hadoop详细笔记(十九)原理加强Yarn调度策略详解
免费视频教程 https://www.51doit.com/ 或者联系博主微信 17710299606
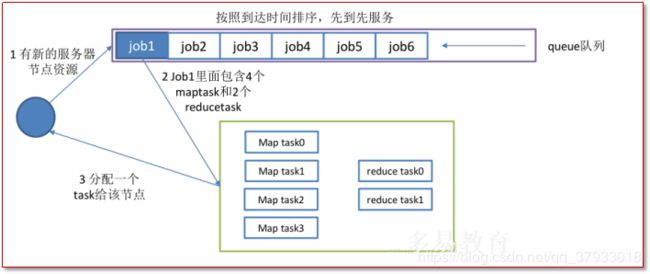
1 FIFO
hadoop1.x使用的默认调度器就是FIFO。FIFO采用队列方式将一个一个job任务按照时间先后顺序进行服务。比如排在最前面的job需要若干maptask和若干reducetask,当发现有空闲的服务器节点就分配给这个job,直到job执行完毕。
2 Capacity Scheduler
在Yarn框架中,调度器是一块很重要的内容。有了合适的调度规则,就可以保证多个应用可以在同一时间有条不紊的工作。最原始的调度规则就是FIFO,即按照用户提交任务的时间来决定哪个任务先执行,但是这样很可能一个大任务独占资源,其他的资源需要不断的等待。也可能一堆小任务占用资源,大任务一直无法得到适当的资源,造成饥饿。所以FIFO虽然很简单,但是并不能满足我们的需求。
2.1 Capacity
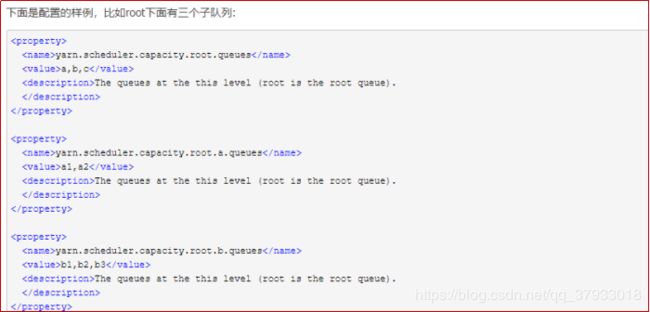
Capacity调度器说的通俗点,可以理解成一个个的资源队列。这个资源队列是用户自己去分配的。比如我大体上把整个集群分成了AB两个队列,A队列给A项目组的人来使用。B队列给B项目组来使用。但是A项目组下面又有两个方向,那么还可以继续分,比如专门做BI的和做实时分析的。那么队列的分配就可以参考下面的树形结构:
root
------a[60%]
|---a.bi[40%]
|---a.realtime[60%]
------b[40%]
hadoop2.x使用的默认调度器是Capacity Scheduler。
1、支持多个队列,每个队列可配置一定量的资源,每个采用FIFO的方式调度。
2、为了防止同一个用户的job任务独占队列中的资源,调度器会对同一用户提交的job任务所占资源进行限制。
3、分配新的job任务时,首先计算每个队列中正在运行task个数与其队列应该分配的资源量做比值,然后选择比值最小的队列。比如如图队列A15个task,20%资源量,那么就是15%0.2=70,队列B是25%0.5=50 ,队列C是25%0.3=80.33 。所以选择最小值队列B。
4、其次,按照job任务的优先级和时间顺序,同时要考虑到用户的资源量和内存的限制,对队列中的job任务进行排序执行。
5 多个队列同时按照任务队列内的先后顺序一次执行。例如下图中job11、job21、job31分别在各自队列中顺序比较靠前,三个任务就同时执行。
2.2 场景一(指定JOB资源)
Capacity Scheduler是YARN中默认的资源调度器,但是在默认情况下只有root.default 一个queue。而当不同用户提交任务时,任务都会在这个队里里面按优先级先进先出,大大影响了多用户的资源使用率。现在公司的任务主要分为三种:
- 每天晚上进行的日常任务dailyTask,这些任务需要在尽可能短的时间内完成,且由于关乎业务,所以一旦启动就必须提供尽可能多的资源,因为我分配的资源也最多 70%,队列名位dailyTask。
- 白天,通过Hive来获取一些数据信息,这部分任务由其他的同事进行操作,对查询速度要求并不是很高,且断断续续的,我分配的中等20%,队列名hive。
- 最后这种我定义为是其他的类型,长时间的一些数据处理任务,分配资源少一些10%,队列名为default(这个队列一定要存在)。
----- 补充说明
- 单个队列比如dailyTask,如果有多个任务在队列里面,那么只能有一个任务在运行,其他任务在等待。
- 虽然设置了队列的资源容量capacity,但是由于资源是共享式的,所以如果有其他queue的资源处理空闲,那么该queue就会从空闲的queue借资源,但是该queue资源最多不会超过 maximum-capacity。所以dailyTask由于在晚上时候运行,其他queue都是空闲的,所以它的实际资源利用率基本上是 maximum-capacity,也就是100%。而白天只有Hive队列和Default队列在使用,所以他们两会共享dailyTask的空余的70%资源。
- 如果在HIVE队列和Default队列都在运行时候,突然dailyTask队列add进了任务了,dailyTask就会等待借出去的资源被回收再分配。
- 目前这样的配置,刚好符合现在的需求,相比于公平调度器较为复杂的配置,目前容量调度器无疑更合适,所以先选择容量调度器。
在yarn-site.xml中配置调度器类型
| <property> <name>yarn.resourcemanager.scheduler.classname> <value>org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.resourcemanager.scheduler.capacity.CapacitySchedulervalue> property> |
capacity-scheduler.xml
- yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.maximum-capacity,队列最大可使用的资源率。
- capacity:队列的资源容量(百分比)。 当系统非常繁忙时,应保证每个队列的容量得到满足,而如果每个队列应用程序较少,可将剩余资源共享给其他队列。注意,所有队列的容量之和应小于100。
- maximum-capacity:队列的资源使用上限(百分比)。由于存在资源共享,因此一个队列使用的资源量可能超过其容量,而最多使用资源量可通过该参数限制。
- user-limit-factor:单个用户最多可以使用的资源因子,默认情况为1,表示单个用户最多可以使用队列的容量不管集群有空闲,如果该值设为5,表示这个用户最多可以使用5capacity的容量。实际上单个用户的使用资源为 min(user-limit-factorcapacity,maximum-capacity)。这里需要注意的是,如果队列中有多个用户的任务,那么每个用户的使用量将稀释。
- minimum-user-limit-percent:每个用户最低资源保障(百分比)。任何时刻,一个队列中每个用户可使用的资源量均有一定的限制。当一个队列中同时运行多个用户的应用程序时中,每个用户的使用资源量在一个最小值和最大值之间浮动,其中,最小值取决于正在运行的应用程序数目,而最大值则由minimum-user-limit-percent决定。比如,假设minimum-user-limit-percent为25。当两个用户向该队列提交应用程序时,每个用户可使用资源量不能超过50%,如果三个用户提交应用程序,则每个用户可使用资源量不能超多33%,如果四个或者更多用户提交应用程序,则每个用户可用资源量不能超过25%。
- maximum-applications :集群或者队列中同时处于等待和运行状态的应用程序数目上限,这是一个强限制,一旦集群中应用程序数目超过该上限,后续提交的应用程序将被拒绝,默认值为10000。所有队列的数目上限可通过参数yarn.scheduler.capacity.maximum-applications设置(可看做默认值),而单个队列可通过参数yarn.scheduler.capacity..maximum-applications设置适合自己的值。
- maximum-am-resource-percent:集群中用于运行应用程序ApplicationMaster的资源比例上限,该参数通常用于限制处于活动状态的应用程序数目。该参数类型为浮点型,默认是0.1,表示10%。所有队列的ApplicationMaster资源比例上限可通过参数yarn.scheduler.capacity. maximum-am-resource-percent设置(可看做默认值),而单个队列可通过参数yarn.scheduler.capacity.. maximum-am-resource-percent设置适合自己的值。
- state :队列状态可以为STOPPED或者RUNNING,如果一个队列处于STOPPED状态,用户不可以将应用程序提交到该队列或者它的子队列中,类似的,如果ROOT队列处于STOPPED状态,用户不可以向集群中提交应用程序,但正在运行的应用程序仍可以正常运行结束,以便队列可以优雅地退出。
- acl_submit_applications:限定哪些Linux用户/用户组可向给定队列中提交应用程序。需要注意的是,该属性具有继承性,即如果一个用户可以向某个队列中提交应用程序,则它可以向它的所有子队列中提交应用程序。配置该属性时,用户之间或用户组之间用“,”分割,用户和用户组之间用空格分割,比如“user1, user2 group1,group2”。
- acl_administer_queue:为队列指定一个管理员,该管理员可控制该队列的所有应用程序,比如杀死任意一个应用程序等。同样,该属性具有继承性,如果一个用户可以向某个队列中提交应用程序,则它可以向它的所有子队列中提交应用程序。
yarn.scheduler.capacity.maximum-applications
10000
Maximum number of applications that can be pending and running.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.maximum-am-resource-percent
0.1
Maximum percent of resources in the cluster which can be used to run
application masters i.e. controls number of concurrent running
applications.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.resource-calculator
org.apache.hadoop.yarn.util.resource.DefaultResourceCalculator
The ResourceCalculator implementation to be used to compare
Resources in the scheduler.
The default i.e. DefaultResourceCalculator only uses Memory while
DominantResourceCalculator uses dominant-resource to compare
multi-dimensional resources such as Memory, CPU etc.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.queues
default,dailyTask,hive
The queues at the this level (root is the root queue).具有三个子队列
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.capacity
20
Default queue target capacity.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.user-limit-factor
1
Default queue user limit a percentage from 0.0 to 1.0.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.maximum-capacity
100
The maximum capacity of the default queue.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.state
RUNNING
The state of the default queue. State can be one of RUNNING or STOPPED.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.acl_submit_applications
*
The ACL of who can submit jobs to the default queue.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.acl_administer_queue
*
The ACL of who can administer jobs on the default queue.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.dailyTask.capacity
70
Default queue target capacity.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.dailyTask.user-limit-factor
1
Default queue user limit a percentage from 0.0 to 1.0.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.dailyTask.maximum-capacity
100
The maximum capacity of the default queue..
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.dailyTask.state
RUNNING
The state of the default queue. State can be one of RUNNING or STOPPED.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.dailyTask.acl_submit_applications
hadoop
The ACL of who can submit jobs to the default queue.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.dailyTask.acl_administer_queue
hadoop
The ACL of who can administer jobs on the default queue.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.capacity
10
Default queue target capacity.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.user-limit-factor
1
Default queue user limit a percentage from 0.0 to 1.0.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.maximum-capacity
100
The maximum capacity of the default queue..
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.state
RUNNING
The state of the default queue. State can be one of RUNNING or STOPPED.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.acl_submit_applications
*
The ACL of who can submit jobs to the default queue.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.acl_administer_queue
*
The ACL of who can administer jobs on the default queue.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.node-locality-delay
40
Number of missed scheduling opportunities after which the CapacityScheduler
attempts to schedule rack-local containers.
Typically this should be set to number of nodes in the cluster, By default is setting
approximately number of nodes in one rack which is 40.
yarn.scheduler.capacity.queue-mappings
A list of mappings that will be used to assign jobs to queues
The syntax for this list is [u|g]:[name]:[queue_name][,next mapping]*
Typically this list will be used to map users to queues,
for example, u:%user:%user maps all users to queues with the same name
as the user. 进行过映射后,user只能访问对应的quue_name,后续的queue.name设置都没用了。
yarn.scheduler.capacity.queue-mappings-override.enable
false
If a queue mapping is present, will it override the value specified
by the user? This can be used by administrators to place jobs in queues
that are different than the one specified by the user.
The default is false.
JOB使用队列
mapreduce:在Job的代码中,设置Job属于的队列,例如hive:
conf.setQueueName("hive");
hive:在执行hive任务时,设置hive属于的队列,例如dailyTask:
set mapred.job.queue.name=dailyTask;
刷新配置
生产环境中,队列及其容量的修改在现实中是不可避免的,而每次修改,需要重启集群,这个代价很高,如果修改队列及其容量的配置不重启呢:
- 在主节点上根据具体需求,修改好mapred-site.xml和capacity-scheduler.xml
- 把配置同步到所有节点上
- yarn rmadmin -refreshQueues 这样就可以动态修改集群的队列及其容量配置,不需要重启了
刷新mapreduce的web管理控制台可以看到结果。 注意:如果配置没有同步到所有的节点,一些队列会无法启用。 可以查看http://hadoop-master:8088/cluster/scheduler
2.3 场景二(指定JOB运行节点)
Yarn Node Labels + Capacity-Scheduler 实现不同任务队列运行在不同机器节点上
在yarn-site.xml中开启capacity-schedule
yarn.resourcemanager.scheduler.class
org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.resourcemanager.scheduler.capacity.CapacityScheduler
capacity-scheduler.xml
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.queues
default,area0,area1,area2
The queues at the this level (root is the root queue).
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.capacity
25
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area0.capacity
25
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area1.capacity
25
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area2.capacity
25
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.maximum-capacity
100
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area0.maximum-capacity
100
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area1.maximum-capacity
100
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area2.maximum-capacity
100
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.accessible-node-labels
*
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area0.accessible-node-labels
area0
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area1.accessible-node-labels
area1
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area2.accessible-node-labels
area2
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.accessible-node-labels.area0.capacity
33
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.accessible-node-labels.area1.capacity
33
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.accessible-node-labels.area2.capacity
34
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area0.accessible-node-labels.area0.capacity
100
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area1.accessible-node-labels.area1.capacity
100
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area2.accessible-node-labels.area2.capacity
100
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default-node-label-expression
area0,area1,area2
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.default-node-label-expression
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area0.default-node-label-expression
area0
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area1.default-node-label-expression
area1
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.area2.default-node-label-expression
area2
添加Yarn Node Labels
添加标签
yarn rmadmin -addToClusterNodeLabels area0,area1,area2
节点添加标签
yarn rmadmin -replaceLabelsOnNode Host1:45454,area0
yarn rmadmin -replaceLabelsOnNode Host2:45454,area1
yarn rmadmin -replaceLabelsOnNode Host3:45454,area2
查看标签
yarn node -status Host1:45454
#也可以通过Yarn管理页面查看Node Label
配置Yarn Node Labels存储目录,
这样不用每次重启服务后重新配置Yarn Node Labels 在yarn-site.xml中添加下列信息
|
|
3 Fair Scheduler
3.1 简介
1、支持多个队列,每个队列可以配置一定的资源,每个队列中的job任务公平共享其所在队列的所有资源。
2、队列中的job任务都是按照优先级分配资源,优先级越高分配的资源越多,但是为了确保公平每个job任务都会分配到资源。优先级是根据每个job任务的理想获取资源量减去实际获取资源量的差值决定的,差值越大优先级越高。
Fair调度器的设计目标是为所有的应用分配公平的资源(对公平的定义可以通过参数来设置)。在上面的“Yarn调度器对比图”展示了一个队列中两个应用的公平调度;当然,公平调度在也可以在多个队列间工作。举个例子,假设有两个用户A和B,他们分别拥有一个队列。当A启动一个job而B没有任务时,A会获得全部集群资源;当B启动一个job后,A的job会继续运行,不过一会儿之后两个任务会各自获得一半的集群资源。如果此时B再启动第二个job并且其它job还在运行,则它将会和B的第一个job共享B这个队列的资源,也就是B的两个job会用于四分之一的集群资源,而A的job仍然用于集群一半的资源,结果就是资源最终在两个用户之间平等的共享。过程如下图所示:
3.2 启用Fair Scheduler
调度器的使用是通过yarn-site.xml配置文件中的yarn.resourcemanager.scheduler.class参数进行配置的,默认采用Capacity Scheduler调度器。如果我们要使用Fair调度器,需要在这个参数上配置FairScheduler类的全限定名: org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.resourcemanager.scheduler.fair.FairScheduler。
3.,3 队列的配置
Fair调度器的配置文件位于类路径下的fair-scheduler.xml文件中,这个路径可以通过yarn.scheduler.fair.allocation.file属性进行修改。若没有这个配置文件,Fair调度器采用的分配策略,这个策略和3.1节介绍的类似:调度器会在用户提交第一个应用时为其自动创建一个队列,队列的名字就是用户名,所有的应用都会被分配到相应的用户队列中。
我们可以在配置文件中配置每一个队列,并且可以像Capacity 调度器一样分层次配置队列。比如,参考capacity-scheduler.xml来配置fair-scheduler:
|
|
队列的层次是通过嵌套
Fair调度器中的队列有一个权重属性(这个权重就是对公平的定义),并把这个属性作为公平调度的依据。在这个例子中,当调度器分配集群40:60资源给prod和dev时便视作公平,eng和science队列没有定义权重,则会被平均分配。这里的权重并不是百分比,我们把上面的40和60分别替换成2和3,效果也是一样的。注意,对于在没有配置文件时按用户自动创建的队列,它们仍有权重并且权重值为1。
每个队列内部仍可以有不同的调度策略。队列的默认调度策略可以通过顶级元素
尽管是Fair调度器,其仍支持在队列级别进行FIFO调度。每个队列的调度策略可以被其内部的
尽管上面的配置中没有展示,每个队列仍可配置最大、最小资源占用数和最大可运行的应用的数量。
3.4 列的设置
Fair调度器采用了一套基于规则的系统来确定应用应该放到哪个队列。在上面的例子中,
当然,我们可以不配置queuePlacementPolicy规则,调度器则默认采用如下规则:
上面规则可以归结成一句话,除非队列被准确的定义,否则会以用户名为队列名创建队列。
还有一个简单的配置策略可以使得所有的应用放入同一个队列(default),这样就可以让所有应用之间平等共享集群而不是在用户之间。这个配置的定义如下:
实现上面功能我们还可以不使用配置文件,直接设置yarn.scheduler.fair.user-as-default-queue=false,这样应用便会被放入default 队列,而不是各个用户名队列。另外,我们还可以设置yarn.scheduler.fair.allow-undeclared-pools=false,这样用户就无法创建队列了。
3.5 抢占(Preemption)
当一个job提交到一个繁忙集群中的空队列时,job并不会马上执行,而是阻塞直到正在运行的job释放系统资源。为了使提交job的执行时间更具预测性(可以设置等待的超时时间),Fair调度器支持抢占。
抢占就是允许调度器杀掉占用超过其应占份额资源队列的containers,这些containers资源便可被分配到应该享有这些份额资源的队列中。需要注意抢占会降低集群的执行效率,因为被终止的containers需要被重新执行。
可以通过设置一个全局的参数yarn.scheduler.fair.preemption=true来启用抢占功能。此外,还有两个参数用来控制抢占的过期时间(这两个参数默认没有配置,需要至少配置一个来允许抢占Container):
- minimum share preemption timeout
- fair share preemption timeout
如果队列在minimum share preemption timeout指定的时间内未获得最小的资源保障,调度器就会抢占containers。我们可以通过配置文件中的顶级元素
与之类似,如果队列在fair share preemption timeout指定时间内未获得平等的资源的一半(这个比例可以配置),调度器则会进行抢占containers。这个超时时间可以通过顶级元素