to[++tot]=b,next[tot]=head[a],head[a]=tot;
to[++tot]=a,next[tot]=head[b],head[b]=tot;
}
dfs(1);for (k=1;k<=n;dfn[k++]=0) if (rt[k]) fa[k]=rt[k];
top[1]=1;tree::tot=0;tree::dfs1(1);
tree::dfs2(1);
build(1,1,scc);
while (Q--) {
if ((k=gi())==3) printf("%d\n",tree::ask(gi()));
else tree::rev(gi(),k);
}
return 0;
} 仙人掌分治问题
[UOJ23]跳蚤国王下江南
一个仙人掌,求对 i∈[1,n) 输出从 1 出发的长度为 i 的简单路径有多少条。答案对 998244353 取模。点数 N≤105
我们先考虑暴力 DP 算法:
记 f[u][l] 为从节点 u 开始,只能向远离根的方向走,长度为 l 的路径条数。
那么对于 u 的每个儿子 v ,如果 v 是一个节点,就把 f[v][l−1] 加到 f[u][l] 里;如果是一个环,那么枚举这个换上的每个儿子 z ,把 f[z][l−d1]+f[z][l−d2] 加到 f[u][l] 里(其中 d1,d2 表示 x 到 z 的两条路径的长度 )。
不过上述算法是 A 不掉的,我们发现, f[u] 可以看做一个多项式,每次从 u 的一个儿子 v 注意过来时,相当于是把 f[v] 乘上 x 或乘上 xd1+xd2 并加到 f[u] 中。
首先是分治,每次分治时,找到重心 u 以后,分治每个连通块,然后将根到 u 的多项式求出来,记为 f(x) ,再将 u 的所有儿子的答案求出来相加,记为 g(x) 。 我们只要将 f(x)⋅g(x) 和每个连同快当然答案加起来即可。
我们在求 f(x) 时,如果将重心到根的多项式用分治+ FFT 乘起来起来,总的时间复杂度为 O(Nlog32N) (这里点分治 log2N ,分治 log2N , FFT Nlog2N ),然而这样的话我们并没有充分利用信息,而导致了多余的计算:分治是不必要的,我们只需在点分治的时候记录一下根到重心的的多项式,然后一个一个乘回去,这样就可以在 O(Nlog2N) 的时间复杂度内完美地解决问题。
代码 by Vfleaking
#include recoverEdgeType;
inline recoverEdgeType delEdge(int v, int u)
{
for (halfEdge *e = adj[v], **prev = &adj[v]; e; prev = &e->next, e = e->next)
if (e->u == u)
{
*prev = e->next;
return recoverEdgeType(prev, e);
}
assert(false);
}
inline void recoverEdge(const recoverEdgeType &r)
{
*r.first = r.second;
}
inline halfEdge *oppoE(halfEdge *e)
{
return adj_pool + ((e - adj_pool) ^ 1);
}
int dfsCnt;
int dfn[MaxN + 1];
halfEdge *faE[MaxN + 1], *moE[MaxN + 1];
void dfs(int v)
{
dfn[v] = ++dfsCnt;
for (halfEdge *e = adj[v]; e; e = e->next)
if (e != faE[v] && e != moE[v])
{
if (!dfn[e->u])
{
faE[e->u] = oppoE(e), moE[e->u] = NULL;
dfs(e->u);
}
else if (dfn[e->u] < dfn[v])
{
assert(moE[v] == NULL);
int u = v;
halfEdge *lastE = e;
while (u != e->u)
{
moE[u] = lastE;
lastE = oppoE(faE[u]);
u = faE[u]->u;
}
}
}
}
#define cactus_children_for_each(v, e) for (halfEdge *e = adj[v]; e; e = e->next) if (e != faE[v] && e != moE[v] && faE[e->u] == oppoE(e))
#define cir_for_each(v, vu) for (int vu = v; vu != faE[v]->u; vu = moE[vu]->u)
inline int cir_beg(int v)
{
int u = v;
while (oppoE(faE[u]) == moE[faE[u]->u])
u = faE[u]->u;
return u;
}
inline int cir_end(int v)
{
int u = v;
while (oppoE(moE[u]) == faE[moE[u]->u])
u = moE[u]->u;
return u;
}
inline int cir_len(int v)
{
int l = 1;
cir_for_each(v, u)
l++;
return l;
}
int up_root[MaxN + 1];
int up_vC[MaxN + 1];
int up_vS[MaxN + 1];
int up_inh_l[MaxN + 1];
polyarray up_poly[MaxN + 1];
polyarray calc(int root, int last_vC);
polyarray calc_under(int v, int last_vC)
{
polyarray under;
if (moE[v])
{
recoverEdgeType r1 = delEdge(v, faE[v]->u);
recoverEdgeType r2 = delEdge(v, moE[v]->u);
faE[v] = moE[v] = NULL;
under = calc(v, last_vC);
faE[v] = r1.second;
moE[v] = r2.second;
recoverEdge(r2);
recoverEdge(r1);
}
else
{
recoverEdgeType r = delEdge(v, faE[v]->u);
faE[v] = NULL;
under = calc(v, last_vC);
faE[v] = r.second;
recoverEdge(r);
}
return under;
}
polyarray calc_children_under(int v, int last_vC)
{
polyarray under;
under.resize(1);
under.a[0] = 1;
cactus_children_for_each(v, e)
{
if (moE[e->u])
{
int totL = cir_len(e->u);
int curL = 1;
cir_for_each(e->u, u)
{
polyarray cur = calc_under(u, last_vC);
polyaddto(under, cur, curL);
polyaddto(under, cur, totL - curL);
curL++;
}
}
else
{
polyarray cur = calc_under(e->u, last_vC);
polyaddto(under, cur, 1);
}
}
return under;
}
polyarray calc(int root, int last_vC)
{
int q_n = 0;
static int q[MaxN];
q[q_n++] = root;
for (int i = 0; i < q_n; i++)
{
int v = q[i];
cactus_children_for_each(v, e)
{
if (moE[e->u])
{
cir_for_each(e->u, u)
q[q_n++] = u;
}
else
q[q_n++] = e->u;
}
}
int vC = -1, wC = INT_MAX;
static int wei[MaxN + 1];
for (int i = q_n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
int v = q[i];
int wV = 0;
wei[v] = 1;
cactus_children_for_each(v, e)
{
if (moE[e->u])
{
int curW = 0;
int vU = -1, wU = 0;
cir_for_each(e->u, u)
{
curW += wei[u];
if (vU == -1 || wei[u] > wei[vU])
vU = u;
}
wei[v] += curW;
relax(wV, wei[vU]);
relax(wU, q_n - curW);
cir_for_each(e->u, u)
{
if (e->u != vU)
relax(wU, wei[e->u]);
}
cactus_children_for_each(vU, eu)
{
if (moE[eu->u])
{
cir_for_each(eu->u, k)
relax(wU, wei[k]);
}
else
relax(wU, wei[eu->u]);
}
if (wU < wC)
vC = vU, wC = wU;
}
else
{
wei[v] += wei[e->u];
relax(wV, wei[e->u]);
}
}
relax(wV, q_n - wei[v]);
if (!moE[v])
{
if (wV < wC)
vC = v, wC = wV;
}
}
int vB = moE[vC] ? cir_beg(vC) : vC;
polyarray res;
if (moE[vC])
{
recoverEdgeType r1 = delEdge(faE[vB]->u, cir_end(vB));
recoverEdgeType r2 = delEdge(faE[vB]->u, vB);
res = calc(root, last_vC);
recoverEdge(r2);
recoverEdge(r1);
}
else if (vC != root)
{
recoverEdgeType r = delEdge(faE[vC]->u, vC);
res = calc(root, last_vC);
recoverEdge(r);
}
int inh_l = 0;
polyarray above;
above.resize(1);
above.a[0] = 1;
int vS = moE[vC] ? faE[vB]->u : vC;
if (vS != root)
{
int vT = vS;
if (vT == vC)
{
inh_l++;
vT = faE[vT]->u;
}
for (int v = vT, p = vT; p != root; v = up_vC[v])
{
while (p != up_vS[v])
{
if (moE[p])
{
int s = faE[cir_beg(p)]->u;
int le_l = 0, ri_l = 0;
for (int u = p; u != s; u = faE[u]->u)
le_l++;
for (int u = p; u != s; u = moE[u]->u)
ri_l++;
inh_l += min(le_l, ri_l);
polyaddto(above, above, abs(le_l - ri_l));
p = s;
}
else
{
inh_l++;
p = faE[p]->u;
}
}
inh_l += up_inh_l[v];
polymulto(above, up_poly[v]);
p = up_root[v];
}
}
up_root[vC] = root;
up_vS[vC] = vS;
up_vC[vC] = last_vC;
up_inh_l[vC] = inh_l;
up_poly[vC] = above;
polyarray under;
if (moE[vB])
{
int totL = cir_len(vB);
int curL = 1;
cir_for_each(vB, u)
{
polyarray cur = u != vC ? calc_under(u, vC) : calc_children_under(u, vC);
polyaddto(under, cur, curL);
polyaddto(under, cur, totL - curL);
curL++;
}
}
else
{
under = calc_children_under(vC, vC);
up_inh_l[vC] = inh_l;
up_poly[vC] = above;
}
polymulto(under, above);
polyaddto(res, under, inh_l);
return res;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int v, u;
scanf("%d %d", &v, &u);
addEdge(v, u), addEdge(u, v);
}
dfsCnt = 0;
faE[1] = moE[1] = NULL;
dfs(1);
polyarray res = calc(1, 0);
int res_d = res.getDegree();
for (int k = 1; k < n; k++)
printf("%d\n", k <= res_d ? res.a[k] : 0);
return 0;
} 动态仙人掌
介绍
动态仙人掌问题
一类在仙人掌上动态维护信息的问题,动态维护包含修改形态和修改相关信息两种。
没错,最后我们要讲的就是我们前一段学的 Link-Cut Tree 在仙人掌上的迁移: Link-Cut Cactus.
结构
那么首先面临的一个难题是,什么是实边,什么是虚边?
我们分三种情况进行讨论:

树上的情况
LCT 维护的是熟的一条链,于是我们可以维护仙人掌的一条链。
没有环的话,就跟 LCT 一样,每个结点有一个偏爱孩子,用实边连起来,其它儿子用虚边连起来。
环上的情况
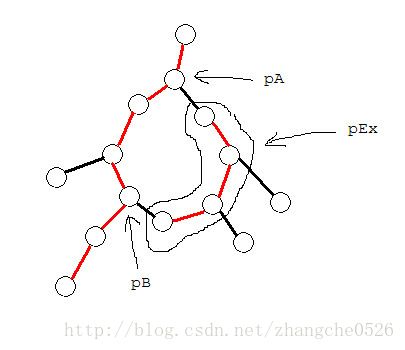
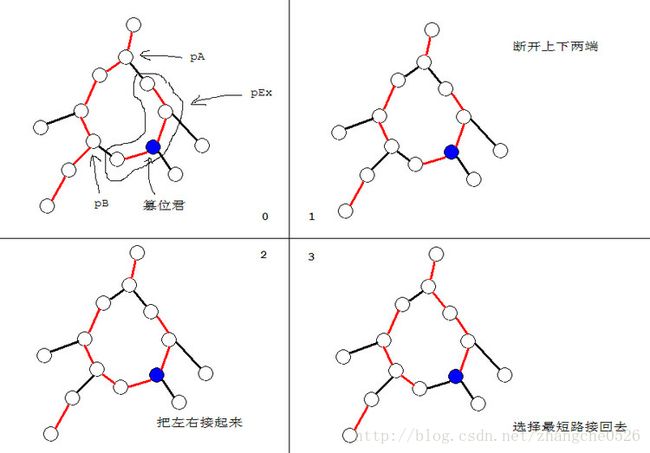
对于一个环,我们定义它的父亲为环上离仙人掌的根最近的节点,记为 A ,我们定义换上单的偏爱孩子为环上最后一次 access 到的节点,记为 B 。
那么根据定义,我们将 A 和 B 的最短路用实边连起来。
对于环上的其他结点构成的链,也用实边连起来,我们称这条链为\textbf{额外链}。
特殊情况
如前图中的二逼情况所示,如果我们 access 一个环的跟的时候,就会出现这种情况,我们需要对此加个特判。
环上信息的处理
为了更为方便地操作环,我们需要对环上的信息进行处理。
需要注意的是:在没有额外链的情况下,会出现有一条黑边没存的情况。
换根操作
我们在仙人掌上换根是不能直接套用树上的方法,因为这样会导致额外链以及 pA, pB 的方向不正确。
不过问题是可解的,我们对于 pA, pB 可以比较其在辅助树中的先后顺序,如果反了就将环信息中的 pA, pB 指针对调。
实现
伪代码 by Vfleaking
void access(x)
{
for (p = x, q = NULL; p; q = p, p = p->fa)
{
splay(p);
if (p->prevE && p->prevE->cir) // 判断p是否在环上。注意环的根不算作在这个环上。
{
isTogether = false; // 判断是否是2B情况。
cir = p->prevE->cir; // 获取p->prevE所在的环的信息
// 由于p可能在额外链上而之前很狗血地splay了,会导致记录的pEx不正确。
if (cir->pEx && !cir->pEx->isRoot())
cir->pEx = p;
splay(cir->pB);
splay(cir->pA);
if (cir->pB->isRoot()) // 2B情况
{
if (cir->pB->fa != cir->pA) // 如果pA、pB顺序不对则进行调整
{
swap(cir->pA, cir->pB);
if (cir->pEx)
cir->pEx->tag_rev(); // 打上翻转标记
}
}
else // 文艺情况
{
isTogether = true;
splay_until(cir->pB, cir->pA); // 把pB splay到pA下面
if (cir->pA->lc == cir->pB) // 如果pA、pB顺序不对则进行调整
{
rotate(cir->pB); // 一次旋转把pB转成根
swap(cir->pA, cir->pB);
if (cir->pEx)
cir->pEx->tag_rev(); // 打上翻转标记
}
cir->pA->rc = NULL;
cir->pA->nextE = NULL; // 暂时断开pA与下面部分的链接转化为2B情况
}
cir->pB->rc = cir->pEx;
// pEx为空的情况,用missingE补上
cir->pB->nextE = cir->pEx ? cir->pEx->msg.firstE : cir->missingE;
if (cir->pEx)
cir->pEx->fa = cir->pB;
// 这样环就被整个地接了起来成为了一棵splay。
p->splay();
// 比较哪边走比较短,如果不是往左走短就调整一下
if (p->getLcTotL() > p->getRcTotL())
{
p->tag_rev();
p->tag_down();
}
cir->pB = p;
cir->pEx = p->rc; // 把较长的那条变为额外链
cir->missingE = p->rc ? NULL : p->nextE; // pEx为空的情况,用missingE补上
if (cir->pEx)
cir->pEx->fa = NULL;
p->rc = q;
p->nextE = q ? q->msg.firstE : NULL;
p->update();
if (isTogether) // 如果是文艺情况还得把pA接回来
{
cir->pA->rc = p;
cir->pA->nextE = p->msg.firstE;
p->splay();
}
}
else // 普通情况
{
p->rc = q;
p->nextE = q ? q->msg.firstE : NULL;
p->update();
}
}
}
[UOJ65]动态仙人掌 III
标程 by Vfleaking
#include lccEAllocator;
BlockAllocator lccCirAllocator;
void cactus_init()
{
for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++)
{
lcc_node *x = lccVer + v;
x->fa = x->lc = x->rc = NULL;
x->prevE = x->nextE = NULL;
x->hasRev = false;
x->hasCoveredCir = false;
x->wBDelta = 0;
x->update();
}
}
bool cactus_link(int v, int u, int wA, int wB)
{
if (v == u)
return false;
edgeWeight ew(wA, wB);
lcc_node *x = lccVer + v, *y = lccVer + u;
x->makeRoot(), y->makeRoot();
if (x->fa)
{
x->access();
if (x->msg.hasCir)
return false;
lcc_circle *cir = lccCirAllocator.allocate();
lcc_edge *e = lccEAllocator.allocate();
e->ew = ew, e->cir = cir;
cir->pA = y, cir->pB = x, cir->pEx = NULL;
cir->missingE = e;
x->tag_coverCir(cir);
x->access();
}
else
{
lcc_edge *e = lccEAllocator.allocate();
e->ew = ew, e->cir = NULL;
x->fa = y, x->prevE = e, x->update();
}
return true;
}
bool cactus_cut(int v, int u, int wA, int wB)
{
if (v == u)
return false;
edgeWeight ew(wA, wB);
lcc_node *x = lccVer + v, *y = lccVer + u;
if (x->findRoot() != y->findRoot())
return false;
y->makeRoot(), x->access();
y->splay_until(x);
lcc_circle *cir = x->prevE->cir;
if (cir && cir->pA == y && !cir->pEx && cir->missingE->ew == ew)
{
lcc_edge *e = cir->missingE;
x->tag_coverCir(NULL);
lccCirAllocator.deallocate(cir);
lccEAllocator.deallocate(e);
return true;
}
if (!y->rc && x->prevE->ew == ew)
{
lcc_edge *e = x->prevE;
lccEAllocator.deallocate(e);
if (cir)
{
if (cir->pEx)
{
cir->pEx->tag_rev();
cir->pEx->fa = y, y->rc = cir->pEx;
y->nextE = cir->pEx->msg.firstE;
x->prevE = cir->pEx->msg.lastE;
}
else
y->nextE = x->prevE = cir->missingE;
y->update(), x->update();
x->tag_coverCir(NULL);
lccCirAllocator.deallocate(cir);
}
else
{
y->fa = NULL, y->nextE = NULL, y->update();
x->lc = NULL, x->prevE = NULL, x->update();
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool cactus_add(int qv, int qu, int delta)
{
lcc_node *x = lccVer + qv, *y = lccVer + qu;
if (x->findRoot() != y->findRoot())
return false;
x->makeRoot(), y->access();
if (y->msg.hasMultiplePath)
return false;
y->tag_addWB(delta);
return true;
}
path_message cactus_query(int qv, int qu)
{
path_message res;
lcc_node *x = lccVer + qv, *y = lccVer + qu;
if (x->findRoot() != y->findRoot())
{
res.setInvalid();
return res;
}
x->makeRoot(), y->access();
res = y->msg.pathMsg;
if (y->msg.hasMultiplePath)
res.setMultiple();
return res;
}
int main()
{
int nQ;
cin >> n >> nQ;
cactus_init();
while (nQ--)
{
char type;
while (type = getchar(), type != 'l' && type != 'c' && type != 'a' && type != 'd');
if (type == 'l')
{
int v = getint(), u = getint(), wA = getint(), wB = getint();
if (cactus_link(v, u, wA, wB))
printf("ok\n");
else
printf("failed\n");
}
else if (type == 'c')
{
int v = getint(), u = getint(), wA = getint(), wB = getint();
if (cactus_cut(v, u, wA, wB))
printf("ok\n");
else
printf("failed\n");
}
else if (type == 'a')
{
int v = getint(), u = getint(), delta = getint();
if (cactus_add(v, u, delta))
printf("ok\n");
else
printf("failed\n");
}
else if (type == 'd')
{
int v = getint(), u = getint();
path_message ret = cactus_query(v, u);
printf("%d %d\n", ret.minLA, ret.minWB);
}
else
{
puts("error!");
}
}
return 0;
} 广义圆方树
经过前面各类仙人掌题目的讲解,大家恐怕已经对仙人掌产生了恐惧,而事实上,有难度的仙人掌题在近几年也只是在国家集训队水平的比赛里才会出现。
不过,这不是说仙人掌对国集水平以下的选手意义不大:
首先,仙人掌暴力 DP 问题难度并不大,在省选、 NOI 甚至 NOIP 中可能出现;
其次,仙人掌问题的处理能很好锻炼选手的特殊情况全面考虑并正确处理的能力,提升对超长代码的把握;
我们在点双题目中,如果对每个点双建立方点,然后对点双中的每个点连边,这样也可以构造出一种新的圆方树,我们称之为广义圆方树
根据圆方树和仙人掌等价性定理,我们可以为一张一般的图建立一棵等效仙人掌:一个环代表一个点双。
这样的一种思想可能在思路枯竭时解救我们。
Tourists
据说,这是一道 NOIP 难度的仙人掌题。
题目
给出一张带点权图,每次询问两点之间的简单路径中,权值最小的权值是多少。点数 N 、边数 M 、询问数 Q 均 ≤106
由于路径太多,直接考虑点双不方便,我们考虑建立圆方树、转化为等效仙人掌;
这样问题就转化为:两点所有简单路径的并集中权值的最小值;
只需将每个方点上的权值设为其连出所有圆点的最小值,这样问题就转化为链上的最小值。
之后只需并查集求 LCA 时顺便求一下最小值即可,本题是 NOIP 难度得证。
参考文献
[1] immortalCO. Making Graph into Trees[R]. 绍兴:中国计算机学会, 2017.
[2] Gintoki. 浅谈仙人掌问题[R]. 绍兴:中国计算机学会, 2017.
[3] 王逸松. 仙人掌相关算法及其应用[R]. 杭州:中国计算机学会, 2015.