ArrayDeque
Deque接口的大小可变数组的实现。
特性:
- 底层实现时循环数组
- 没有容量限制,在数组元素装满时自动扩容
- 禁止插入null元素
- 作为Stack和Queue时比LinkedList实现更好(前提是减少频繁的扩容和remove数组移动操作)
- 不是线程安全的
结构:
public class ArrayDeque extends AbstractCollection implements Deque, Cloneable, Serializable
所有方法:
主要字段:
// 存储元素数组大小是2的幂
transient Object[] elements;
// head指针指向当前元素并插入时由后向前移动
transient int head;
// tail指针指向下个添加元素的位置。插入由前往后
transient int tail;
// 数组的最小长度
private static final int MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 8;
循环数组
循环数组通过保持数组头部head和尾部tail两个元素指针按对应的插入顺序访问元素。类似与链表的访问
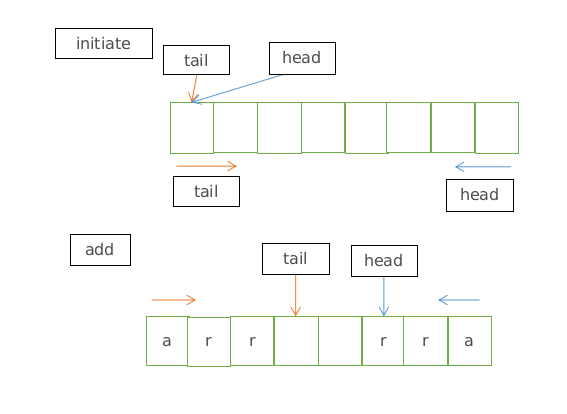
插入
初始化后,tail和head指针都指向数组下标0。
addFirst将元素插入数组尾部(head-1) & length,插入后head指向当前最近访问元素,插入时需要将head指针向前移动一位head-1。
addLast将元素插入到数组头部tail & length,插入后tail指向下一个插入位置(tail + 1) & length,插入时直接在tail位置插入,不需要移动。
插入图示:
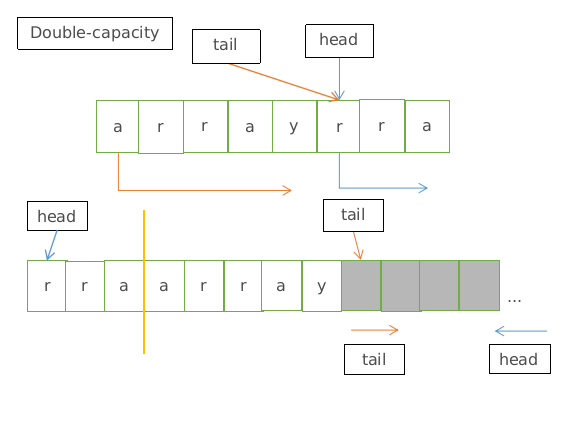
扩容
当tail==head时触发扩容操作。在插入数组最后一个空位时,相应指针会移动一位使得tail == head。
将数组容量扩大一倍,并将元素复制到新数组中。将 head部分移动到新数组前边 ,tail部分移动到head部分后面,扩大新增的数组部分在最后面,这样保证head像新数组中由后往前<--移动,tail指针由前往后-->移动
扩容图示:
删除
删除两端元素十分简单,这里解释循环数组中任意位置的删除
删除指定位置有2种情况
- 删除位置i更靠近head位置,根据删除位置i是否与head在同一端分为head <= i(同端)和head > i(异端)
- 删除位置i更靠近tail位置,根据删除位置i是否与tail在同一端分为tail >= i(同端)和tail < i(异端)
这里的同一端指都在循环数组的尾部或头部
下面以head与删除位置i的情况举例,tail的删除与head同理:
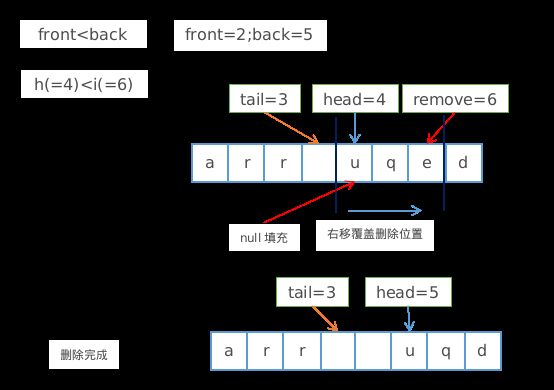
注意:此时front <= back 即删除位置i更接近head ,应该结合删除的源代码理解
同端(head <= i)
同端即head和删除位置i在同一部分尾部或头部,此时只需要将 删除位置左边的头部元素右移覆盖删除位置 即可
另一种形式仍然是同端的删除:
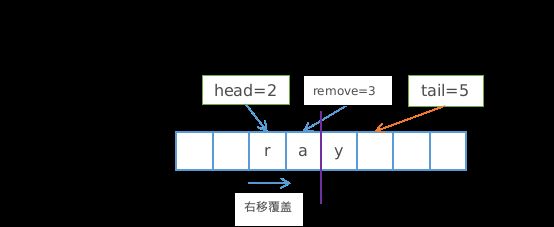
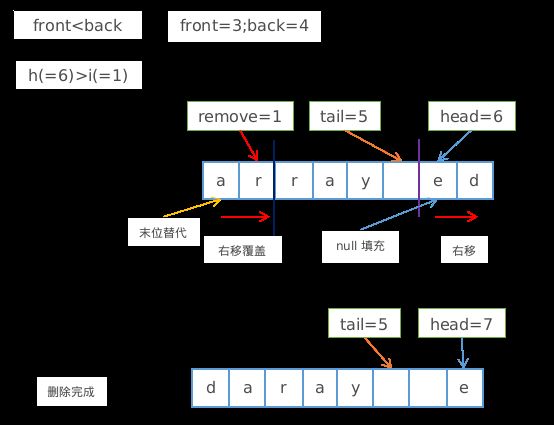
异端(head > i)
异端即head与删除位置i分开在尾部和头部(顺序不定),由于head和删除位置i在数组前端和后端(顺序不定),删除该位置需要将 删除位置i前元素右移覆盖删除位置和将head部分右移一位 即可
- 删除位置i前的所有元素右移一位覆盖删除位置i
- 将数组位置0使用head部分数组末位元素替换
- 移动head部分到数组末端并将head的元素置为null
delete源码
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in the elements array,
* adjusting head and tail as necessary. This can result in motion of
* elements backwards or forwards in the array.
*
* This method is called delete rather than remove to emphasize
* that its semantics differ from those of {@link List#remove(int)}.
*
* @return true if elements moved backwards
*/
/*
* 删除指定位置的元素。如果指定位置元素为null即删除null时无论那种情况都不会报错,而且能够正常工作
* 这个指定的null元素会被数组元素移动覆盖。
* 注意!!该方法返回值不表示删除是否失败!!返回false表示右移覆盖删除,返回true表示左移覆盖删除
*/
private boolean delete(int i) {
// assert 检查
checkInvariants();
final Object[] elements = this.elements;
final int mask = elements.length - 1;
final int h = head;
final int t = tail;
// 删除元素下标i与head间隔front个,如:h=10,i=12,2&mask=2或h=8,i=2,t=3.-6&mask=10
// 注意tail往左<--数组,head往右走-->
final int front = (i - h) & mask;
// 下标i与tail间隔长度back如:h=8,i=2,t=3.1&mask=1
final int back = (t - i) & mask;
// Invariant: head <= i < tail mod circularity
// t-h&mask表示数组中含有这个多元素如16中t=3,h=8,共11个元素。3-8 & 15 = 11
if (front >= ((t - h) & mask))
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// Optimize for least element motion
// 删除元素位置i更接近与head指针
if (front < back) {
// head和i在同一端 将[head...i-1]这些元素往后移动一位
if (h <= i) {
System.arraycopy(elements, h, elements, h + 1, front);
}
// head和i不在同一端,需要移动i之前的元素后再移动head端的元素
else { // Wrap around
// 删除位置i前的所有元素右移一位覆盖i
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, elements, 1, i);
// 数组末位元素替换移动后的重复索引1位置的索引0的元素
elements[0] = elements[mask];
// 移动head部分即数组head到末端右移一位
System.arraycopy(elements, h, elements, h + 1, mask - h);
}
// 将移动后的head位置元素删除
elements[h] = null;
// 更新head位置
head = (h + 1) & mask;
// 注意!!!这个false不是表示删除失败,而是表示通过右移覆盖删除
return false;
}
// 删除位置更接近tail位置
else {
// 删除位置与tail在同一端
if (i < t) { // Copy the null tail as well
// 将删除位置i后面的tial部分元素左移一位覆盖删除位置
System.arraycopy(elements, i + 1, elements, i, back);
tail = t - 1;
}
// 删除位置与tail不在同一端
else { // Wrap around
System.arraycopy(elements, i + 1, elements, i, mask - i);
elements[mask] = elements[0];
System.arraycopy(elements, 1, elements, 0, t);
tail = (t - 1) & mask;
}
// 注意tail端不需要置tail位置为null,因为tail本为null,移动后用null覆盖前面的位置了
// 注意!!!这个true不是表示删除成功,而是表示通过左移覆盖删除
return true;
}
}
总结
- 在数组中删除元素都是移动元素覆盖该位置。无论时同端还是异端都是将删除位置前的元素移动一位覆盖删除位置,只不过由于异端时移动不能连续而已
- 指定位置靠近head时通过右移覆盖删除,指定位置靠近tail时通过左移覆盖删除
指针位置
在ArrayDeque为空时有head == tail,head != tail时ArrayDeque一定存在元素(在add时可能有短暂的head==tail触发扩容操作)
读取时 head指针指向最近插入的head元素。tail指针指向下一个插入的tai元素位置即指向null,在addX插入扩容时短暂与head相等而不指向null。
插入时 head需要向前移动一位插入新元素并置为head-1。tail直接插入当前位置并指向下一个空位置
插入
在插入时必定tail <= head
删除
删除时tail和head的位置大小无法确定,哪一种都有可能
tail < head,指针head或tail都没有过界,head仍然在尾部,tail在头部
tail > head,指针head或tail有一个过界,head可能删除到了头部,或tail删除到了尾部。不存在同时过界
tail == head,所有元素全部删除完时tail == head,此时指针可能在数组任何位置
典型的指针位置图示:
扩容
分配空间
/**
* Allocates empty array to hold the given number of elements.
*
* @param numElements the number of elements to hold
*/
// 将指定数量numElements置为接近2^n如:numElements=56 被置为64.
private void allocateElements(int numElements) {
// 默认数组最小长度为8
int initialCapacity = MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
// Find the best power of two to hold elements.
// Tests "<=" because arrays aren't kept full.
// 如果是1<<30传入进来,最后所有30位都是1,++后就为2<<31溢出,溢出就取最大值2<<30
if (numElements >= initialCapacity) {
initialCapacity = numElements;
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 1);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 2);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 4);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 8);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 16);
initialCapacity++;
//溢出就取最大值2<<30
if (initialCapacity < 0) // Too many elements, must back off
initialCapacity >>>= 1;// Good luck allocating 2 ^ 30 elements
}
elements = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
注意
- allocateElements使用位操作将指定元素数量置为刚好大于该数量的2的次幂
下面是使用8bit模拟上面的过程
0100 1010 // numElements=74
0100 1010
0010 0101 | => 0110 1111 // >>>1
0110 1111
0001 1011 | => 0111 1111 // >>>2
0111 1111
0000 0111 | => 0111 1111 // >>>4
0111 1111 +1 => 1000 0000 // initialCapacity=128
- 如果使用2的次幂指定ArrayDeque的大小仍然会将增大一倍。如指定为
new ArrayDeque<>(16)==> elements.length=32 即等价与new ArrayDeque<>(31)
// 在源代码包中创建才能调用private elements[]
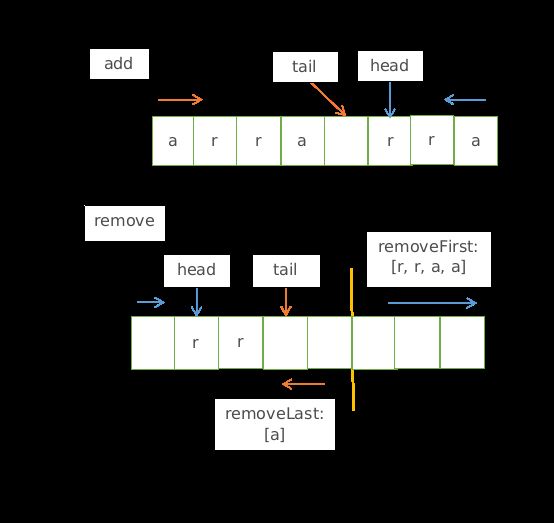
static void deleteTest() {
ArrayDeque deque = new ArrayDeque<>(8);
deque.addFirst("d");
deque.addFirst("e");
deque.addLast("a");
deque.addLast("r");
deque.addLast("r");
deque.addLast("a");
deque.addLast("y");
// 输出:elements.length=16
System.out.println("elements.length=" + deque.elements.length);
// 输出:[a, r, r, a, y, null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null, e, d]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(deque.elements));
}
下面以指定大小参数为8分配后容量为16的过程:
numElements=8 initialCapacity=8 //
0000 1000
0000 0100 | => 0000 1100 // >>>1
0000 1100
0000 0011 | => 0000 1111 // >>>2
0000 1111
0000 0000 | => 0000 1111 // >>>4
0000 1111 +1 => 0001 0000 // initialCapacity=16
双倍扩容
/**
* Doubles the capacity of this deque. Call only when full, i.e.,
* when head and tail have wrapped around to become equal.
*/
// 仅当数组装满元素才扩大一倍
private void doubleCapacity() {
// 检查只有head与tail相等时才允许扩容
assert head == tail;
int p = head;
int n = elements.length;
// p的右边的元素个数
int r = n - p; // number of elements to the right of p
// 容量扩大一倍
int newCapacity = n << 1;
// 2<<30溢出
if (newCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big");
Object[] a = new Object[newCapacity];
// 右边head开始到原数组最后r个元素复制到新数组0开始到r-1
System.arraycopy(elements, p, a, 0, r);
// head左边的从0开始p个元素赋值到新数组从r开始到最后
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, r, p);
elements = a;
head = 0;
tail = n;
}
注意
- ArrayDeque的扩容只有在head==tail时即插入数组最后一个空位置时执行扩容操作,使得数组扩大一倍。扩容后的新数组与初始化时一样,head指针由后往前,tail指针由原length位置往后
- ArrayDeque指定容量大小为2的次幂,如果不是2的次幂,会将指定容量提高为当前最接近的2次幂
- 不应该指定容量为2的次幂,ArrayDeque仍然会扩大一次2的次幂,会增大一倍容量,如果已经考虑过最大容量,那么这样的设置将会增大一倍的空间浪费
构造器
/**
* Constructs an empty array deque with an initial capacity
* sufficient to hold 16 elements.
*/
public ArrayDeque() {
elements = new Object[16];
}
/**
* Constructs an empty array deque with an initial capacity
* sufficient to hold the specified number of elements.
*
* @param numElements lower bound on initial capacity of the deque
*/
public ArrayDeque(int numElements) {
// 取num的2次幂
allocateElements(numElements);
}
/**
* Constructs a deque containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator. (The first element returned by the collection's
* iterator becomes the first element, or front of the
* deque.)
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into the deque
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayDeque(Collection c) {
allocateElements(c.size());
addAll(c);
}
注意
- 默认的ArrayDeque构造器创建的数组长度为16,而ArrayDeque能创建的最小数组长度即为16。根据
allocateElements()与MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY=8当capacity<=8时仍然会调用allocateElements导致使用8增加一倍16。
队列Queue
插入
- boolean add(E e)
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the end of this deque.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
- boolean offer(E e)
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the end of this deque.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #offerLast}.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
return offerLast(e);
}
注意
- 与LinkedList一样属于无界队列,不存在因为容量限制而添加失败,所以addX和offerX系列的方法本质都是一样的,但是作为queue使用时仍然应该区分这两种形式的api。
offer和add底层调用为addLast(E e),但是在这两个方法中一个前者可以返回false(实际仍然不可offerLast),后者返回固定值true。在需要使用true/false验证时可以使用推荐offer方法
删除
- E remove()
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head of the queue represented by this deque.
*
* This method differs from {@link #poll poll} only in that it throws an
* exception if this deque is empty.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #removeFirst}.
*
* @return the head of the queue represented by this deque
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
- E poll()
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head of the queue represented by this deque
* (in other words, the first element of this deque), or returns
* {@code null} if this deque is empty.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #pollFirst}.
*
* @return the head of the queue represented by this deque, or
* {@code null} if this deque is empty
*/
public E poll() {
return pollFirst();
}
注意
- remove和poll方法在队列为空时前者抛出异常而后者返回null。底层实现均调用pollFirst(),区别在于前者判断为null时抛出异常而后者返回null
检查
- E element()
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of the queue represented by
* this deque. This method differs from {@link #peek peek} only in
* that it throws an exception if this deque is empty.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #getFirst}.
*
* @return the head of the queue represented by this deque
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
- E peek()
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of the queue represented by
* this deque, or returns {@code null} if this deque is empty.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #peekFirst}.
*
* @return the head of the queue represented by this deque, or
* {@code null} if this deque is empty
*/
public E peek() {
return peekFirst();
}
注意
- element和peek方法底层实现都是返回head指针位置的数组元素,区别在于当队列为空时前者抛出异常而后者返回null
总结
- 将ArrayDeque作为队列实现比LinkedList更好,因为其禁止插入null和有更好的性能
链表在访问时不容易缓存命中,且需要更大的内存,作为队列唯一的好处是在迭代时更容易删除。
ArrayDeque作为队列针对与数组两端add/remove操作时要快于LinkedList,而且数组访问速度更快
但是,ArrayDeque在删除时需要移动复制数组,所以尽量避免在迭代中删除数组元素。另外需要减少在add时扩容操作,所以在创建ArrayDeque时应该指定容量
参考: Why is ArrayDeque better than LinkedList
堆栈Stack
入栈
/**
* Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this deque. In other
* words, inserts the element at the front of this deque.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #addFirst}.
*
* @param e the element to push
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
出栈
/**
* Pops an element from the stack represented by this deque. In other
* words, removes and returns the first element of this deque.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #removeFirst()}.
*
* @return the element at the front of this deque (which is the top
* of the stack represented by this deque)
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
检查
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of the queue represented by
* this deque, or returns {@code null} if this deque is empty.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #peekFirst}.
*
* @return the head of the queue represented by this deque, or
* {@code null} if this deque is empty
*/
public E peek() {
return peekFirst();
}
双端队列Deque
插入
- void addFirst(E e)
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the front of this deque.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// 对head指针取余,如head=0时,-1&15=15,14&15=14,将head指针从数组后面开始
// 从head=e.length-1开始
elements[head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] = e;
// 扩容
if (head == tail)
doubleCapacity();
}
- void addLast(E e)
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the end of this deque.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #add}.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public void addLast(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// 直接插入tail位置
elements[tail] = e;
// 将tail只想后一个位置 判断tail == head就扩容
if ( (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head)
doubleCapacity();
}
- boolean offerFirst(E e)
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
- public boolean offerLast(E e)
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
注意
- addX和offerX在存在容量限制时插入失败前者抛出异常,后者返回false。但ArrayDeque不存在容量限制因此两者并无本质区别
- addFirst与addLast在插入时使用位操作代替取余操作提高速度
ArrayDeque的底层数组大小为2的次幂,这样可以使用位操作提高取余的速度
下面是使用8bit(最高位为符号位)进行addFirst的取余操作过程:
head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)
head = 0 elements.length = 16 // 初始化时的设置
// 第一次插入
1111 1111 // (complement) head-1 =-1
0000 1111 & // elements.length - 1=15
0000 1111 // -1 & 15 = 15
// 第二次插入
0000 1110 // (complement) head(15)-1 = 14
0000 1111 & // elements.length - 1 = 15
0000 1110 // 14 & 15 = 14
- 所有的插入方法都不允许插入null元素,否则抛出异常
- head指针指向最近插入头部的元素,tail指针指向最近插入尾部元素的下一个空位置
删除
- E removeFirst()
/**
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E removeFirst() {
E x = pollFirst();
if (x == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
- E removeLast()
/**
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E removeLast() {
E x = pollLast();
if (x == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
- E pollFirst()
// 移除head指针元素并指向head+1
public E pollFirst() {
int h = head;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[h];
// Element is null if deque empty
if (result == null)
return null;
// 移除当前头部元素
elements[h] = null; // Must null out slot
// head指针往前移动一位,指向新的头部元素
head = (h + 1) & (elements.length - 1);
return result;
}
- E pollLast()
// 移除尾部元素
public E pollLast() {
// 将tail指针向前移动一位为删除元素位置
int t = (tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[t];
if (result == null)
return null;
elements[t] = null;
tail = t;
return result;
}
注意
- removeX和pollX方法都是移除双端元素,底层方法也一致,区别在于当队列为空时前者抛出异常,后者返回null。
- 双端队列Deque是对两端元素的移除,不会对队列中的元素移除,所以不需要进行数组元素移动的操作
检查
- E getFirst()
/**
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E getFirst() {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[head];
if (result == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return result;
}
- E getLast()
/**
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E getLast() {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)];
if (result == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return result;
}
- E peekFirst()
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E peekFirst() {
// elements[head] is null if deque empty
return (E) elements[head];
}
- E peekLast()
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E peekLast() {
return (E) elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)];
}
注意
- getX和peekX方法都是返回两端元素,底层均为读取数组元素,区别在于当队列为空时前者抛出异常,后者返回null
- First使用head指针,读取时head指针指向头部元素,Last使用tail指针,读取时需要往前移动到尾部元素
移除内部元素
- boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o)
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element in this
* deque (when traversing the deque from head to tail).
* If the deque does not contain the element, it is unchanged.
* More formally, removes the first element {@code e} such that
* {@code o.equals(e)} (if such an element exists).
* Returns {@code true} if this deque contained the specified element
* (or equivalently, if this deque changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this deque, if present
* @return {@code true} if the deque contained the specified element
*/
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
// ArrayDeque不允许null元素 直接返回false
if (o == null)
return false;
// 掩码 对head以后的下标取余运算
int mask = elements.length - 1;
int i = head;
Object x;
// 从头部元素head开始遍历整个队列(到尾部元素完为止)
while ( (x = elements[i]) != null) {
if (o.equals(x)) {
delete(i);
return true;
}
i = (i + 1) & mask;
}
return false;
}
- boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o)
/**
* Removes the last occurrence of the specified element in this
* deque (when traversing the deque from head to tail).
* If the deque does not contain the element, it is unchanged.
* More formally, removes the last element {@code e} such that
* {@code o.equals(e)} (if such an element exists).
* Returns {@code true} if this deque contained the specified element
* (or equivalently, if this deque changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this deque, if present
* @return {@code true} if the deque contained the specified element
*/
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null)
return false;
int mask = elements.length - 1;
// 从tail开始遍历
int i = (tail - 1) & mask;
Object x;
while ( (x = elements[i]) != null) {
if (o.equals(x)) {
// 删除元素
delete(i);
return true;
}
i = (i - 1) & mask;
}
return false;
}
注意
- delete相关源码在循环数组部分已经给出详细解释
集合Collection
添加
- boolean add(E e)
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the end of this deque.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
- boolean addAll(Collection c)
抽象类AbstractCollection的实现,通过c的迭代器调用add方法添加到arraydeque
移除
- void clear()
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this deque.
* The deque will be empty after this call returns.
*/
public void clear() {
int h = head;
int t = tail;
// 验证当前ArrayDeque是否为空
// 注意如果arraydeque不为空则head!=tail成立(在add时可能短暂的相等)
if (h != t) { // clear all cells
head = tail = 0;
int i = h;
int mask = elements.length - 1;
// 按照head--tail指针遍历移除元素 避免遍历整个数组
do {
elements[i] = null;
i = (i + 1) & mask;
} while (i != t);
}
}
- boolean remove(Object o)
/**
* Removes a single instance of the specified element from this deque.
* If the deque does not contain the element, it is unchanged.
* More formally, removes the first element {@code e} such that
* {@code o.equals(e)} (if such an element exists).
* Returns {@code true} if this deque contained the specified element
* (or equivalently, if this deque changed as a result of the call).
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #removeFirstOccurrence(Object)}.
*
* @param o element to be removed from this deque, if present
* @return {@code true} if this deque contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeFirstOccurrence(o);
}
详情参考Deque部分的移除内部元素内容
- boolean removeAll(Collection c)
由抽象类AbstractCollection实现。使用在arraydeque的迭代器中将元素包含在c中的调用iterator.remove删除
- boolean retainAll(Collection c)
有抽象类AbstractCollection实现,与removeAll仅有的区别为不包含的调用iterator.remove删除
注意
- 数组的移除需要移动数组元素,代价高昂
- clear()操作仍然保留底层数组,而且只在head--tail之中移除已设置的元素为null,不用遍历完整的数组
查询
- boolean contains(Object o)
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this deque contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this deque contains
* at least one element {@code e} such that {@code o.equals(e)}.
*
* @param o object to be checked for containment in this deque
* @return {@code true} if this deque contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (o == null)
return false;
int mask = elements.length - 1;
int i = head;
Object x;
// 由head开始遍历 直到遇到与指定对象相等的元素或找不到相等元素
while ( (x = elements[i]) != null) {
if (o.equals(x))
return true;
i = (i + 1) & mask;
}
return false;
}
- boolean containsAll(Collection c)
由抽象类AbstractCollection实现,使用c的迭代器在每个元素上调用contains()
- boolean isEmpty()
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this deque contains no elements.
*
* @return {@code true} if this deque contains no elements
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == tail;
}
- int size()
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this deque.
*
* @return the number of elements in this deque
*/
public int size() {
// 如:0 -- tail=3 -- head=7-- length=8 即tail-head=-4 & 7 = 4
return (tail - head) & (elements.length - 1);
}
比较和哈希
抽象类AbstractCollection使用Object类的默认实现
迭代器
- Iterator
iterator()
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this deque. The elements
* will be ordered from first (head) to last (tail). This is the same
* order that elements would be dequeued (via successive calls to
* {@link #remove} or popped (via successive calls to {@link #pop}).
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this deque
*/
public Iterator iterator() {
return new DeqIterator();
}
- Iterator
descendingIterator()
public Iterator descendingIterator() {
return new DescendingIterator();
}
// 该类是DeqIterator类的镜像,用tail代替head操作
private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator {
/*
* This class is nearly a mirror-image of DeqIterator, using
* tail instead of head for initial cursor, and head instead of
* tail for fence.
*/
private int cursor = tail;
private int fence = head;
private int lastRet = -1;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != fence;
}
public E next() {
if (cursor == fence)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
cursor = (cursor - 1) & (elements.length - 1);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[cursor];
if (head != fence || result == null)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
lastRet = cursor;
return result;
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (!delete(lastRet)) {
cursor = (cursor + 1) & (elements.length - 1);
fence = head;
}
lastRet = -1;
}
}
并行迭代器
不熟悉暂不讨论
实现
private class DeqIterator implements Iterator {
/**
* Index of element to be returned by subsequent call to next.
*/
private int cursor = head;
/**
* Tail recorded at construction (also in remove), to stop
* iterator and also to check for comodification.
*/
// 用于迭代完成检查和结构修改检查
private int fence = tail;
/**
* Index of element returned by most recent call to next.
* Reset to -1 if element is deleted by a call to remove.
*/
private int lastRet = -1;
public boolean hasNext() {
// 是否迭代到tail位置 即完成迭代
return cursor != fence;
}
public E next() {
// 迭代完成 没有元素了
if (cursor == fence)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E result = (E) elements[cursor];
// This check doesn't catch all possible comodifications,
// but does catch the ones that corrupt traversal
// 如果有其他线程修改了结构 仅能保证正确的遍历
if (tail != fence || result == null)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
lastRet = cursor;
// 下一个元素位置
cursor = (cursor + 1) & (elements.length - 1);
return result;
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
// 如果是左移 导致下一个元素移动到删除位置lastRet即cursor-1上,类似与删除数组上一个元素,需要将当前cursor-1使在next能够读取到
if (delete(lastRet)) { // if left-shifted, undo increment in next()
// 设置为上一个位置 原cursor表示的元素被移动到cursor-1位置了
cursor = (cursor - 1) & (elements.length - 1);
// tail被改变 -1
fence = tail;
}// 如果时右移 不会影响当前cursor位置上的元素,类似删除数组下一个元素,保持当前cursor 虽然head改变了 但是不影响cursor继续遍历
lastRet = -1;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
Object[] a = elements;
int m = a.length - 1, f = fence, i = cursor;
// 调用foreachremaining方法后不能在调用next方法
cursor = f;
// 从当前位置cursor开始遍历直到fence即tail为止
while (i != f) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E)a[i];
i = (i + 1) & m;
if (e == null)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
action.accept(e);
}
}
}
注意
- 循环数组的迭代有点类似与链表迭代,都是从head开始都tail结束,不同是循环数组的下一个元素需要用取余操作实现。
- 循环数组与链表在迭代的唯一劣势就是remove(),因为数组删除元素需要移动数组元素。在循环数组中还需要考虑左移开始右移来判断下一个位置元素是否被替换,左移被替换后需要更新当前cursor为cursor-1
这里要说一个坑了,由于方法 delete的注释中可能是想说,这个方法语义和remove不同,即执行delete操作而已。 The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are
* maintained by this deque. (In other words, this method must allocate
* a new array). The caller is thus free to modify the returned array.
*
* This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based
* APIs.
*
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this deque
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
return copyElements(new Object[size()]);
}
If this deque fits in the specified array with room to spare
* (i.e., the array has more elements than this deque), the element in
* the array immediately following the end of the deque is set to
* {@code null}.
*
* Like the {@link #toArray()} method, this method acts as bridge between
* array-based and collection-based APIs. Further, this method allows
* precise control over the runtime type of the output array, and may,
* under certain circumstances, be used to save allocation costs.
*
* Suppose {@code x} is a deque known to contain only strings.
* The following code can be used to dump the deque into a newly
* allocated array of {@code String}:
*
* 参考:private boolean delete(int i)返回一个boolean值,最初没有在意,以为表示是否删除成功,当我写看到注释This method is called delete rather than remove to emphasize that its semantics differ from those ofList.remove(int).什么叫强调与List.remove()不同,然后就忘记了这回事,等我写完循环数组的删除时,没什么感觉,脑壳昏,没有注意到frontif(delete(lastRet)),还能删除失败吗,回去看了一眼,卧槽,front转换数组
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this deque
* in proper sequence (from first to last element).
*
*
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this deque in
* proper sequence (from first to last element); the runtime type of the
* returned array is that of the specified array. If the deque fits in
* the specified array, it is returned therein. Otherwise, a new array
* is allocated with the runtime type of the specified array and the
* size of this deque.
*
* {@code String[] y = x.toArray(new String[0]);}
*
* Note that {@code toArray(new Object[0])} is identical in function to
* {@code toArray()}.
*
* @param a the array into which the elements of the deque are to
* be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the
* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this deque
* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array
* is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in
* this deque
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public 实现
/**
* Copies the elements from our element array into the specified array,
* in order (from first to last element in the deque). It is assumed
* that the array is large enough to hold all elements in the deque.
*
* @return its argument
*/
// 复制elements数组到指定数组。需要指定数组长度至少为deque的元素个数
private 注意